Lacrimal Apparatus
Objectives
- Recognize different causes of tearing in children and adults (Congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction, Acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction).
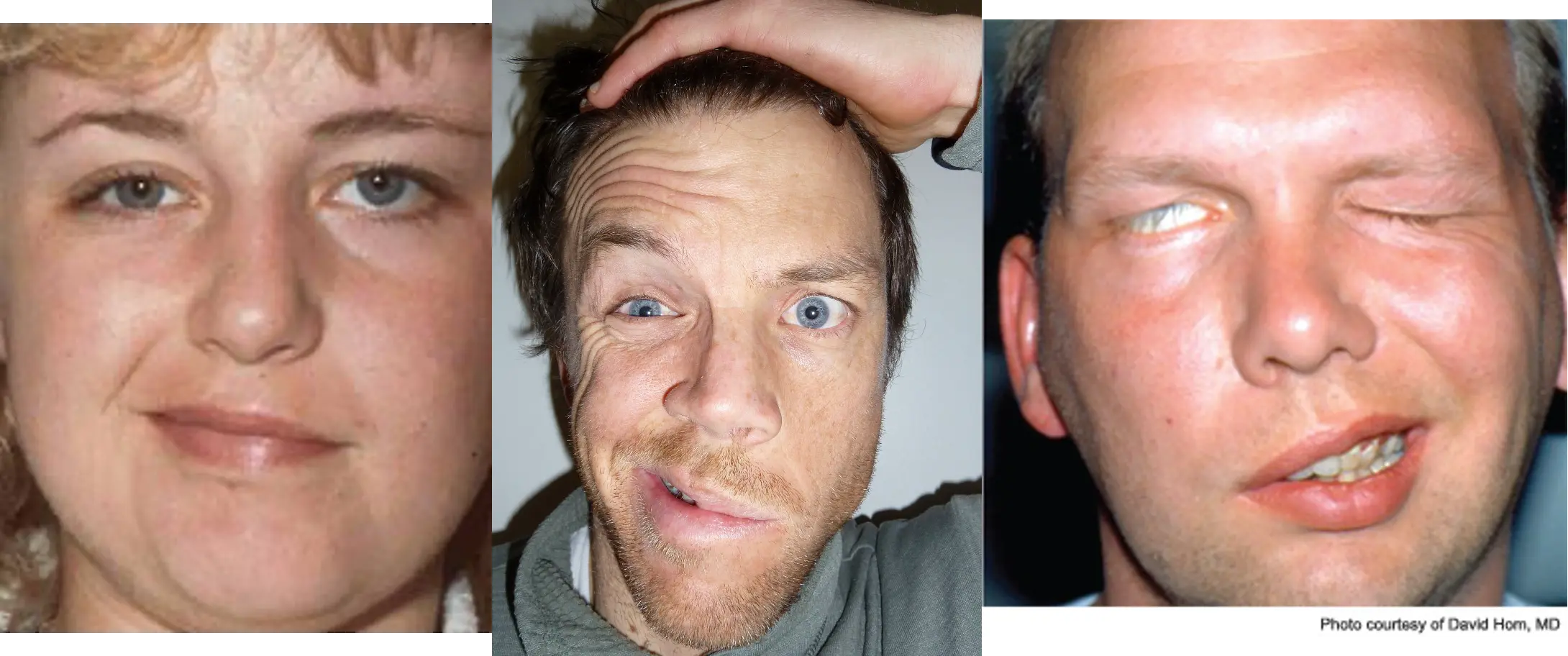
- Recognize the manifestation of Chronic dacryocystitis and Facial nerve palsy as a cause of tearing.
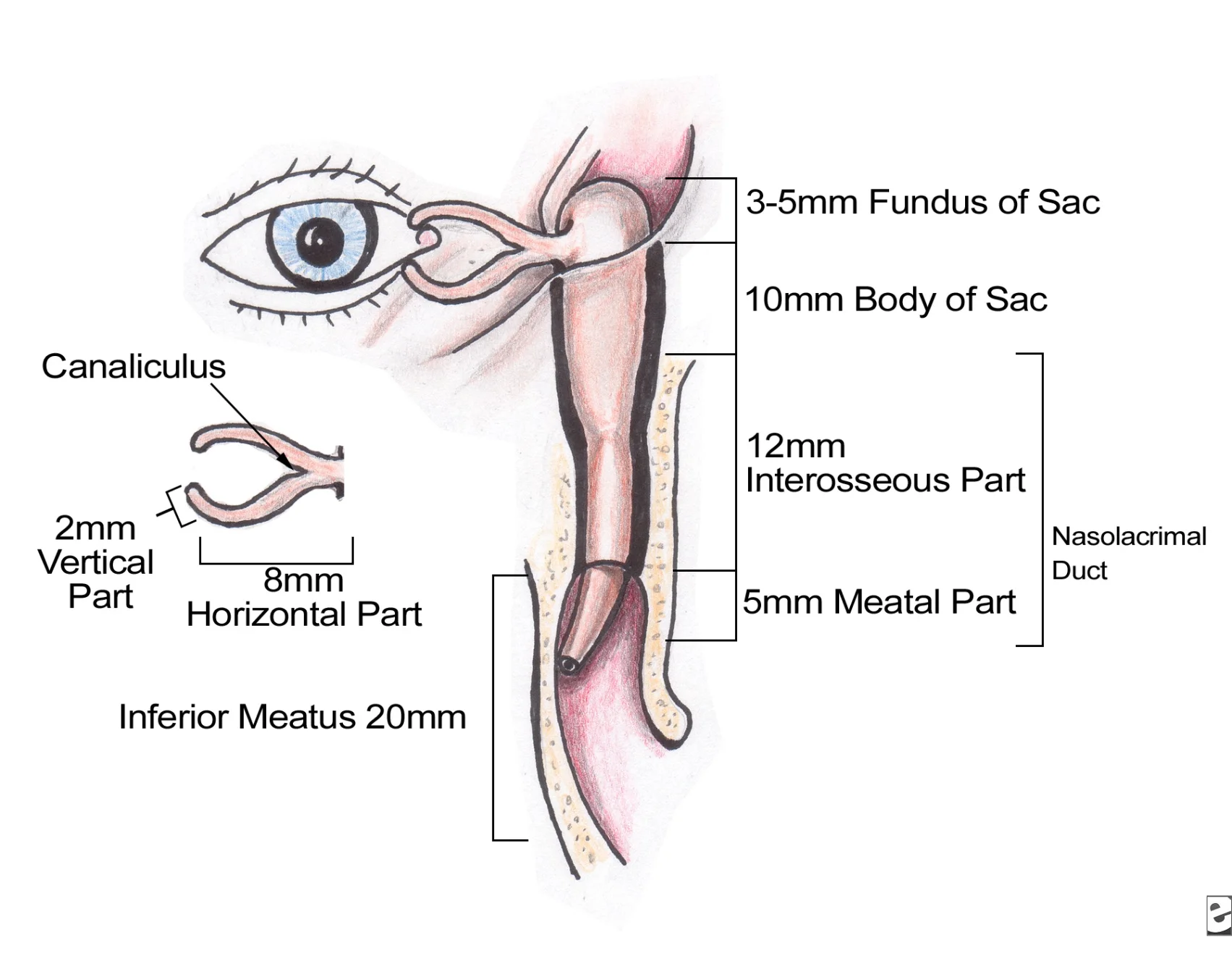
Nasolacrimal Duct System
Excessive Watering
- Lacrimation: reflex over-production of tears (hypersecretion).
- Epiphora: mechanical obstruction of tear drainage system.
- Lacrimal pump failure secondary to facial nerve palsy.
Classification of Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction
- Congenital NLD obstruction.
- Acquired NLD obstruction.
Examination of Lacrimal System
- The eyelids contour and position.
- The dynamics of eyelid closure.
- The puncta size and position.
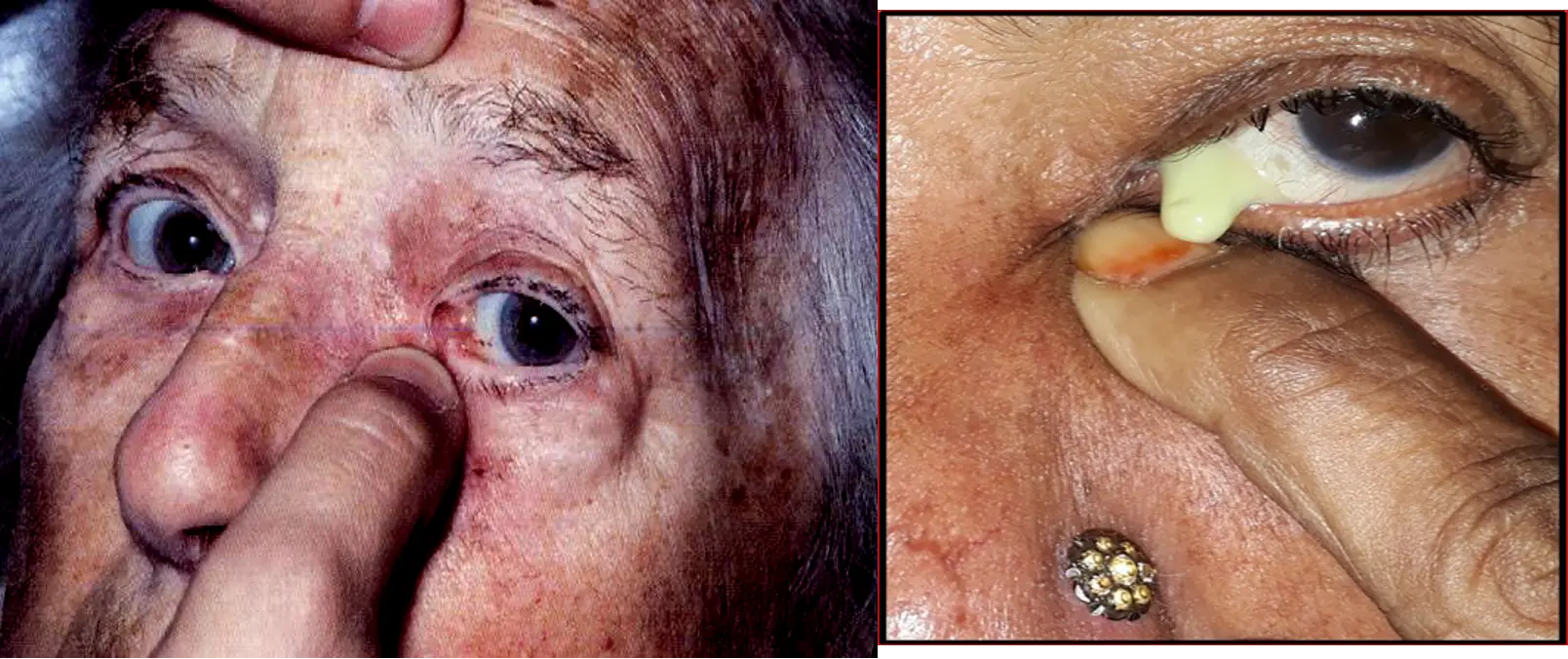
- The lacrimal sac swelling and presence of regurgitation on pressing on the sac.
- Irrigation of the NLS.
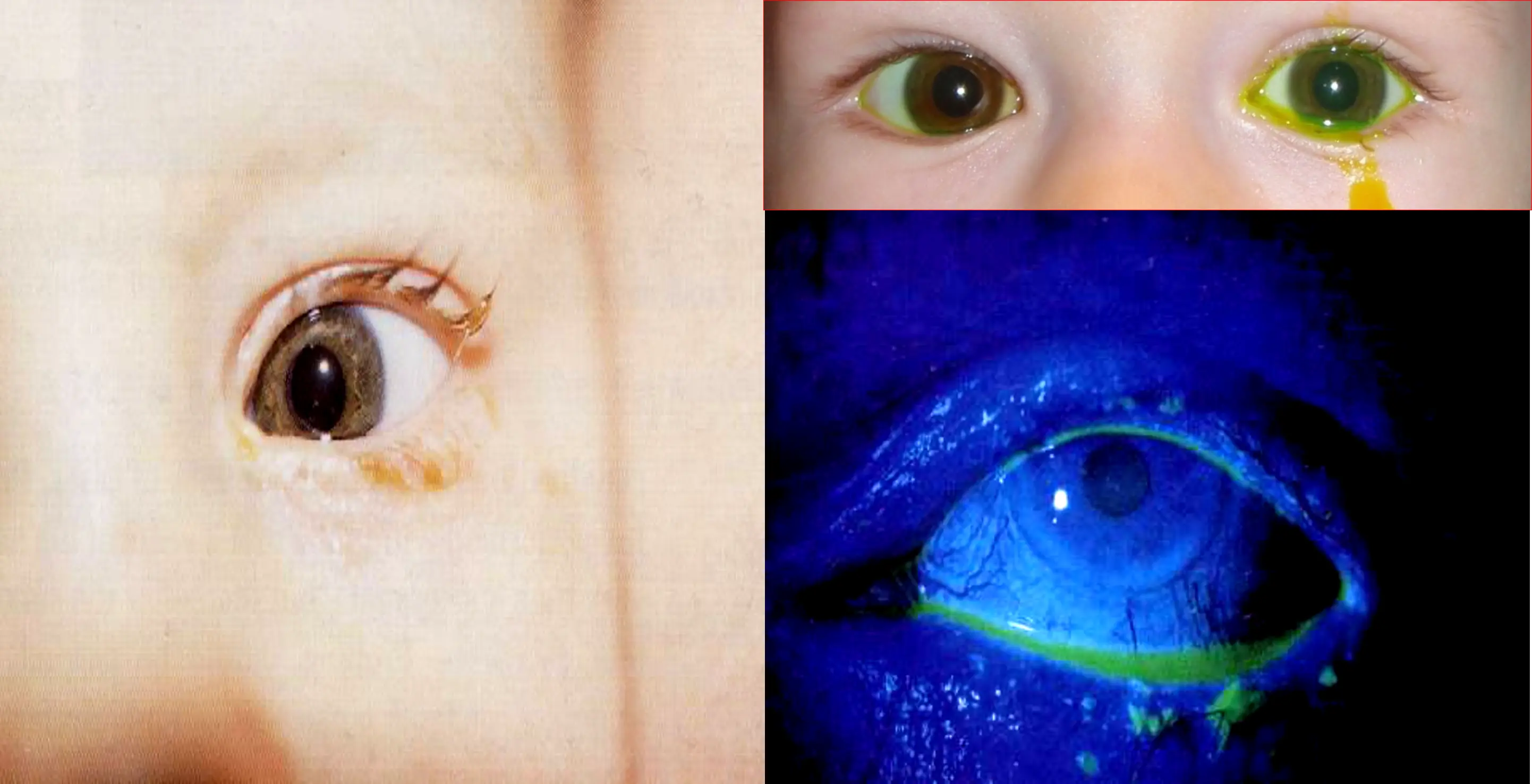
Congenital Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction
- Symptoms
- Signs
- Dye Disappearance Test.
- Management:
- Massage of the lacrimal sac.
- Topical antibiotics.
- Probing and syringing ± stenting after the age of 1 year.
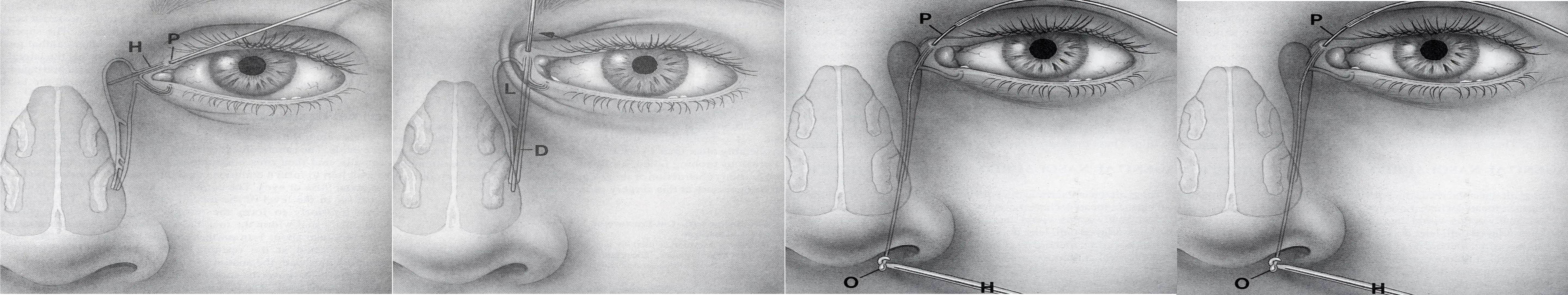
Acquired NLS Obstruction
(Chronic Dacryocystitis)
- Symptoms: epiphora + mucopurulent discharge
- Signs: painless swelling
- +ve regurgitation test
- irrigation will confirm the obstruction
- Treatment: Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) ± stenting