Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTN)
TTN is a self-limited disease and common condition in term and late preterm infants. Transient tachypnea of the newborn is the result of a delay in clearance of fetal lung liquid. Common with C-section delivery.
Symptoms
Present within the first few hours of life with:
- Increased oxygen requirement
- Tachypnea
- Nasal flaring
- Grunting
- Retractions
- Cyanosis in extreme cases
Resolves usually within 40 hours after birth. Prolonged course >48 hours or clinical deterioration may suggest other diagnoses.
Risk Factors
- Prematures (34–36 weeks)
- Pre-labour cesarean section
- Delayed cord clamping or cord milking, promoting placental-fetal transfusion, leads to an elevation in the central venous pressure.
- Macrosomia and multiple gestations
- Maternal administration of large amounts of IVF or heavy analgesia
Treatment
Supportive as it is self-limited; oxygen (nasal cannula) if needed.
Diagnosis
Clinically, should resolve within 48 hours. If other diagnoses are suspected, investigations include:
- Full septic workup (antibiotics may be initiated)
- CBC and differential
- Regular blood-gas measurements
- Chest radiography
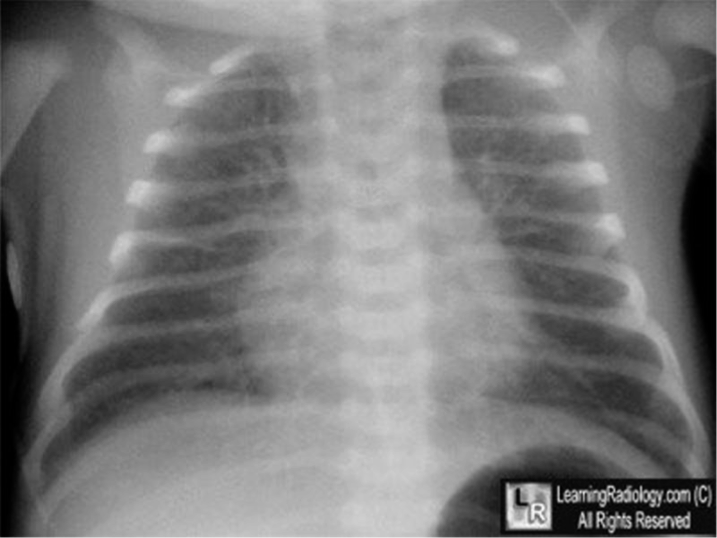
Radiographic Findings
- Prominent perihilar streaking reflecting fluid in the interstitium
- Patchy infiltrates
- Fluids in the horizontal fissure on fifth right costal
- Hyperinflated lung