GIT
History
Symptoms
- GIT and hepatobiliary symptoms
- Halitosis
- Abdominal Pain
- Steatorrhoea
- Vomiting & weight loss
- Other Git Symptoms - Constipation, Dysphagia, Acute Diarrhea etc..
- Heart Burn
- GI tract diseases
- Drugs and alcohol
- Functional
- Psychogenic
Past Hx
- History of a similar problem .
- Pancreatitis, bleeding peptic ulcer or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Coexisting peripheral vascular disease, hypertension, heart failure or atrial fibrillation may suggest aortic aneurysm or mesenteric ischaemia.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis are associated with thyroid disease,
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with diabetes and obesity.
- Ask about previous abdominal surgery.
- Antibiotics cause diarrhoea
- Glucocorticoids cause weight gain
- Rifampicin, Paracetamol cause jaundice
- Coamoxiclav, Flucloxaclin cause cholestatic jaundice
patients with irritable bowel syndrome often report specific food intolerances, including wheat, dairy products and others.
Painless diarrhoea may indicate high alcohol intake, lactose intolerance or coeliac disease.
Examination
Inspection:
Position
Is the patient well or unwell, comfortable or in pain, moving easily or lying motionless? e.g. peritonitis? Writhing in agony, e.g. ureteric or biliary colic?
Pulse, temperature, respiration VITALS
Is the patient flushed, suggesting pyrexia? Pulse and temperature are raised in inflammatory conditions, with bowel infarction. An increased respiratory rate : pneumonia referring pain to the abdomen
- Hand: anemia; multiple scars, clubbing, palmar erythema, pulse; diminished CLD
-
Clubbing - Also indicates IBD, Cirrhosis
-
leukonychia; due to low albumin liver - (Stigmata of CLD) hepatosplenomegaly
-
Kolionychia (spooning); Iron deficiency anemia - GI Bleeding, Gastric Cancer, Gastrectomy
-
Palmar Erythema (Hypothenar Eminence) - Stigmata of CLD
-
Dupuytren’s contracture - Palmar tendon becomes thickened Stigmata of CLD - Alcohol
-
Hepatic tremor Flapping Tremor - indicating Hepatic encephalopathy;
-
Move your hands on forearm - look for AV fistula indicate renal failure (patient undergoes dialysis)
-
-
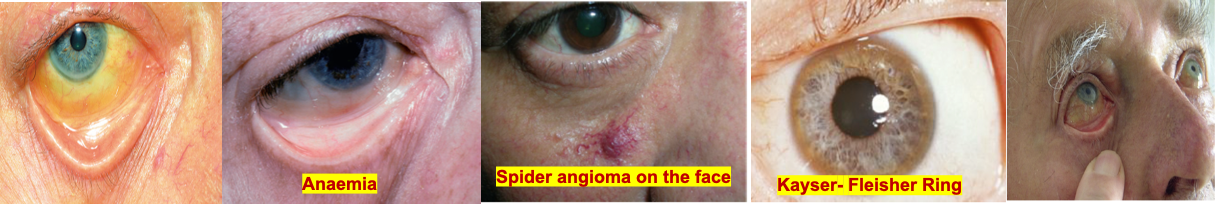
Face: Jaundice, corneal arcus…
-
Greet - check for Gingival Hyperplasia indicating Transplanted Kidney; due Immunosuppressants (cyclosporins) + Acute Myeloid Leukemia in children
-
In children, a bleeding tendency and splenomegaly can be symptoms of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
-
then go to the face look for Jaundice (Look Down) & Anemia (Look Up) - use your thumb, makes sure there is good light source if not mention so Unilateral Jaundice - Retinoblastoma - must be replaced for glass eye
-
Anterior uveitis and scleritis are eye conditions that typically present with pain.
-
Episcleritis is an eye condition that generally does not present with pain.
-
Crohn’s disease, an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can cause red eyes.
-
Wasting temporalis muscle due cachexia manifestation; indicating tumors and stigmata of CLD
-
Cushingoid features - possibly due to Crohn’s disease treatment or post-transplant medications
-
Parotid Enlargement - stigmata CLD - Alcohol
-
Hepatitis C due Needles; drug use, re use of needles
-
Hepatitis B due STDs; sex worker
-
Thalasemia = Hepatomegaly + zygomatic bone prominence +
-
palmar erythema may indicate stigmata of CLD
-
Hemochromatosis or Recurrent blood transfusion; (± Infection hep. B & C) - results in increased iron can cause CLD CLD correlation with Normochromic normocytic (IBD;Crohns affect ileum b12 absorption) and microcytic hypochromic anemia (GI bleeding)
-
Pallor if CLD; portal hypertension; GI Bleeding; Varicosed veins + Dysfunction B12 due of Ileum malabsorption ± Crohns + Renal involvement
-
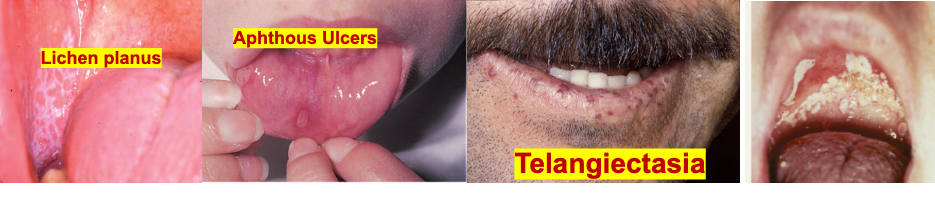
Angular Stomatitis (Geographic Tongue) - Malabsorption, B12 deficiency Ulcerative Colitis,
-
Aphthous ulcers; painful - due Crohns
-
Gingival Hyperplasia may result from following (Cyclosporin’s, CCB, Poor oral hygiene, Braces, Vitamin C deficiency)
-
Smooth Tongue - Iron Deficiency Anemia
-
Autoimmune hepatitis = CLD
-
Assess Thyroid Gland - association of other autoimmune diseases in liver
-
Phigner granumulatosis & aspergillosis cause unilateral eye exophthalmos along with saddle nose deformity - precipitating behind eye resulting in vasculitis
-
-
Neck:
-
LN: All body lymph nodes
-
Chest: surgeries, hair distribution, spider angioma; contraceptives, CLD, …
-
Spider naevus - press on it then remove your hand to check for any changes/reappearance is positive (stigmata CLD of chest) diagnostic +2
-
Gynecomastia (stigmata of CLD) - test for fluctuation with two fingers to assess firm tissues - may be using spironolactone which participates gynecomastia
-
Axilla hair distribution Acanthosis nigricans - indicating GI malignancy
-
-
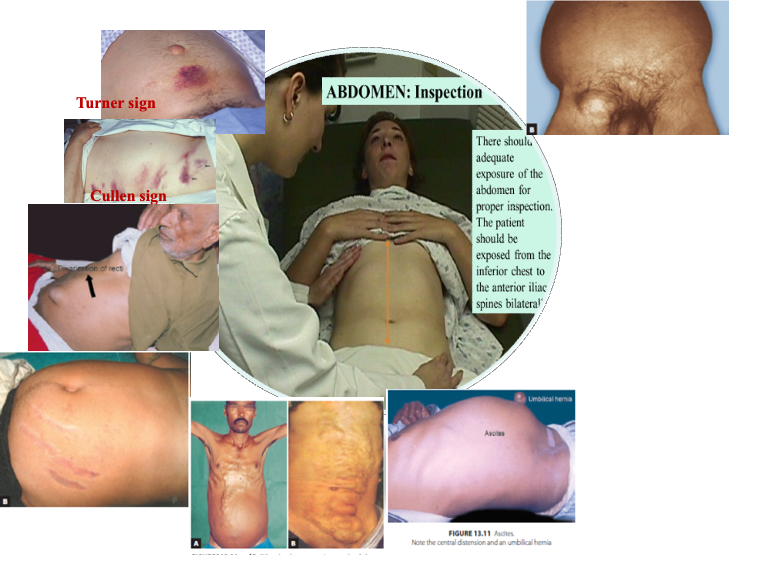
Abdomen: Venous distention, Ascites, hernias; cough, umbilicus, cullens & grey turner; Pancreatitis
-
go infront patient
-
Ask to cough, check for hernias
-
Exposure flat, Until pubic symphysis - chest clear for stigmas
-
Abdomen Distended; Ascites, Umbilicus status
-
Scars; Liver transplant (mercedes benz scar).
-
if full of scars; (may not reached to diagnosis due to multiple scars)
- Crohn’s disease
- Familial Mediterranean Fever
- Porphyria; Enzyme Malfunction may lead to multiple skin scars
-
Caput Medusa (stigmata of CLD)
-
Cullen’s sign; Periumbilical + Grey Turner’s sign; Flank hemorrhages - (acute pancreatitis)
-
==Chronic liver = ++ Estrogen; Inverted hair distribution?== (check answer)
-
Scar of renal transplant is at the area of appendix
-
-
Lower limbs: Edema, hernias… Pitting Edema (CLD) - warm your hand before palpation - press with two sides at same time for tibia, check patient eyes for any pain - comment findings
Palpation:
after expiration move hand from palpation all nine regions Sit, Start from right iliac fossa with your eyes on the patient to check for any pain - ask patient if there’s any pain and avoid location if patient comment before hand (move in clockwise)
-
Keep your hand constant in movement, dont remove your hand for palpation position
-
Superficial palpation: Guarding, Pulsatile lesions, LN; ask pain
-
Deep Palpation: Organomegaly, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, mass, Liver span + percussion
Hepatomegaly
At ends of liver palpate deeping with your finger, like wave form when going inside open your hands to palpate liver margins
Liver span is normally 6 to 12 cm in the midclavicular line
Avoid tender areas, look patient eyes to assess.
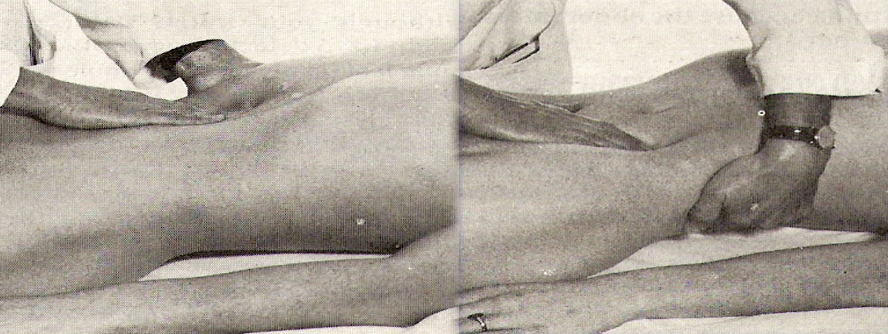
Spleenomegaly
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rKsqO1tAKvs
- Deep breath for palpation
- waveform
- Dont Act - Relax your fingers
- Not palpable in healthy patient
pyelonephritis
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=obIdJsgi_gs https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tr6CYu3GiKE
- Renal transplant Scar - located at Appendix right iliac fossa
bimanual examination
- costrophrenic angle one hand, other on abdomen on both sides
- Percussion
- comment on mass/tenderness
Causes of Tender Hepatomegaly
- Portal Hypertension; 1st answer
- Right sided Heart Failure
- Bud Chiari malformation (BCS) - pip on hepatic vein closed = congested
- Early Stage Cirrhosis
- Liver Fibrosis - Schistosoma mansoni ( or schistosomiasis hematuria)
- Schwannoma cell carcinoma - spleen, shifting dullness
- Infections - Malaria - visceral leishmaniasis (kalazar)
- Hodgkin’s lymphomas, Thalasemia, Leukemias
- Hepatomegaly; Hypoglycemia due - Glycogen Stomach disease - gusher disease
- Metastasis (with irregular surface)
- Primary liver tumor - alpha toxins
- Thalasemia
- malaria-visceral leishmaniasis
Causes of Hepatosplenomegaly
-
heptosplenomegally + stigamta of CLD = CLD even if you find one stigmata
-
hepatosplenomegally + jaundice + pallor = likely thalasemia/hemolytic anaemia
-
hepatosplenomegally + pallor = likely myloprolifertive disorder like leukemia
-
hepatosplenomegally + pallor lymphnodes =
- likely lymphoproliferative disorder like lymphoma or
- visceral leishmaniasis ( kalazar )
-
Hepatosplenomegally only + frequent attacks of hypoglycemia in young patient = most likely this glycogen storage disease like von geirk disease
-
hepatosplenomegally + short stature and mental retardation = lysosomal storage disease
Splenomegaly causes
-
splenomegaly only with skin rash induced by amoxicilin think about infectious mononucleosis
-
splenomegally only with Rhumatoid hand think about feltys syndrome
-
thalassemia + portal hypertension + malaria & Visceral leishmania
Causes of palpable kidneys:
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Hydronephrosis
- Tumor; Renal cell carcinoma
- Wilms Tumor in children
- Amyloidosis infiltration
- HTN
How to differentiate kidney, spleen
-
Spleen has notch, enlarges Diagonally/Oblique, moves with respiration, not palpable, under rib cage cant go above it
-
Kidney enlarges Vertically, largely unrelated, Palpable , Ballottable, does not move with respiration
Masses of Abdomen
Mass in RUQ:
- Ca. hepatic flexure, enlarged gallbladder, enlarged right kidney, hepatomegaly
Mass in epigastric region:
- Liver, gastric carcinoma, abdominal aortic aneurysm (Palliation)
Mass in LUQ:
- Splenomegaly, carcinoma descending colon, swelling in tail of pancreas,
- Enlarged left kidney
Mass in periumbilical region:
- PUH, ca. transverse colon, tumour deposit (Sister Mary Joseph’s nodule)
Mass in LLQ:
- Descending colon (Benign, malignant Carcinoma) Sigmorectal
Mass in the suprapubic region:
- Distended urinary bladder, pregnancy, ovarian mass
Mass in RLQ:
- Appendiceal disease, ca. ascending colon, Crohn’s disease of ileo-caecal area
Mass in inguinal region:
- Hernia, lymphadenopathy, aneurysm
Percussion:
-
Organomegaly (differentiating organs and extent),
- Spleen & Liver Dull
- Kidney is resonant; bimanual
Liver size Start below then above costal margin by cm or finger width
-
Fluid thrill & Shifting dullness Shifting Dullness Percussion from below sternum - until dullness from bladder - then becomes resonance, change position of hand to vertical by then https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Eog7addNRwc M ild to moderate ascites are usually on flanks - You can check by percussion -
-
dullness progressively getting more by flanks Light percussion middle midline for shifting dullness - Between 3rd and 1st space between umbilicus then percussion rest check for ressonance/Dullness
-
to assure its ascites or mass; keep hand same position by 20-30 seconds;
-
do the percussion again after shift other side, then after 10 seconds for viscera of fluids to descend - percuss to check… switching patient to other side; if mass it will be dull - if ascites the fluid directed downwards resulting in shifting dullness & resonance - reverse shifting dullness? Ascites? if huge Fluid Thrill
Fluid Thrill bilateral test flick, not advised Severe ascites, will resulted in … 1. main indicator by simple touch, with slight movement of abdominal region 2. Put hand on other side, and stimulate the abdomen from opposite side - (((whilst asking patient put their hand in midline))); to prevent transmission of fluid through anterior abdominal wall
Causes of Ascites; Ascites assessment: Fluid thrill and shifting dullness
Transudate; Protein is low in fluid
- Heart Failure; Hydrostatic Pressure
- Liver Failure; Cirrhosis; Fibrosis
- Renal Failure; Nephrotic Syndrome
- Protein loosing enteropathy
exudate: Increased protein
- Infection - Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis - SBP -
- Cancer of abdomen
- Meigs syndrome (benign ovarian tumor presents along with ascites and pleural effusion)
- Pseudoxanthoma peritonii - reticuli ??? (check answer)
- SBP + chemical peritonitis - pancreatitis
Auscultation:
Comment on
-
Bowel sounds: Healthy persons may have no bowel sounds for several minutes (silent intestinal contractions). Bowel sounds are exaggerated (borborygmus), and increased in rate in mechanical intestinal. Absent (paralytic ileus),
-
venous hum: (indicate portal hypertension) - soft systolic murmur - large volume of blood flows in umbilical and paraumbilical veins in falciparum ligament (portosystemic shunt)
-
hepatic bruit: (indicating increase vasculature) - Heard over the liver, usually due to hepatocellular carcinoma, or vascular hepatic tumours
-
Aortic bruit: Just above the umbilicus
-
Renal bruit: Occurs in renal artery stenosis due to turbulent flow through a narrowed vessel
-
Succussion splash: Excess fluid in the gut, e.g. from pyloric stenosis, or advanced intestinal obstruction, may splash when the abdomen is shaken, or the patient rolled from side to side
After finishing all examination mention and examine
- Lymph nodes,
- lower limbs,
- Per Rectal examination,
- Per vaginal if female
- Melenas,
- Temperature,
- Sacral Edema
Other Notes
- Abdominal E
- 45 degrees if patient presents with ascites
- Patient with chronic liver disease case will be given in exam -
- uncold your hand prior to palpation
- Dont Wear Gloves, Wash your hands
- Dont percuss below umbilicus (Urinary Bladder)
- Dont wait validation from examiner - if he commented to do it again do so
- Dont raise your arm when going with continuem of percussion
- smooth muscle irritation such as stone, has cloiky like pain
- Vascular event, ischemic - sharp tearing acute pain
- percussing liver span hard from costal, and soft on abdomen
- Testicular pain may innervate to the abdomen
- US - liver blood flow direction changes pathologies
cause of bloody stools? Blanching skin? Purpura vs Petechia? Cloudy Omentum? Tumor Markers?
Cases
C1
female with ascites
C2
33 year old indian medically free presented to hospital w/ 1M progressive dull epigastric pain, jaundice, fatigue. patient also experienced night sweats, weight loss, but with no fever. patient was in india this year, recently came to saudi arabia.
- SOB
- no vomiting , no nausea, no urinary symptomps, no neurological
- no chest pain
- tombak 8 yrs
O/E
- patient is alert conscious orientated
- connected to urin cath
- connected to IV line and drainage tube
Differential
- CKD
- COPD
- Amboieasis
- Malaria
Investigations
- Culture negative
- CT scan with contrast showing multiple pyogenic large disseminated abbesses of liver
- X-ray pleural effusion
- low HB, Albumin, Creatinine
- increased WBC, Urea, LDH, ALT, AST, Direct billirubin, pro BNB due ARF
- Lipase amylase is normal.
- ESR 28
Management
- Ceftriaxone IV empiric + Metriandazole, Dialysis
C3
30 year old male bangaladesh driver with known case of DM, High CL & HTN presented to ER with 7d hx of abdominal pain, fever, subsided dysuria, severe oliguria, back pain, headache.
- Hematuria,
- Foley catheter
- no vomitting
- no nausea
O/E
No abnormal finding, patient improved
Differential
- Acute Renal Failure
- Obstructive; tumor etc…
- Liver abscess
- Cyst