Rapid decline in renal function:
1. Anti-GMB IV Col
- Causes:
- Anti-GBM disease (Goodpasture syndrome): Z Antibodies against type 4 collagen present in the basement membrane of the kidney and alveoli. Patients present with GN and hemoptysis.
- Diagnosis: Renal biopsy showing linear deposits.
- Treatment: Immunosuppressants and plasmapheresis. (Caution with renal transplantation in these patients.) -
cyclosporin IL-2 Inhibitor; gum hyperplesia, HTN,
corticosteroids; safer option
LINEAR DEPOSITS OF GPS
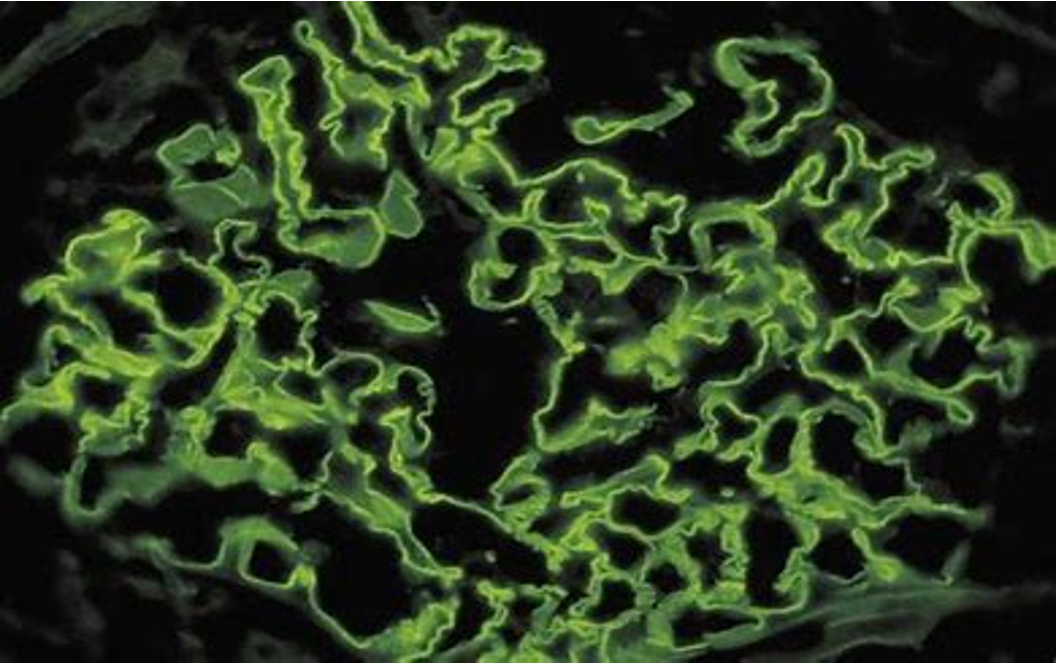
- Anti-GBM disease (Goodpasture syndrome): Z Antibodies against type 4 collagen present in the basement membrane of the kidney and alveoli. Patients present with GN and hemoptysis.
2. Immune complex diseases: IgA
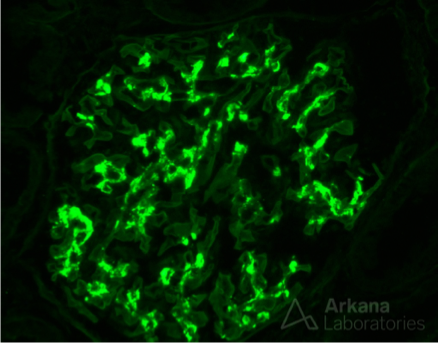
IgA nephropathy: Can be isolated GN or part of a systemic illness like Henoch-Schonlein purpura; systemic. Abnormal IgA antibodies have delayed clearance. IgA is attacked by antibodies/IgG, and the antibody/antibody complex deposits in the mesangial cells.
Problem: Damage to the kidney.
Note: C3 levels are normal.
History: Upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) or (GI) infection 1-3 days before GN onset or systemic illness. - due IgA mucous protective mechanism
Period: —/
Diagnosis: Renal biopsy showing mesangial deposits.
Treatment: Immunosuppressants and plasmapheresis in severe cases.
MESINGAL DEPOSITS IgA
3. Post-streptococcal GN: IgG - C3
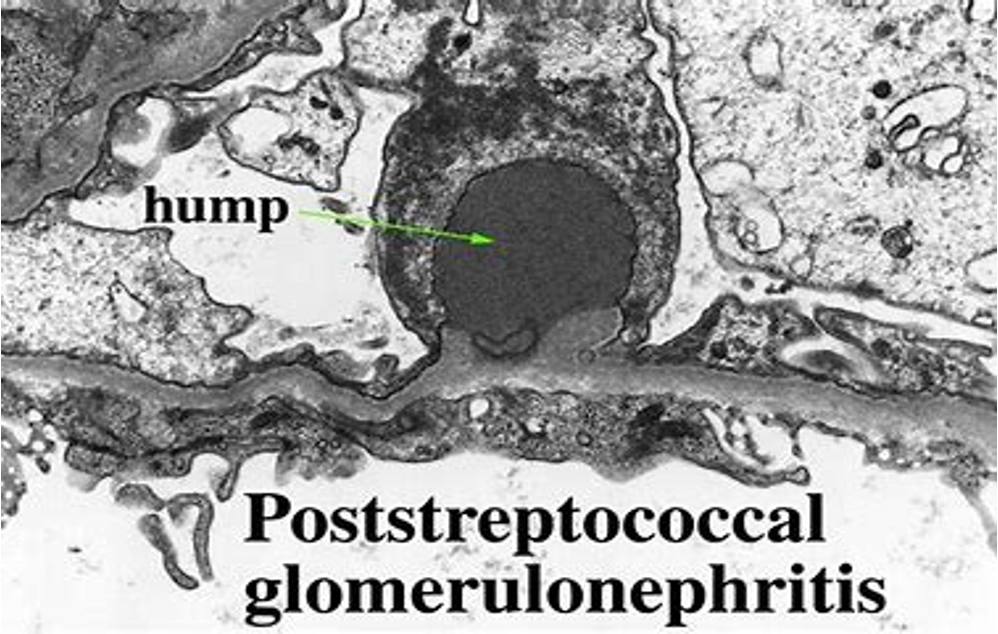
Occurs after infection with Streptococcus pyogenes, either throat or skin infection. Symptoms appear 2-3 weeks after the initial infection. * Mechanism: Antigen and antibody (IgG) complex deposits in the subepithelial space. Complement system activation consumes C3, lowering its level. * Diagnosis: Typical history, blood tests showing high ASO titer, renal biopsy showing lumpy-bumpy subepithelial deposits. * Treatment: Antibiotics.
SUBEPITHELIAL DEPOSITS (EM)
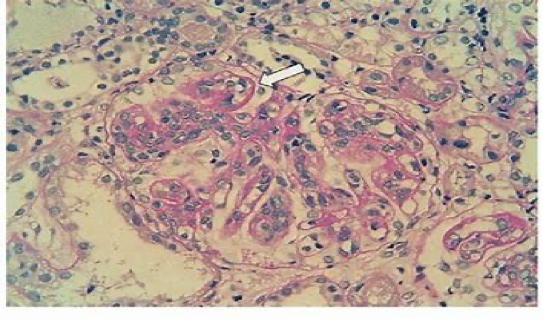
4. Diffuse proliferative GN (Lupus nephritis): wire loop
50% of the glomeruli are affected (diffuse). Antigen/antibody complex deposits in the blood vessels (subendothelial). Z * Appearance: Blood vessels become thickened, showing a wire-loop appearance in renal biopsy. * Treatment: Immunosuppressants, e.g., IL2 inhibitors.
WIRE LOOPING(LM WITH STAIN); SLE
5. Pauci-immune disease:
Primarily caused by vasculitis. Examples: Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis), c-ANCA positive. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome), p-ANCA positive +- UC * Renal biopsy: Shows no immunocomplex deposition. * Treatment: Immunosuppresants