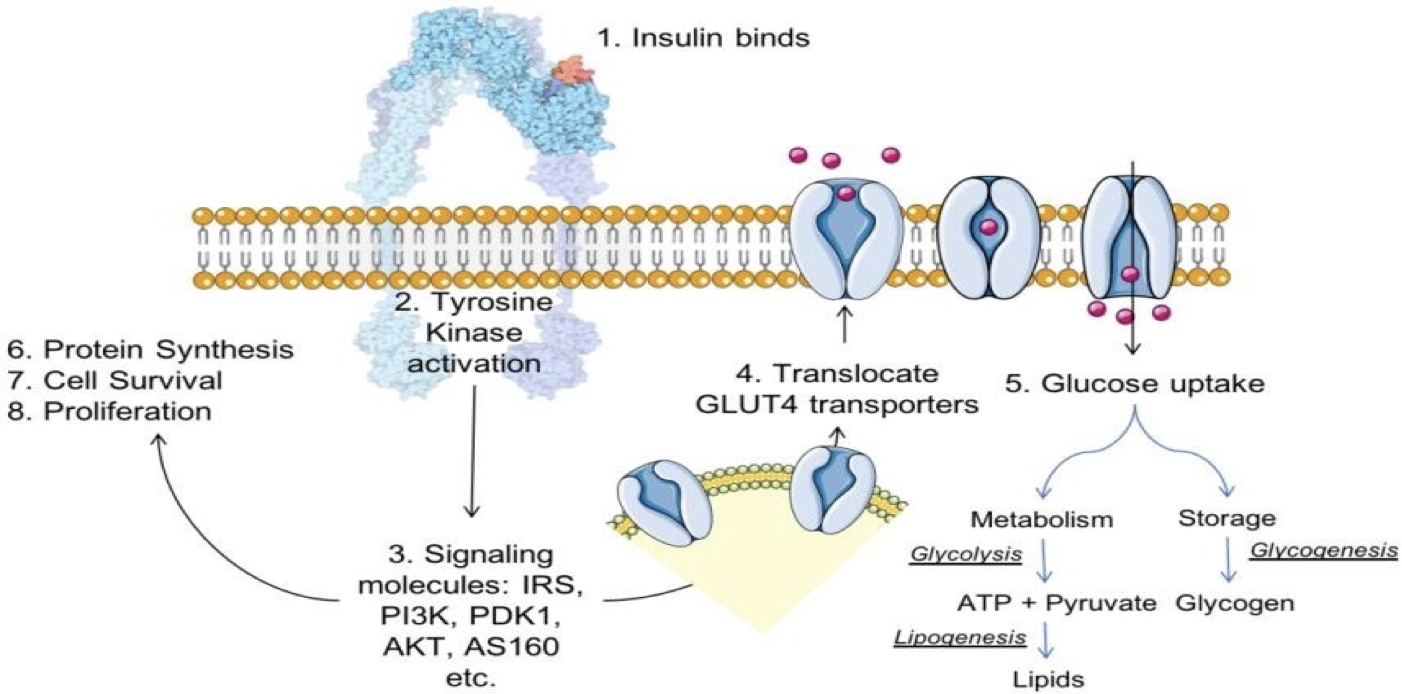
Insulin receptor (IL) stimulation
-
Insulin binds to the target cell’s plasma membrane-bound receptor and coordinates the integrative anabolic action of nutrient availability.
-
IR, a tyrosine kinase, consists of α and β chains and is activatedby insulin-like growth factors I and II and insulin. There are two IR isoforms, A and B, but the B isoform is the primary isoform and is more specific for insulin.
-
The B isoform is expressed in the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue and is thus thought to mediate most of insulin’s metabolic effects.
-
The binding of insulin to the α chain of IR causes structural changes in the β chain by inducing auto‐phosphorylation in tyrosine residues.
-
These changes are essential for downstream events such as the recruitment of the adaptor proteins IR substrates.
-
The downstream of IR activation can be functionally divided into mitogenic and metabolic signals.
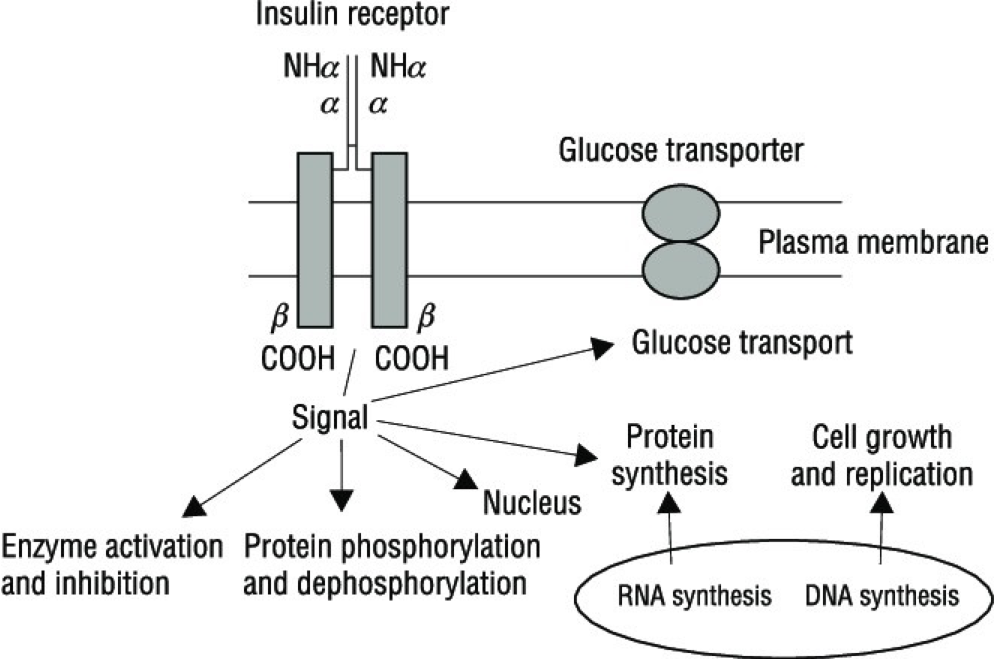
Insulin hormone – receptor reaction