Case 1 Z
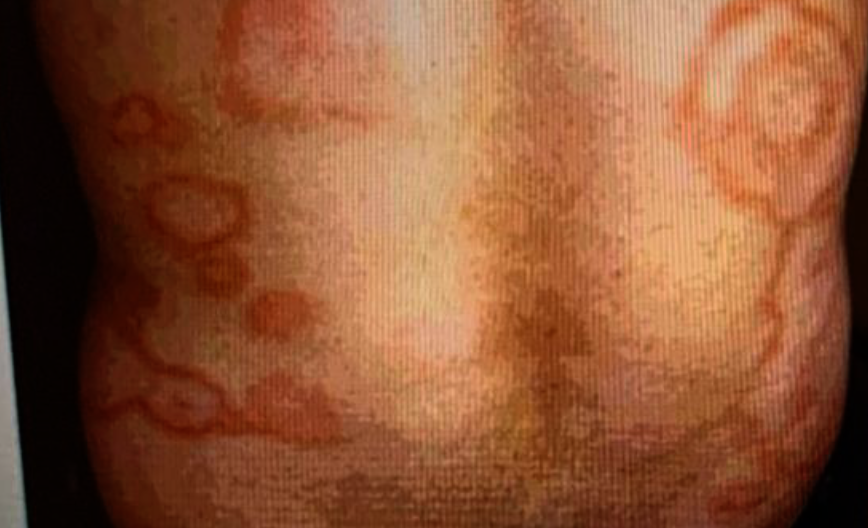 This patient has a history of recurrent sore throat. Now he has: Non-itching rash, fever, and choreiform movements of the hands and face.
A clinical diagnosis of rheumatic fever was made.
This patient has a history of recurrent sore throat. Now he has: Non-itching rash, fever, and choreiform movements of the hands and face.
A clinical diagnosis of rheumatic fever was made.
- Name 2 serological tests used for the diagnosis of group A streptococcal infection? Positive throat culture, anti ASO titer.
- Name any 3 major Jones’ criteria for the diagnosis of rheumatic fever? Carditis, arthritis, Sydenham chorea.
- Which heart valve is most commonly affected by rheumatic fever? Mitral valve.
- Name 1 auscultatory finding in mitral stenosis? Mid-diastolic murmur.
- What is the treatment of rheumatic fever? Eradication of streptococcal infection by Penicillin for 10 days, Supportive treatment: NSAIDS for arthritis, bed rest for carditis and ACE inhibitor and diuretics if indicated, prophylaxis antibiotic to prevent second RF.
Case 2
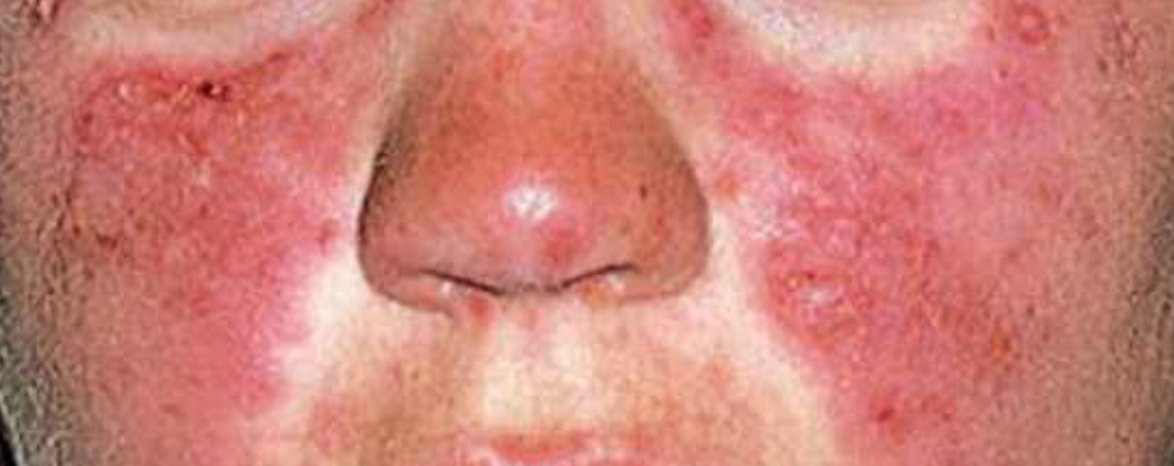 A 25 years old female complained of a facial rash for a few months.
The rash gets worse when she goes out, and complains of tiredness and arthralgias.
A 25 years old female complained of a facial rash for a few months.
The rash gets worse when she goes out, and complains of tiredness and arthralgias.
-
What is your clinical diagnosis?
- SLE (clinical sign malar rash can be found also in dermomyositis)
-
Mention 2 blood tests which you will do for the diagnosis of this diseases?
- Anti-ds DNA antibody (Anti double stranded DNA Antibody)
- ANA (Antinuclear antibody) #Z
-
Mention 3 characteristic features of this rash
- Involve both cheeks
- crosses nasal bridge
- Spares naso-labial fold
-
Name 2 medicine which you can give patient for the rash - and what advice you would give?
- Topical Corticosteroids
- Hydroxycholorquine
- Advise her to avoid sun exposure and use sunscreen when going out
-
Name any drug which can cause this disease?
- INH (Isoniazid)
-
What is the commonest cause of death in this disease?
- Coronary artery disease
-
Name any renal complication of this disease?
- Lupus nephritis & MN PGN #Z
-
What is the effect of this disease fertility in females?
It does not directly affect fertility in females, but planning of pregnancy is needed as some medications can be teratogenic. -
mention 2 pulmonary manifestations of SLE? Z
- 1- shrunk lung
- 2- pleurisy
-
Name the pulmonary complications of SLE?
- Pleurisy / pleural effusion
- Shrunken lung
- Atelectasis
- Name some cardiac complications of SLE? Z
- Pericarditis
- Myocarditis
- Nonbacterial endocarditis (LibmanSacks endocarditis)**
- Which drug can cure SLE?
- None
- Name the 2 types of glomerulonephritis seen in SLE? Z
- Membranous nephropathy (MN),
- membranoproliferative GN (MPGN)
Case 3
-
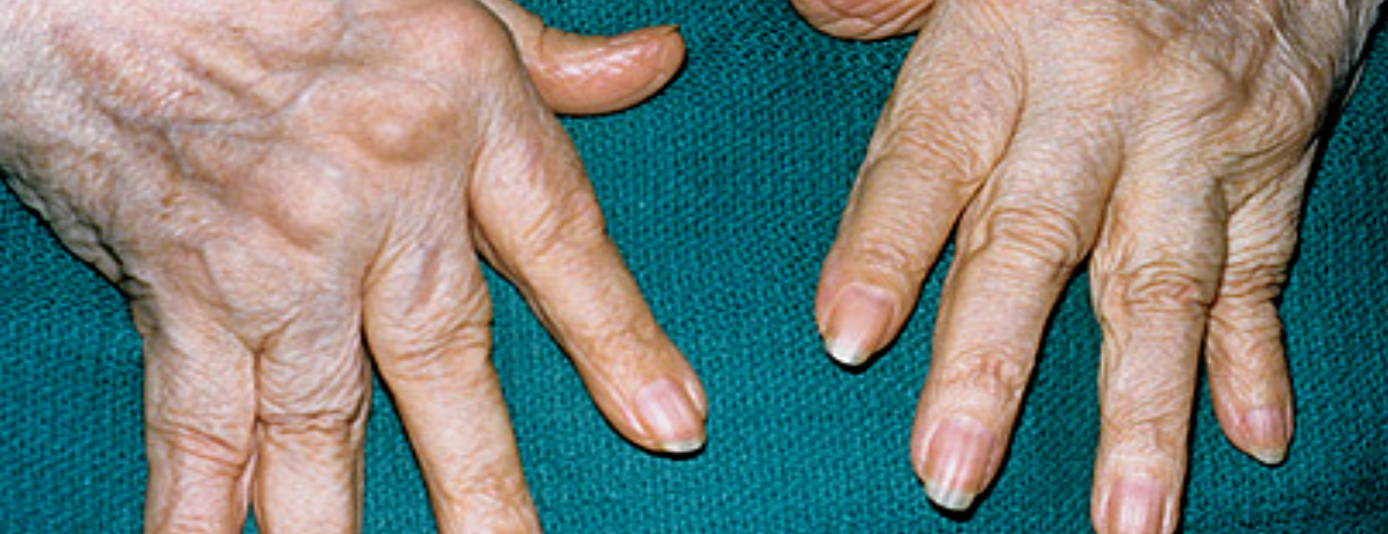
Name 2 hand deformities which occur in Rheumatoid arthritis?
- **a) Swan neck deformity/ Boutonniere deformity
- b) Ulnar deviation of the fingers/ Dislocation of carpo metacarpal joints
-
Name 2 serological tests of diagnostic importance? Z
- a) Rheumatoid factor (RF)
- b) Anti Citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA)
-
Name any 2 pulmonary complications of Rheumatoid arthritis?
- a) Pleural effusion
- b) Pulmonary nodules/ ILD/ bronchiectasis
-
Name any 2 disease modifying agents (drugs) used in the treatment? Z
- a) Methotrexate
- b) Sulfasalazine/ Gold/ TNF alpha antagonists
Case 4
-
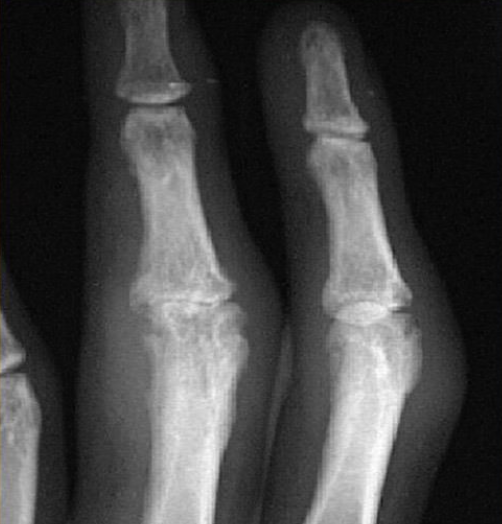
Name 2 radiological abnormalities?
a. Erosion of proximal interpharyngeal joint
b. Swelling of the in the middle finger
c. sublaxation of the joints -
What is likely etiology of arthritis
a. rheumatoid arthritis -
Which blood test will you do for diagnosis?
ACPA , RF
Case 5
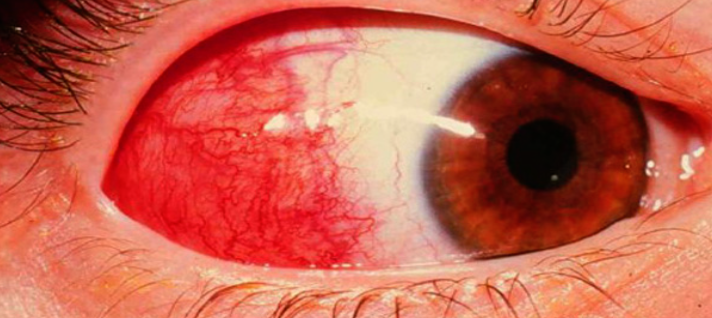 This patient is a known case of rheumatoid arthritis. She presented with painless redness affecting her right eye for 2 weeks. She had similar lesion in the same eye a year ago.
This patient is a known case of rheumatoid arthritis. She presented with painless redness affecting her right eye for 2 weeks. She had similar lesion in the same eye a year ago.
-
What is the diagnosis?
- Episcleritis
-
Name 2 serological tests of diagnostic importance?
- ACPA, RF IgM
-
Describe common involvement of lungs in rheumatoid arthritis? Z
- Interstitial lung disease
Case 6
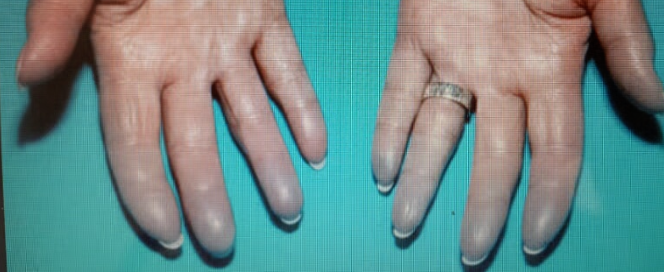 Patient complaining of Dysphagia & heart burn..
Patient complaining of Dysphagia & heart burn..
A) What is this sign?
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
B) What is ur diagnosis?
- Scleroderma Disease, SLE
Case 7
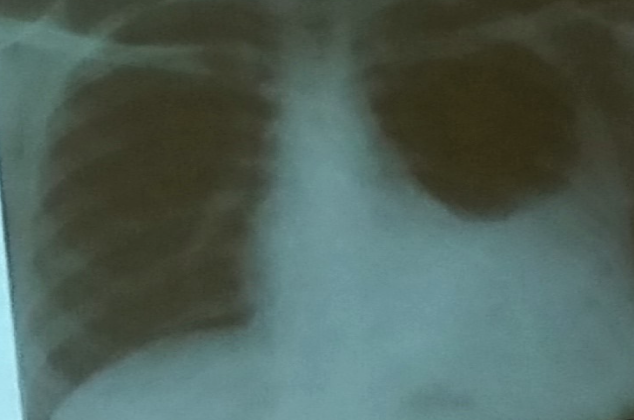 33 year old female presented with malaise, joint discomfort and general feeling unwell. She was diagnosed Graves’ disease four years ago and rendered euthyroid. She had also suffered from celiac disease since her teens. She had no respiratory complaint. She had recent chest X-ray which showed right pleural effusion of moderate size.
33 year old female presented with malaise, joint discomfort and general feeling unwell. She was diagnosed Graves’ disease four years ago and rendered euthyroid. She had also suffered from celiac disease since her teens. She had no respiratory complaint. She had recent chest X-ray which showed right pleural effusion of moderate size.
Pleural aspiration was performed which showed:
- Pleural fluid sample
- Total protein 33.2 g/l (NR: (1-2 g/dL)
- LDH 287 IU/l (NR: <50% of plasma)
- pH 7.036 (NR: 7.60-7.64)
- Microbiology Nil seen
- Amylase 65U/l
- Rheumatoid factor 557IU/l
-
Name 2 abnormalities of pleural aspirate? Z a. ---ldh high---
b. ---Protein high--- -
What is the cause of her pleural effusion? Z a. ---Rheumatoid Arthritis---
Case 8
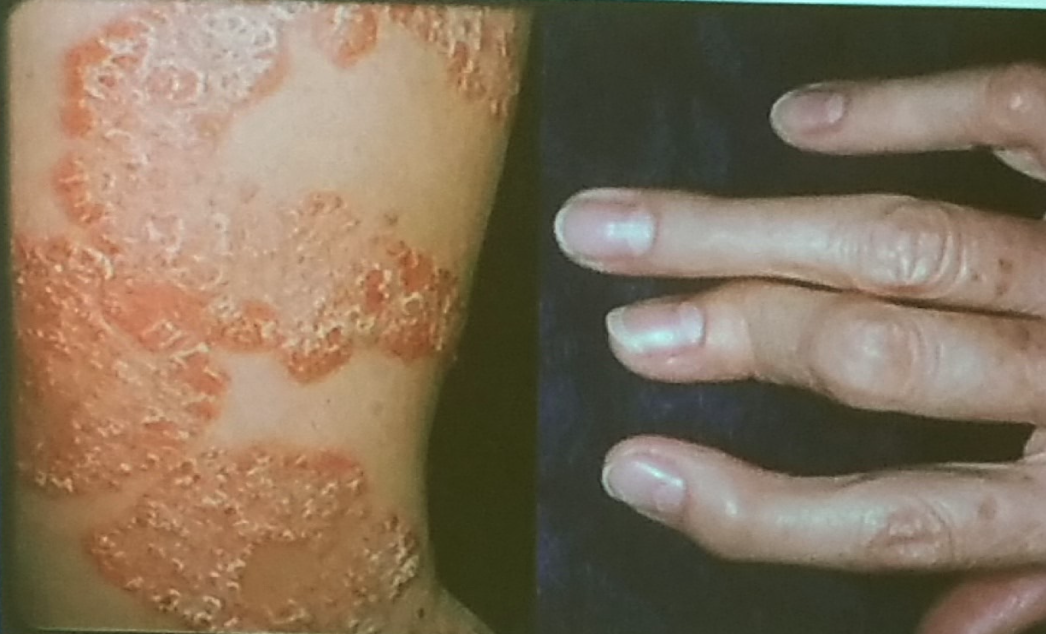 This patient had long standing skin condition as shown in clinical photograph. She developed deformity in joints as shown in photograph.
This patient had long standing skin condition as shown in clinical photograph. She developed deformity in joints as shown in photograph.
-
What is the skin disease?
Psoriasis -
What is the likely cause of deformity of hand?
Psoriatic Arthritis
Case 9 Z
40 Year man presented with painful lesion on his chest
-
What is anatomical localization of the lesion?
groupe of herptiform vesicles with erythematous base on T3 dermatomes -
What is diagnosis?
herpes zoster
2. reservoir? HSV-1
3. complications?
- Post herpetic neuralgia
- Herpes simplex encephalopathy.
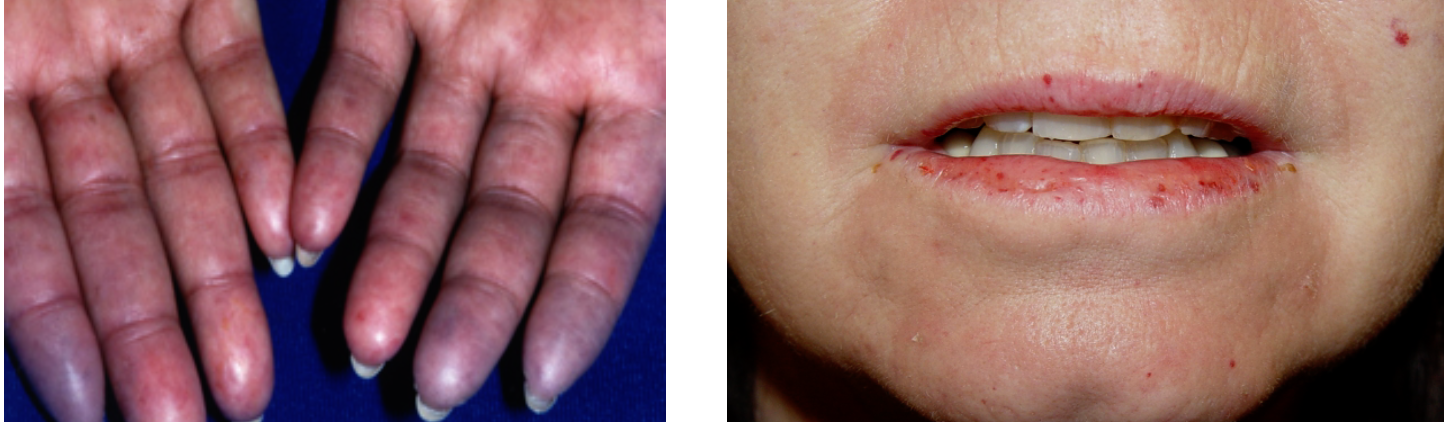 Scleroderma disease - raynaud phenomenon / Angular stomatitis
Scleroderma disease - raynaud phenomenon / Angular stomatitis