Floxacin ~ Fluoroquinolones - General concises
- F- drink more fluids
- L- Long QT Interval
- O- old age; arthalgia
- X- catatonic foods
- A- AVOID children/pregnancy
- C- difficile superinfection
- I- Interactions w/ caffiene, warfarin, phenytoin, theophylline, amiodrane
- N- Neuromuscular exacrebation in Myasthenia gravis
- S- sun sensitivity
 Newest drug, least chance of resistance. mainly UTI Septicemia originally for Quinolones, for Fluoroquinolones (FQs) gave broad spectrum effect
Newest drug, least chance of resistance. mainly UTI Septicemia originally for Quinolones, for Fluoroquinolones (FQs) gave broad spectrum effect
Description
Nalidixic acid is the first quinolone to be introduced and also predecessor to all fluoroquinolones, Numerous structural modifications during the 1980’s with the discovery that addition of fluorine at position-6 of the quinolone nucleus will increase antimicrobial activity and improve pharmacokinetics.
MOA Cidal
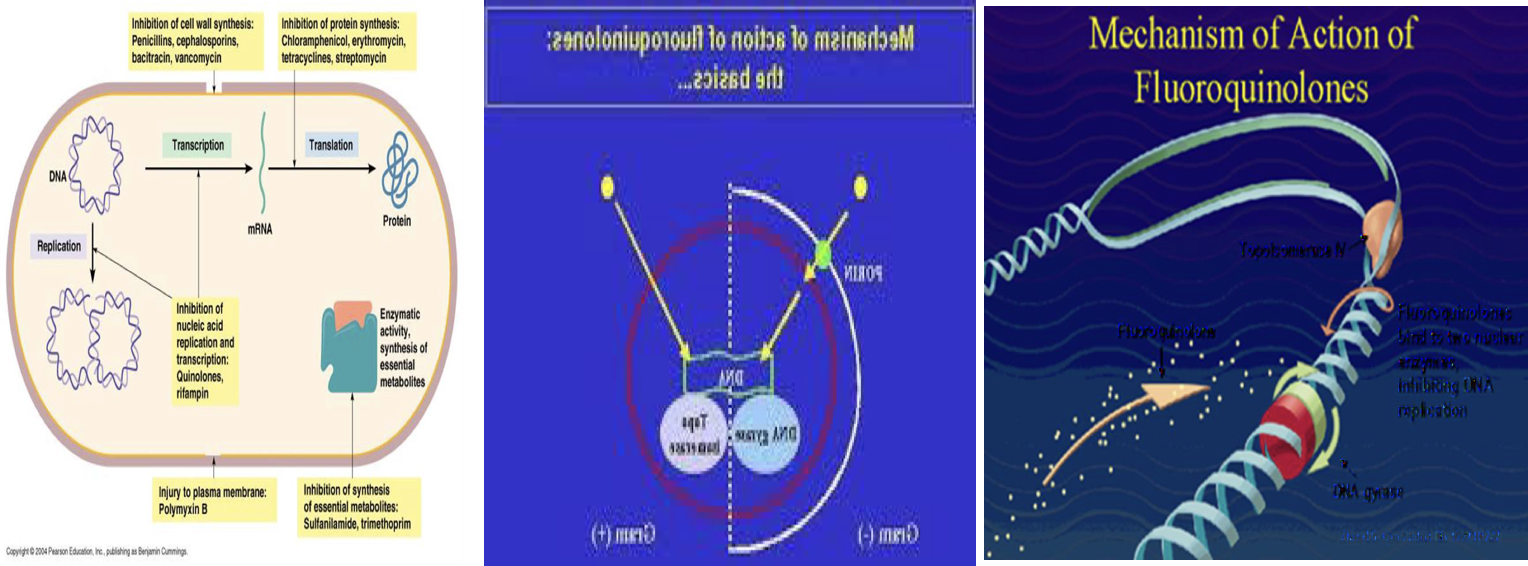
All topoisomerases can relax DNA but only gyrase can also carry out DNA supercoiling (‘supercoiling’ process is necessary to compact the bacterial chromosome which is 1000 times longer than the bacterial cell).
Topoisomerases are also involved in DNA replication, transcription and recombination.
• The main quinolone target is the DNA gyrase which is responsible for cutting one of the chromosomal DNA strands at the beginning of the supercoiling process. The nick is only introduced temporarily and later the two ends are joined back together (i.e., repaired).
• The quinolone molecule forms a stable complex with DNA gyrase thereby inhibiting its activity and preventing the repair of DNA cuts
Spectrum & TRH
fluoroquinolones are effective against: gram-positive organisms and gram-negative organisms, atypical organisms (Legionella, Chlamydia), and some mycobacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis). Fluoroquinolones are typically not used for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus or enterococcal infections
Fluoroquinolones may be classified into “generations” based on their antimicrobial targets:
- Nalidixic acid is considered to be first generation, with a narrow spectrum of susceptible organisms.
2) - Ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin are second generation because of their activity against aerobic gram-negative and atypical bacteria. In addition, these fluoroquinolones exhibit significant intracellular penetration, allowing therapy for infections in which a bacterium spends part or all of its life cycle inside a host cell (for example, chlamydia, mycoplasma, and mycobacteria) is effective in the treatment of many systemic infections caused by gram-negative bacilli. Ciprofloxacin has the best activity against P. aeruginosa Ciprofloxacin is effective for (Traveler’s diarrhea caused by E. coli , typhoid fever caused by Salmonella typhi . And Tuberculosis as a second-line agent).
3) + Levofloxacin is classified as third generation because of its increased activity against gram-positive Bacteria. is l-isomer of ofloxacin and has largely replaced it clinically. Levofloxacin has broad spectrum activity and is used in wide range of infections including: Prostatitis, skin infections, Community acquired pneumonia (CAP), Nosocomial pneumonia. Levofloxacin has excellent activity against S. pneumoniae respiratory infections. Levofloxacin has 100% bioavailability and is dosed once daily.
- Lastly, the fourth generation includes only + moxifloxacin because of its activity against anaerobic and gram-positive organisms. Moxifloxacin also has activity against many anaerobes. not only has enhanced activity against gram positive organisms (for example, S. pneumoniae) but also n has excellent activity against many anaerobes. It has poor activity against P. aeruginosa. Moxifloxacin does not concentrate in urine and is not indicated for the treatment of UTIs.
Levofloxacin and moxifloxacin are sometimes referred to as “respiratory fluoroquinolones,” because they have excellent activity against S. pneumoniae, which is a common cause of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
**Fluoroquinolones are commonly considered alternatives for patients with a documented severe Beta-lactams allergy
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Ingestion of fluoroquinolones can form complex with (chelate) sucralfate, aluminum- or magnesium- containing antacids, or dietary supplements containing iron or zinc as in (multivitamins)so it can reduce the absorption of them. Milk , Calcium and other divalent cations also interfere with the absorption of these agents .
So, separate these agents by at least 2 hours or have your patient take a week off of the supplements, if possible.
- Distribution: Binding to plasma proteins ranges from 10% to 40%. The fluoroquinolones distribute well into all tissues and body fluids. Levels are high in bone, urine (except moxifloxacin), lungs, kidney, and prostatic tissue. Penetration into cerebrospinal fluid is relatively low (except for ofloxacin). Fluoroquinolones also accumulate in macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes, thus having activity against intracellular organisms.
3) Elimination: Most fluoroquinolones are excreted renally therefore, dosage adjustments are needed in renal dysfunction. Moxifloxacin is excreted primarily by the liver, and no dose adjustment is required for renal impairment.
Other Uses in
-
Norfloxacin 2nd gen: is infrequently prescribed due to: poor oral bioavailability and a short half-life. It is effective in treating non-systemic infections, such as: UTIs, prostatitis, and infectious diarrhea
-
Bone and joint infections caused by gram-negative organisms
-
Ophthalmic infections
Adverse Reactions e.g. floxacins
**Several fluoroquinolones have been removed from the market as a result of serious side effects ( trovafloxacin and gatifloxacin) Gatifloxacin (Tequin®) removed from market(diabetes.)
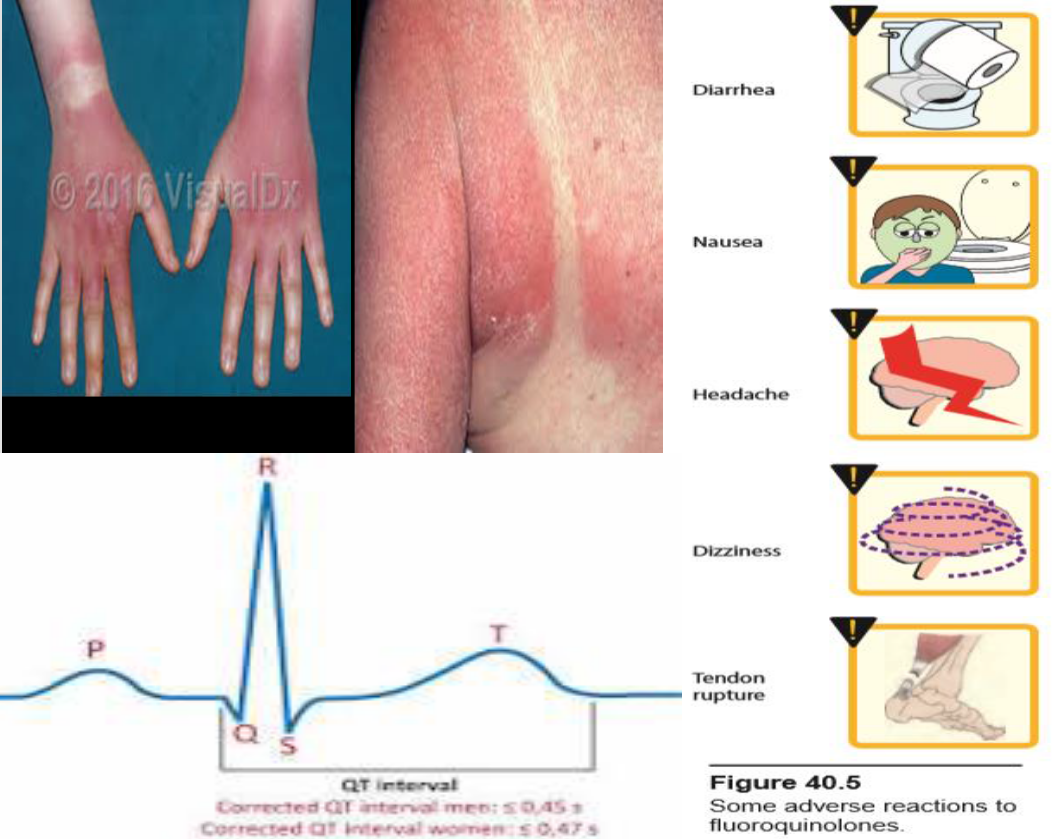
1) Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, dizziness or light- headedness. Patients with central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as epilepsy, should be treated cautiously with these drugs (seizure inducing potential). Peripheral neuropathy and glucose dysregulation (hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia) have also been noted
-
Phototoxicity : patients taking these agents should be advised to use sunscreen and avoid excess exposure to sunlight. if phototoxicity occurs, discontinuation of the drug is advisable.
-
Articular cartilage erosion (arthropathy) has been observed in immature animals exposed to fluoroquinolones. therefore, these agents should be avoided in pregnancy and lactation and in children under 18 years of age.
-
Arthralgia and increased risk of tendinitis or tendon rupture is more common in the elderly, patients with renal dysfunction, and those taking corticosteroids. Tendonitis usually precedes rupture, so complaints of tendon pain should be taken seriously. Less commonly, exacerbations of myasthenia gravis may occur. Vigorous exercise should be avoided during fluoroquinolone therapy, particularly in patients receiving corticosteroids. They can also exacerbate muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis also occur with systemic fluoroquinolone use. (avoid in younger 18 yrs)
-
Interstitial nephritis and crystalluria & pseudomembranous colitis
-
Moxifloxacin 4th gen and other fluoroquinolones may prolong the QTc interval thus, they should not be used in patients who are predisposed to arrhythmias or those who are taking other medications that cause QT prolongation.
-
Quinolones may raise the serum levels of warfarin, caffeine, cyclosporine and theophylline by inhibiting their metabolism (—cytoochrome oxidase enzymes in liver i.e HMEI) Trovafloxacin removed from market very quickly after release cardiac arrhythmias, liver destruction, phototoxicity.