Ortho
Hyperparathyroidism
Common Causes
- Primary: parathyroid adenoma
- Secondary: hyperplasia due to hypocalcemia (destroys the bone)
Effects of Increased PTH ✓
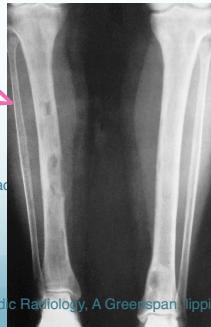
- Increased bone resorption → weak bone
- Increased serum calcium levels
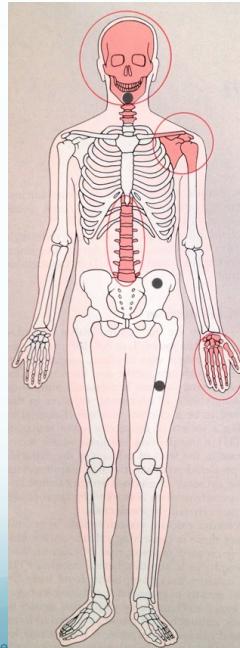
Clinical Manifestations: “Bones, Stones, Moans, Groans”
Bones
- Rarefaction (decreased bone density)
- Brown tumors
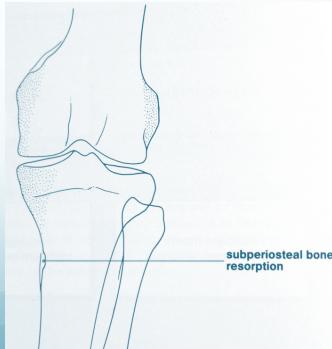
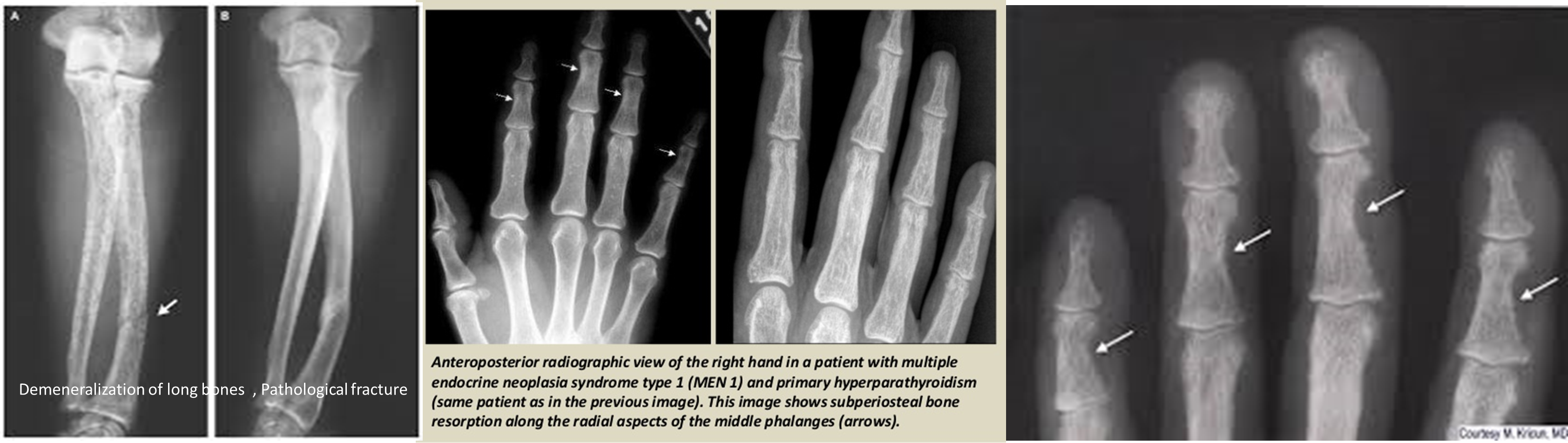
- Sub-periosteal resorption of:
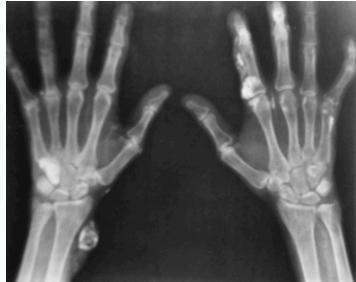
- Middle phalanges
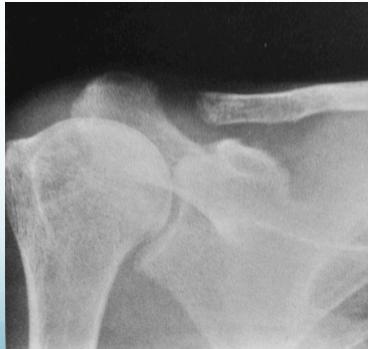
- Lateral end of clavicle
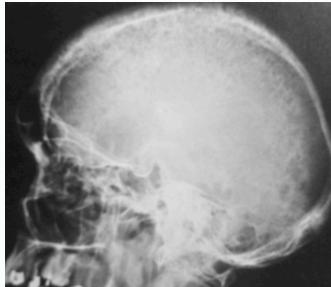
- Skull: “salt & pepper” appearance
- Soft tissue calcification
Stones
- Kidney stones and nephrocalcinosis
Moans
- Abdominal pain
- Renal pain
Groans
- Psychological manifestations: depression, stress
Radiological Features
Characteristic X-ray Findings
- Sub-periosteal bone resorption (most specific finding)
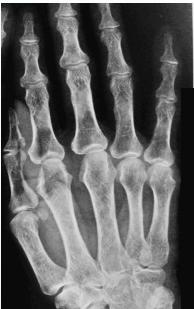
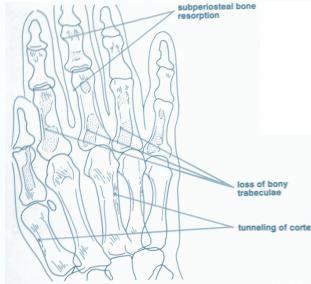
Comprehensive Radiological Manifestations
- Bone changes:
- Rarefaction (generalized osteopenia)
- Bone resorption patterns:
- Sub-periosteal resorption: middle phalanges, tibial shaft
- Lateral end of clavicle resorption
- “Brown tumors”: (coagulated blood-filled cystic spaces)
- Skull: “salt & pepper” appearance
- Soft tissue calcification
Treatment
Medical Management
- Adequate hydration
- Reduced calcium intake
Surgical Management
- If adenoma is present:
- Surgical removal of the adenoma
- Beware of “hungry bone syndrome” post-operatively:
- Bones rapidly take up Ca2+ from blood
- Can cause severe hypocalcemia if not anticipated
Surgery
Causes:
-
Primary hyperparathyroidism: is usually due to a parathyroid benign adenoma (75%) or parathyroid hyperplasia (20%). 1.0% have parathyroid carcinoma.
-
Secondary hyperparathyroidism: is hyperplasia of the gland in response to hypocalcemia (e.g., in chronic renal failure).
-
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism: autonomous secretion of parathormone occurs when the secondary stimulus has been removed (e.g., after renal transplantation).
-
MEN syndromes: (type I (parathyroid adenoma, pancreatic islet cell tumors, pituitary adenoma) and type II (parathyroid adenoma, medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma)
-
Ectopic parathormone production (e.g., from small cell lung cancer).
Pathology:
- Parathormone mobilizes calcium from bone,
- enhances renal tubular absorption and,
- with vitamin D, intestinal absorption of calcium.
- The net result is hypercalcemia.
Clinical features
- Older women, >40 years of age.
- Renal calculi or renal calcification – occurs in 20% of patients, polyuria (‘renal stones’).
- Bone pain or deformity, osteitis fibrosa cystica, pathological fractures (‘painful bones’).
- Muscle weakness, anorexia, intestinal atony, psychosis (‘psychic moans’).
- Peptic ulceration and pancreatitis (‘abdominal groans’).
Symptoms of hypercalcemia
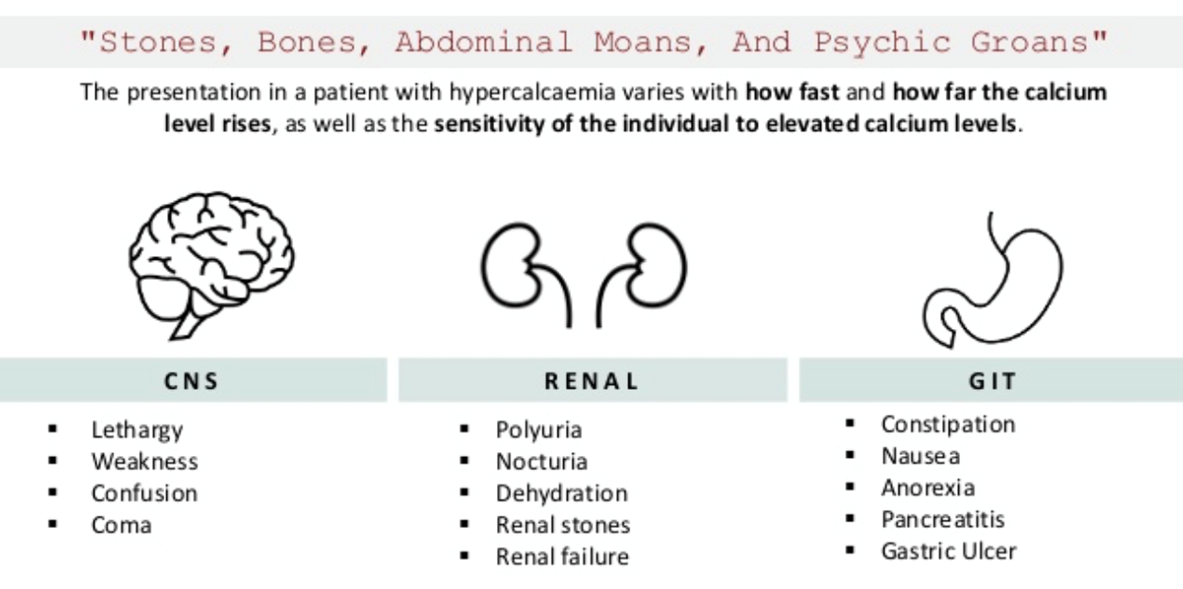
Salt-and-pepper-spots-in-skull
Laboratory:
-
High PTH
-
Elevated serum Ca
-
Low phosphate
-
High Alkaline Phosphatase
-
Low Mg
-
High urinary Ca
-
Elevated PTH in the setting of hypercalcemia.
-
Serum calcium (specimen taken on three occasions with patient fasting, at rest and without a tourniquet). Body Ca:
- 99% stored in the skeleton
- 1% is free
- ½ bound to proteins
- ½ is free ionized (Active)
-
Normal range 2.2–2.6 mmol/L. Calcium is bound to albumin and the level has to be ‘corrected’ when albumin levels are abnormal.
-
May be decreased serum phosphate and elevated alkaline phosphatase
Radiology:
- DEXA: Wrist, spine, and hip
- KUB, IVP, CT (For renal stones)
DEXA: Dual Emission X-ray Absorptiometry Demineralization of long bones, Pathological fracture
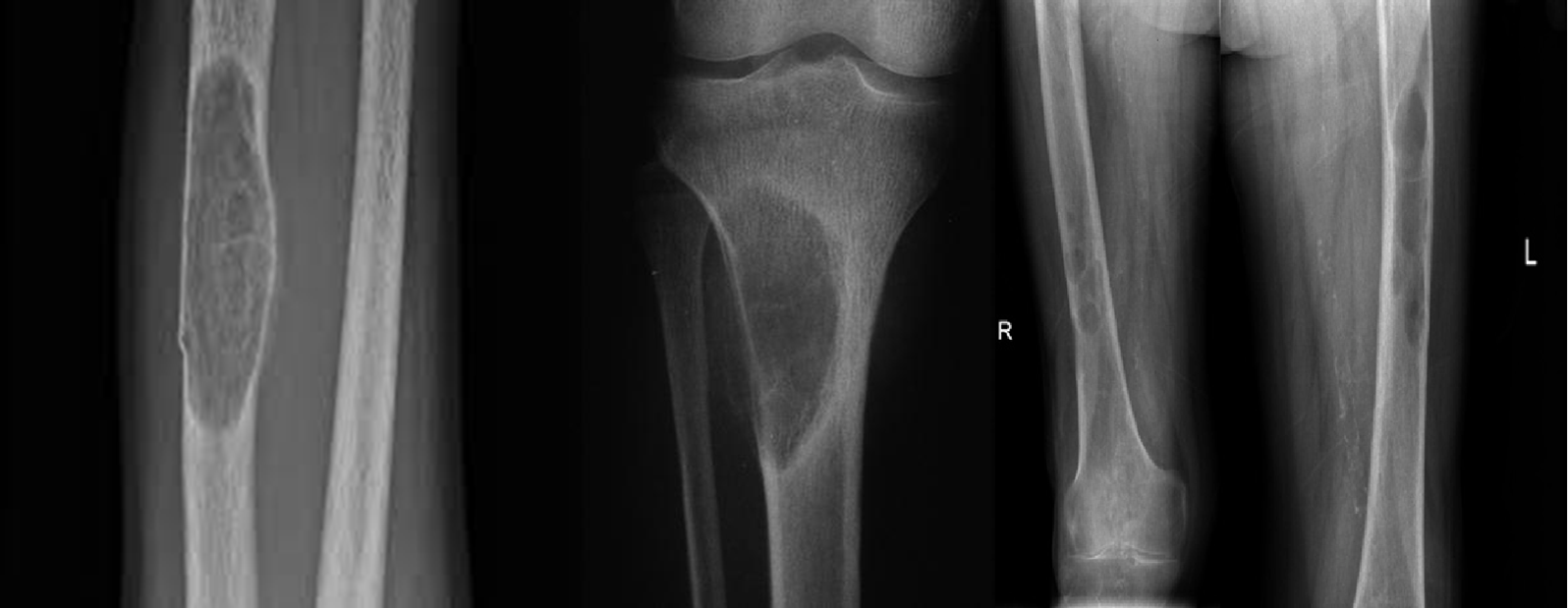 Lytic lesions caused by hyperparathyroidism are called Brown tumors. The term “Brown tumor” is a misnomer because it is not a true neoplasm.
Lytic lesions caused by hyperparathyroidism are called Brown tumors. The term “Brown tumor” is a misnomer because it is not a true neoplasm.
Management of Hypercalcemia
- Rehydration with intravenous saline until urine output of 100 /h.
- Intravenous lasix is given after rehydration.
- Serum potassium must also be replaced.
- Biphosphonate such as disodium pamidronate.
- Calcitonin
- Serum parathyroid hormone concentration must be measured urgently.
- Urgent parathyroidectomy.
Complications of parathyroidectomy:
-
Post-op. bleeding
-
Hematoma:
- Pre tracheal (airway obstruction)
- pre- platysmal
-
Nerve injury
- 1-2% permanent:
- Recurrent laryngeal (hoarseness)
- Superior laryngeal (loss of high pitched sound)
- 1-2% permanent:
-
Hypocalcemia
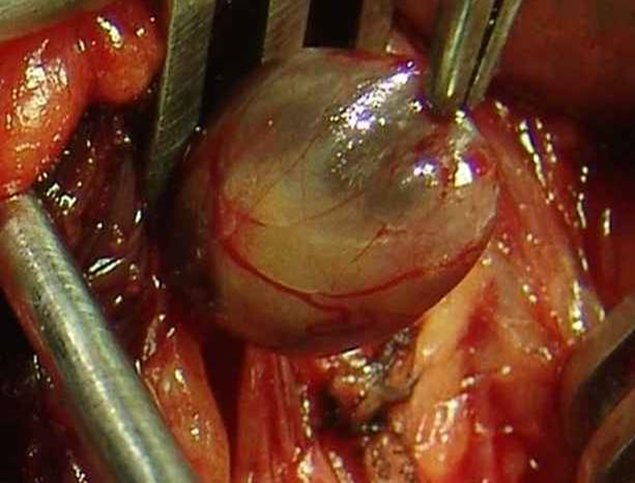
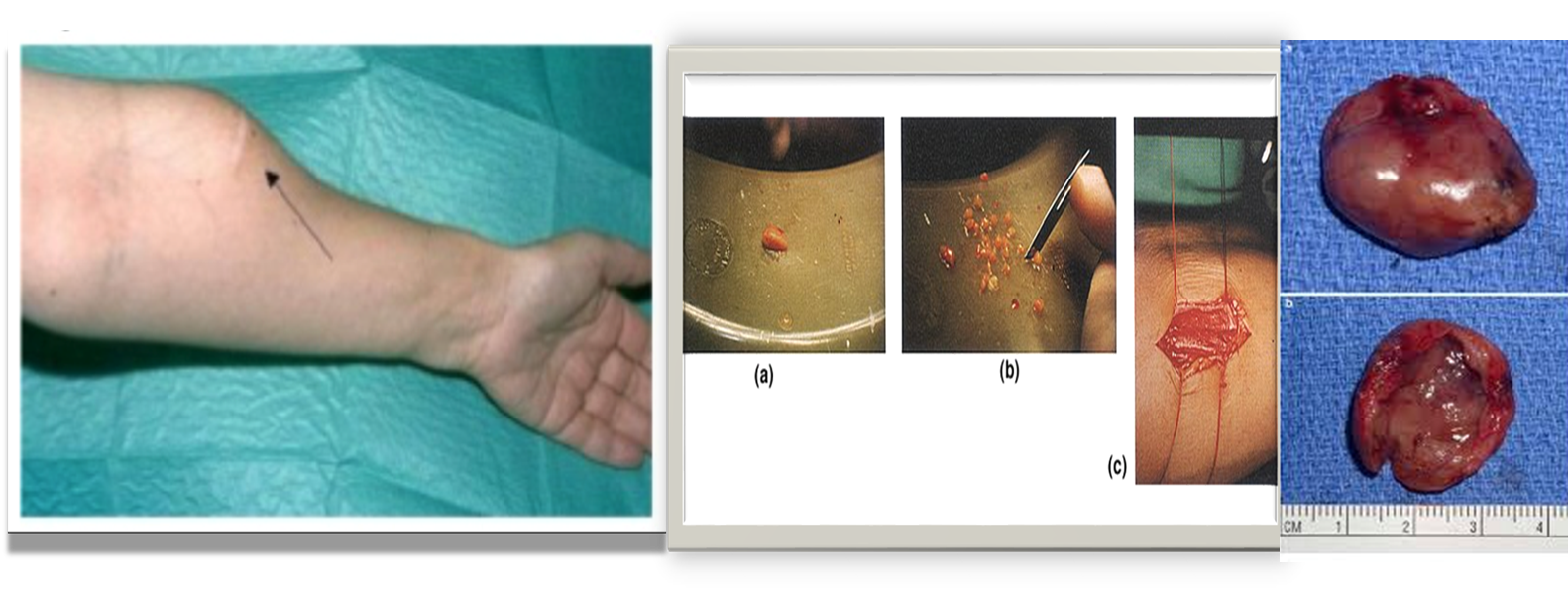 During surgery how will you confirm whether the tissue is parathyroid gland?
During surgery how will you confirm whether the tissue is parathyroid gland?
- Golden yellow color
- Put it in a cup of normal saline.
- Parathyroids usually sink but fat floats.
- Implant the parathyroid into the sternomastoid pocket or into the forearm
Imaging
Two types:
- Primary
- Secondary: Occurs due to renal failure/renal osteodystrophy
Radiological features of hyperparathyroidism
- In hand, sub-periosteal bone resorption .This change usually happen in the middle phalanges, radial aspect in the 2nd or 3rd finger.
- Terminal tuft erosion.
- Salt and pepper skull
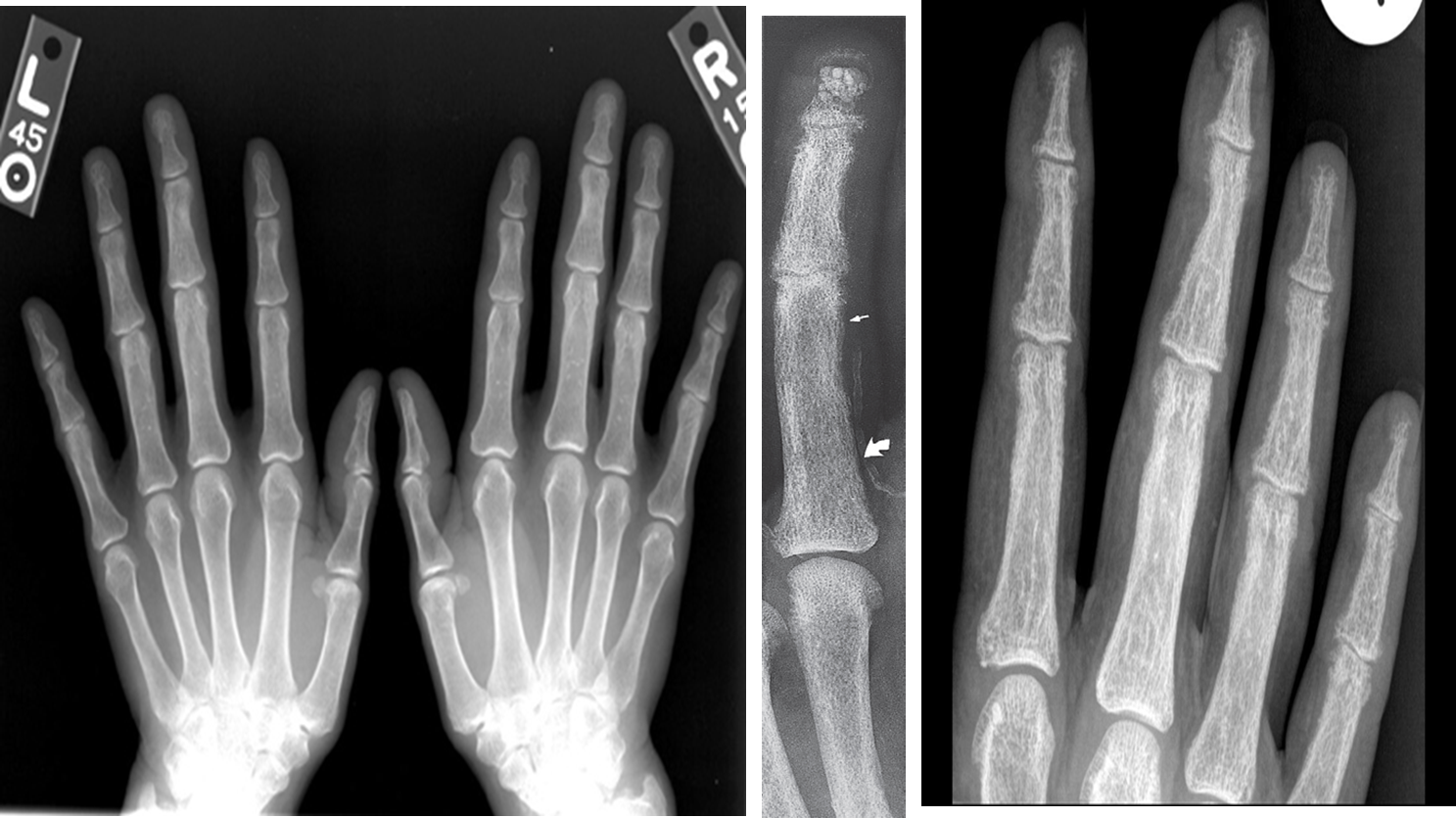
Sub-periosteal bone resorption
- Most useful sign
- Virtually Diagnostic
- Location
Subperiosteal bone resorption (straight arrow), resorption of the tip of the terminal phalanx and the altered bone architecture. Arterial calcification is also present (curved arrow).
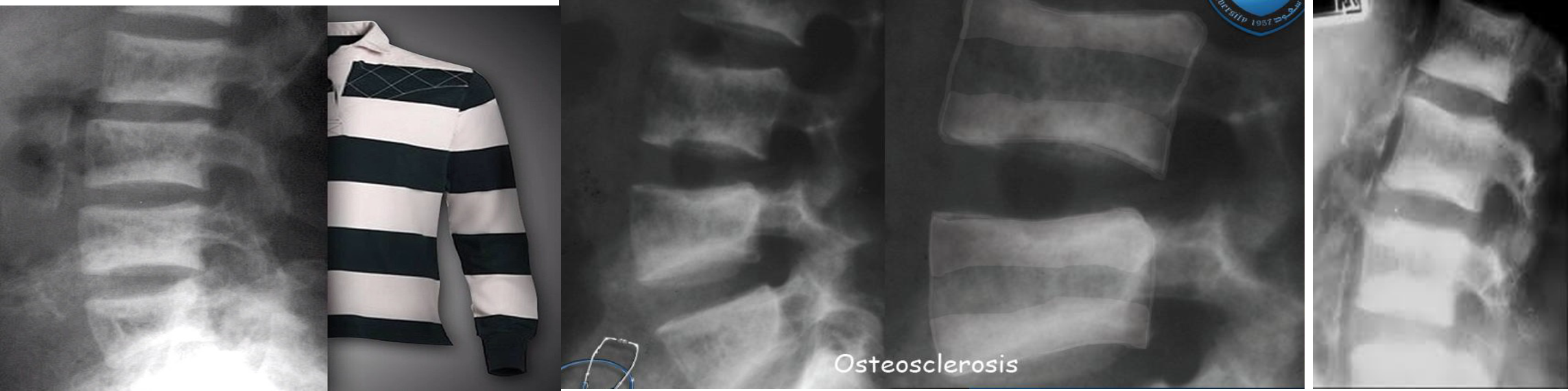
Ruger Jersey spine : secondary hyperparathyroidism z
Occurs due to renal failure/renal osteodystrophy prominent endplate densities at multiple contiguous vertebral levels to produce an alternating sclerotic-lucent-sclerotic appearance
On x-ray white margins with lucent central and vertical trabeculae, which is called( Ruger Jersey spine) these, (changes are due to renal dystrophy.
- Decreased bone density of the central portions (black area)
- Sclerotic vertebral end plates
(renal osteodystrophy). There are sclerotic bands running across the upper and lower ends of the vertebral bodies of the lumbar spine (arrows).
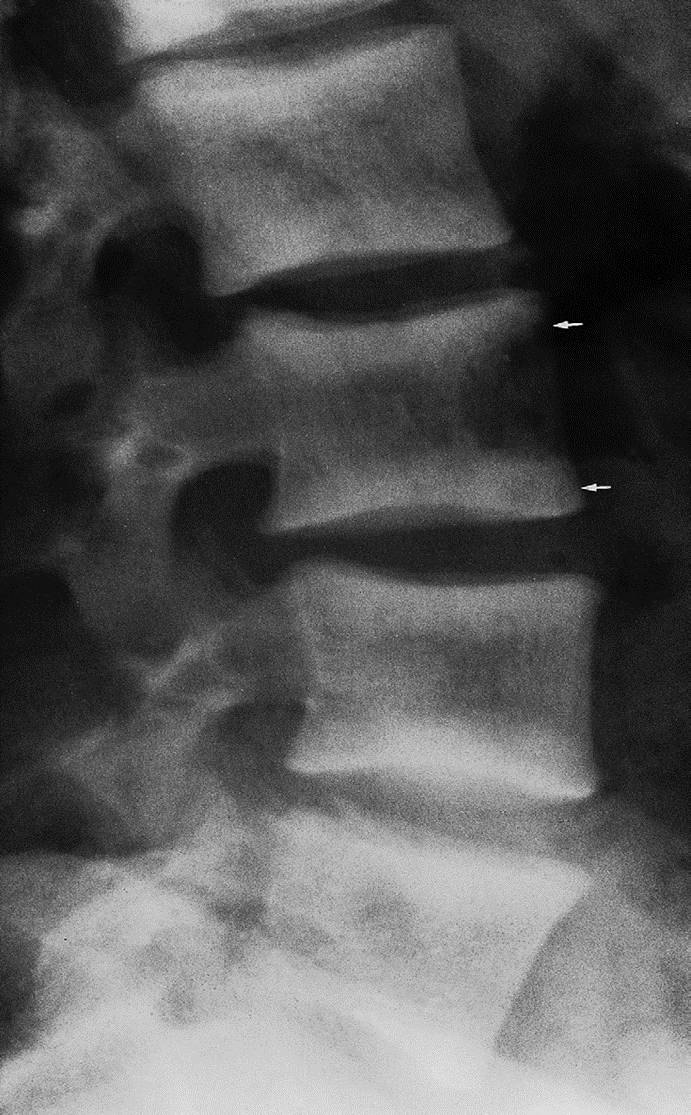
Parathyroid
Hyperparathyroidism - Primary hyperparathyroidism
Routine imaging studies Obtain in ALL patients with confirmed pHPT to evaluate for renal and skeletal manifestations.
Skeletal evaluation
- Assess for osteoporosis
- Preferred modality: Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
- Alternative: ***Vertebral x-ray ***
Renal imaging
- Assess for nephrolithiasis and/or nephrocalcinosis.
- Options include abdominal CT without contrast, renal ultrasound, and abdominal x-ray.
Additional imaging studies Neck imaging
- For surgical planning to determine the location of the abnormal glands
- Options include ultrasound neck and nuclear imaging