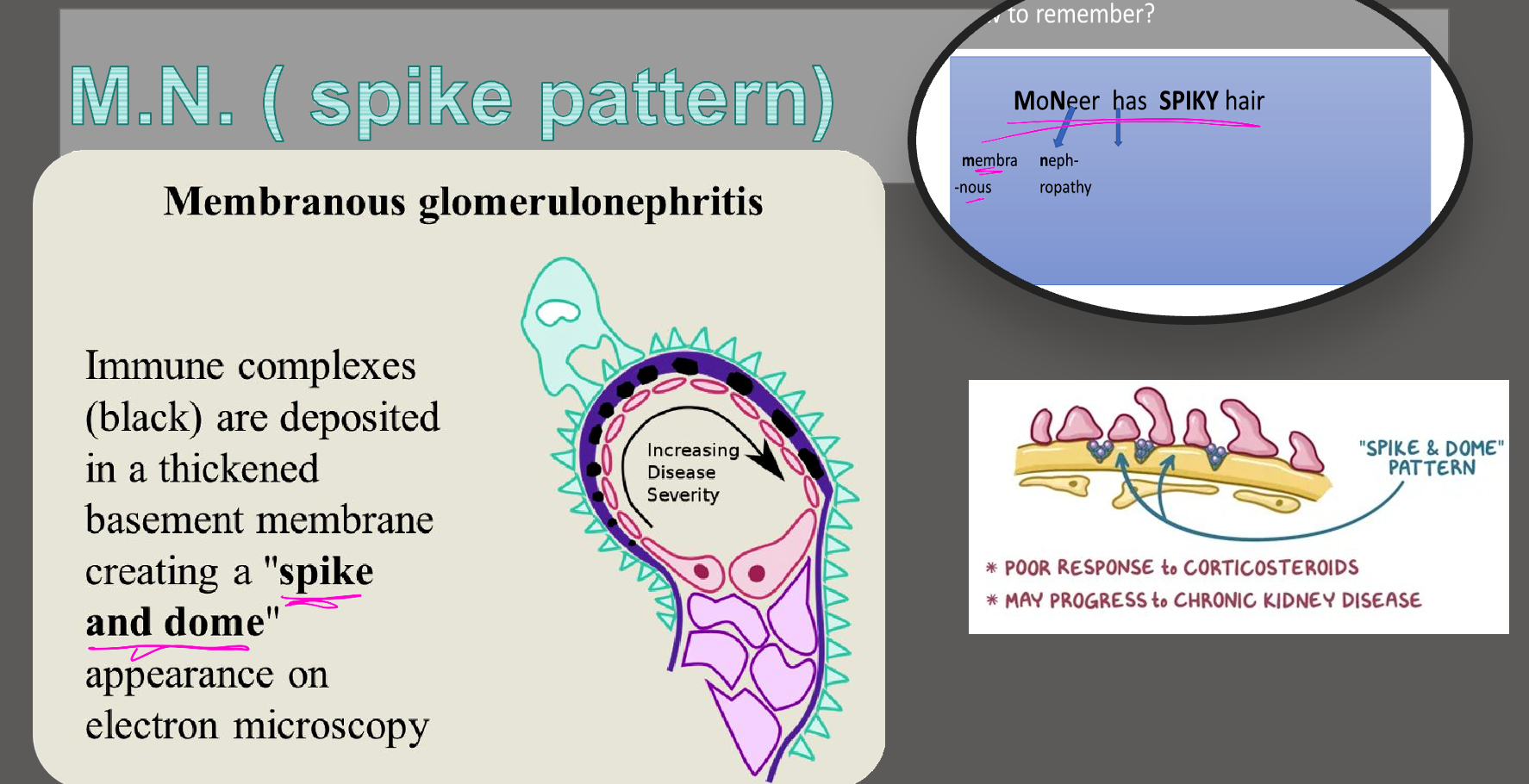
Membranous Nephropathy
Types:
- Primary: Idiopathic: anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibodies (PLA2R) (IgG4).
- Secondary:
- SLE (V), RA, thyroiditis
- HBV, HCV, syphilis, malaria
- Drugs (NSAIDS, penicillamine, gold)
- Solid organ cancers (lung, prostate). (Lymphoma)
Pathology (biopsy):
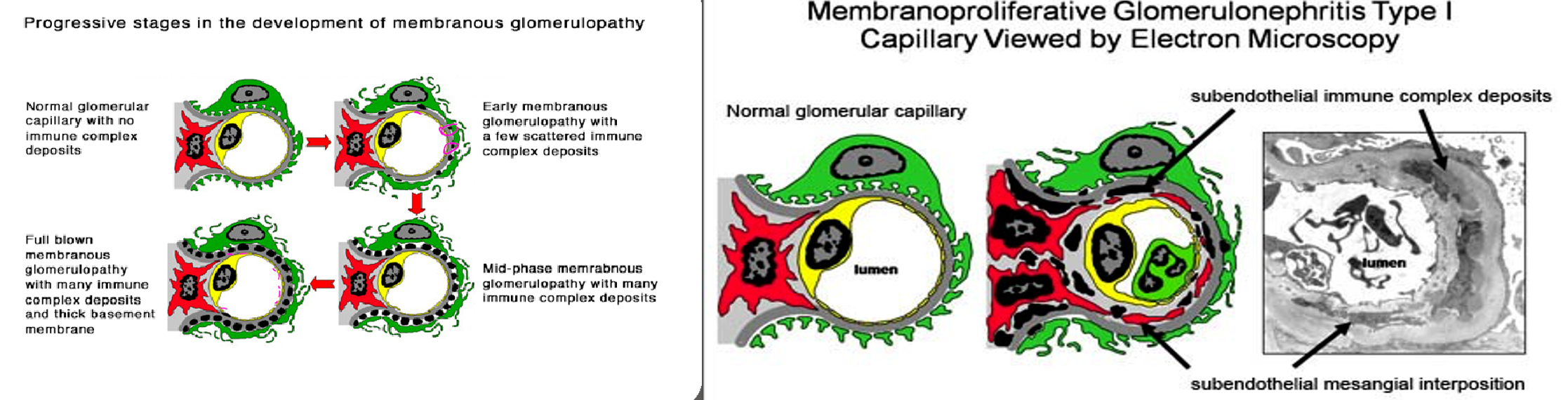
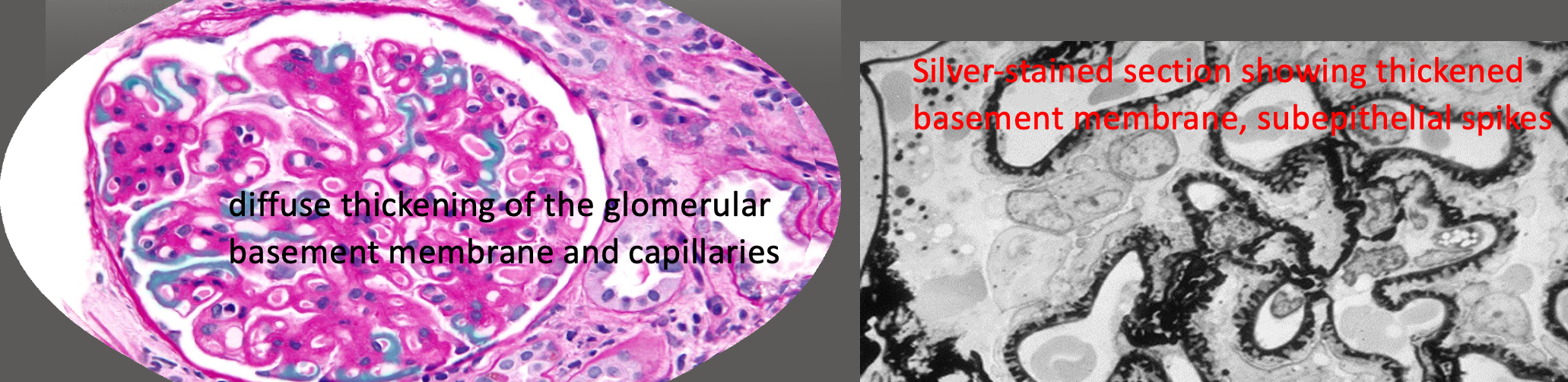
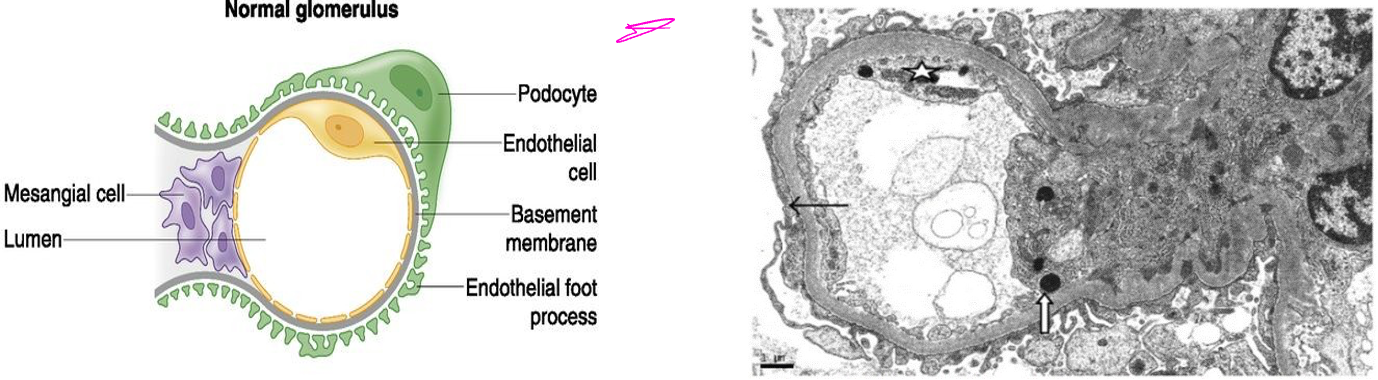
- LM: Thickening of glomerular basement membrane with subepithelial deposits of IgG and C3 (dense deposits) & “spike” formation
Treatment:
- All: ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB)
- Prednisone + cyclophosphamide
- Immunosuppressives: Rituximab
- Anticoagulation for high-risk Pts
Specific groups requiring ttt:
- High chance of progression of the disease.
- Reduced GFR
- Age > 50
Outcomes:
- Spontaneous remission
- Remain proteinuric
- Develop ESRF
Image: Diffuse thickening of the glomerular basement membrane and capillaries. Silver-stained section showing thickened basement membrane, subepithelial spikes.
Untreated FSGS has a < 10% chance of spontaneous remission
Question:
Which one of the following is least recognised as a cause of membranous glomerulonephritis? A. Cryoglobulinaemia B. Malaria C. Lymphoma D. Hepatitis B E. Gold