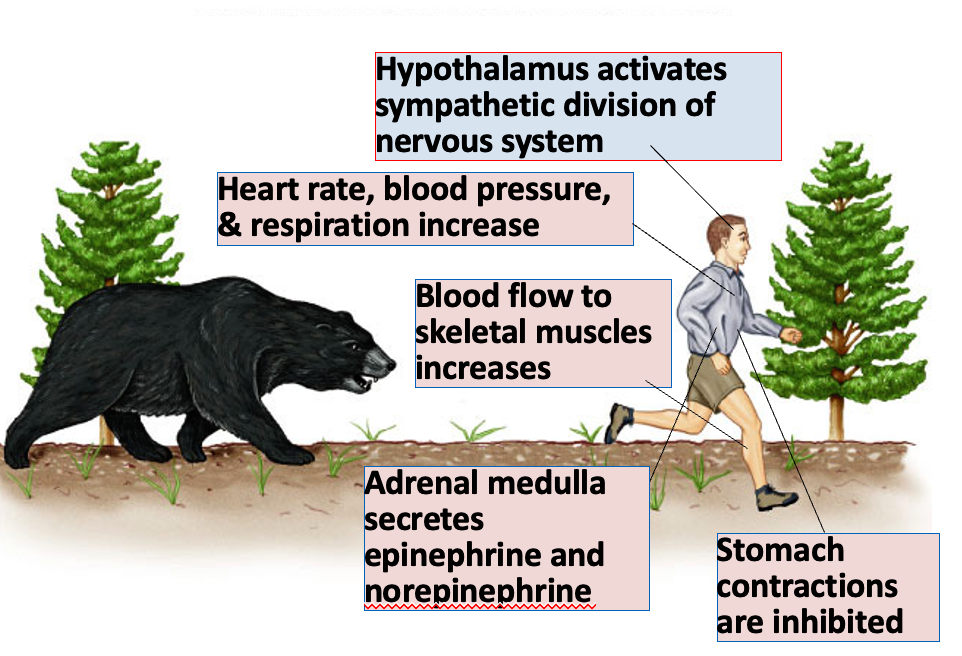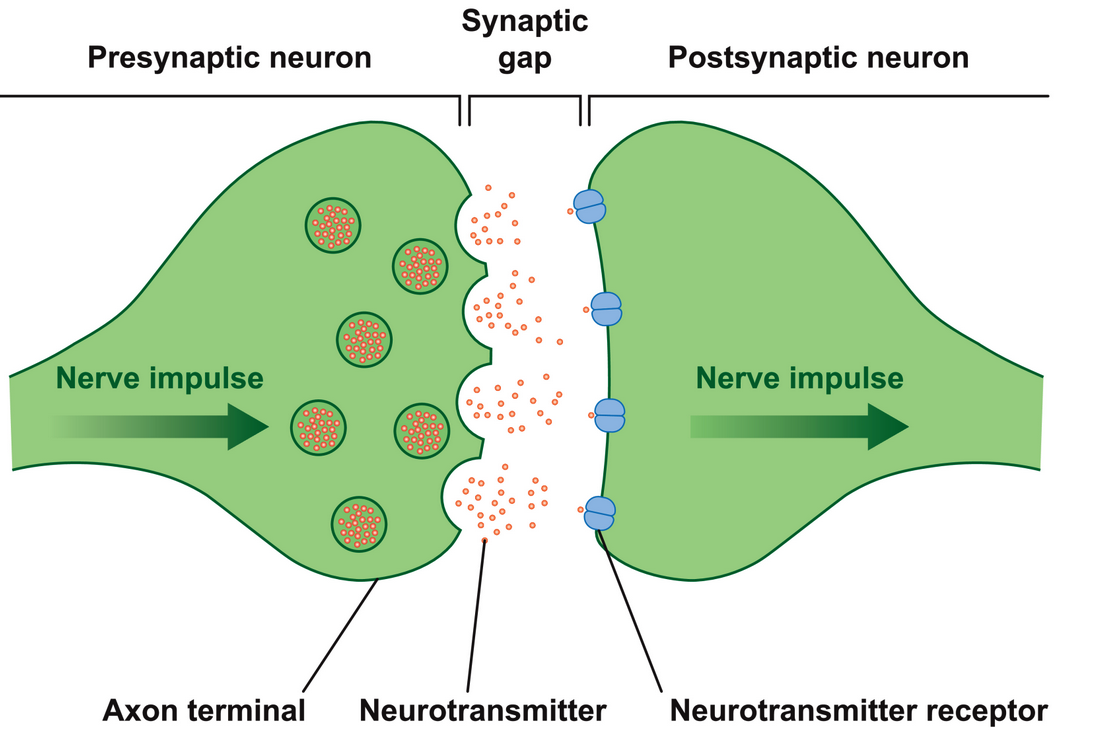
Autonomic ANS
Fate of noradrenaline:
- Re-uptake:
- Neuronal uptake (uptake 1): active transport of NE into the neuronal cytoplasm
- Granular uptake (uptake III): active transport of NE from the cytoplasm of the nerve ends into the storage granules.
- Non-neuronal uptake (uptake II): uptake to the tissue
- Metabolism by specific enzymes: NE and other catecholamines are metabolized into biologically inactive products by oxidation (monoamine oxidase; MAO enzyme) and methylation (cathecol-Omethyl transferase; COMT enzyme)
Autonomic receptors
The released chemical transmitter will produce its physiological or pharmacological action via stimulating the corresponding receptor on the effector cell.
Receptors that respond to acetylcholine are called cholinoceptors and those that respond to epinephrine and NE are called adrenoceptors
Adrenoceptors:
Can be subdivided into alpha and beta adrenoceptor types.