Psychiatry
Causes of Global Burden of Disease
2004
- LRTIs
- Diarrheal diseases
- Unipolar depression
- Ischemic heart disease
- HIV / AIDS
2030
- Unipolar depression
- Ischemic heart disease
- Road traffic accidents
- Cerebrovascular disease
- COPD
MDD:
- 2004: #3 cause of global burden of disease
- 2020: #2 cause of global burden of disease
- 2030: #1 cause of global burden of disease
MDD = major depressive disorder; LRTI = lower respiratory tract infection; HIV = human immunodeficiency virus; AIDS = acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. WHO, 2004.
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization Website. Mental Health. Depression. What is depression? Available at: WHO Mental Health.
Accessed October 28, 2011.
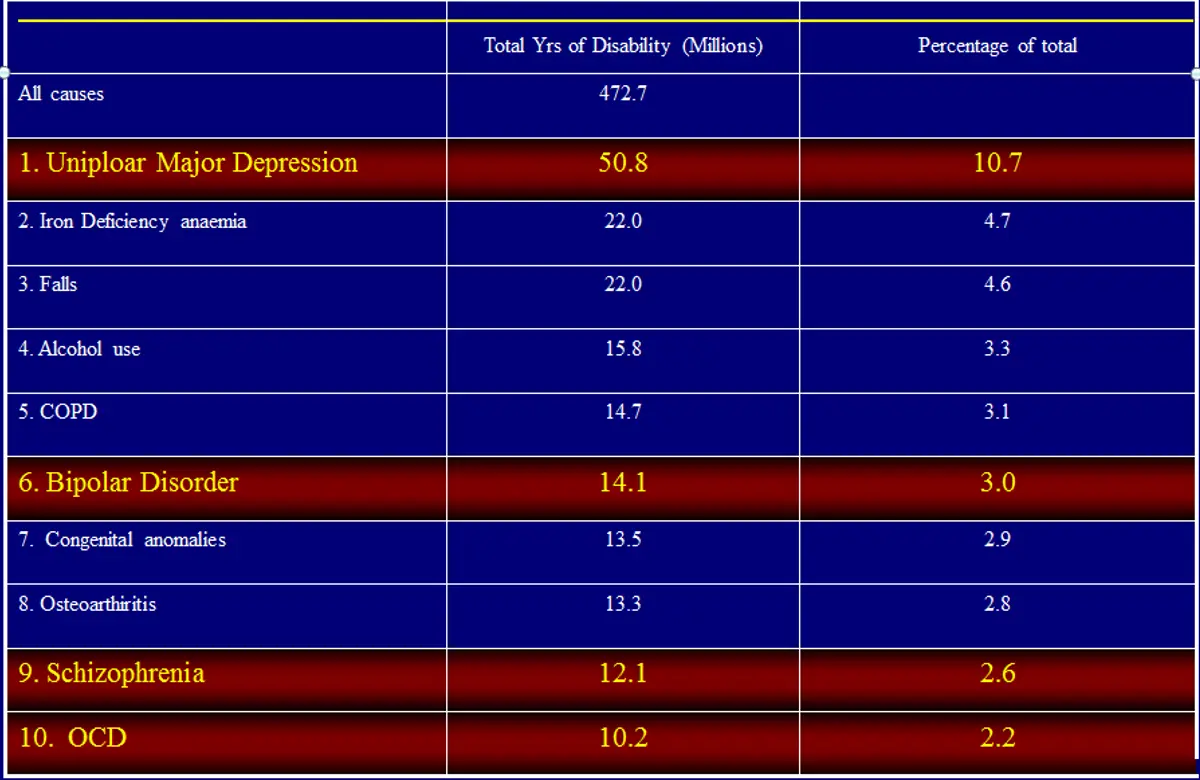
The Leading Causes of Disability Worldwide
- All causes
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 472.7
- Unipolar Major Depression
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 50.8
- Percentage of total: 10.7
- Iron Deficiency Anaemia
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 22.0
- Percentage of total: 4.7
- Falls
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 22.0
- Percentage of total: 4.6
- Alcohol Use
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 15.8
- Percentage of total: 3.3
- COPD
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 14.7
- Percentage of total: 3.1
- Bipolar Disorder
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 14.1
- Percentage of total: 3.0
- Congenital Anomalies
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 1.3
- Percentage of total: 2.9
- Osteoarthritis
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 13.3
- Percentage of total: 2.8
- Schizophrenia
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 12.1
- Percentage of total: 2.6
- OCD
- Total Yrs of Disability (Millions): 10.2
- Percentage of total: 2.2
What is Depression?
Depression is not:
- “Weakness of character”
- “Madness”
- “Something that will pass”
- Incurable
- Inevitable
Depression is …
- Persistent low mood for at least two weeks plus at least 5 of the following:
- Poor appetite or weight loss or increased appetite or weight gain
- Loss of energy or tiredness to the point of being unable to make the simplest everyday decisions
- An observable slowing down or agitation
Depression is …
- A markedly diminished loss of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyed
- Feelings of self-reproach or excessive or inappropriate guilt over real or imagined misdeeds
- Complaints/evidence of diminished ability to think or concentrate
- Recurrent thoughts of death, suicide, suicidal thoughts without a specific plan, or a suicide attempt or plan
Depression: A SAD FACE (S)
- A - Appetite
- S - Sleep
- A - Anhedonia
- D - Depressed mood
- F - Fatigue
- A - Agitation
- C - Concentration
- E - Esteem
- S - Suicidal
Montano, J Clin Psych 1994
Depression: Risk Factors
- Age: Peak age of onset 20-40 yrs
- Gender: Female 2 X higher
- Family history: 1.5 to 3 X higher
- Marital status: Divorced, separated, widowed
- Married vs. unmarried???
Depression: Risk Factors
- Personal history of depression
- 1 episode - 50% relapse
- 2 episodes - 75% relapse
- 3 episodes - 90% relapse
- Postpartum: up to 1 in 10 women
- Chronic medical illness
Functional Impairment in MDD
-
MDD impairs occupational and social functioning
- 87% exhibit at least moderate impairment
- 59% exhibit severe or very severe impairment
-
MDD is associated with:
- Increased number of disability days
- Decreased work productivity, psychosocial disability
-
MDD and work productivity:
- Impact on function at work is substantially higher than missed work days
- Absenteeism represents only a small fraction of workplace cost
- Druss BG et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;731-34.
- Judd LL, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:375-80.
- Kessler RC et al. JAMA. 2003;289:3095-105.
Categories
- Work
- Social
- Family
