IM
STEMI
ST Elevation MI ( STEMI )
ECG changes in myocardial infarction (STEMI) V2 – V5 Anterior
V1 – V3 Anteroseptal
V4 – V6, I, aVL Anterolateral
I, aVL Lateral
II, III, aVF Inferior
V1, V2(Reciprocal) Posterior
- Thrombolytic therapy is given in STEMI
- Thrombolytic therapy is NOT GIVEN IN UNSTABLE ANGINA AND NSTEMI
THROMBOLYTIC GIVE IN PERIPHERY HOSPITAL WHEN PCI NOT AVAILABLE!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
STEMI confirmed what is the next step !!!
Immediately assess eligibility for coronary reperfusion therapy
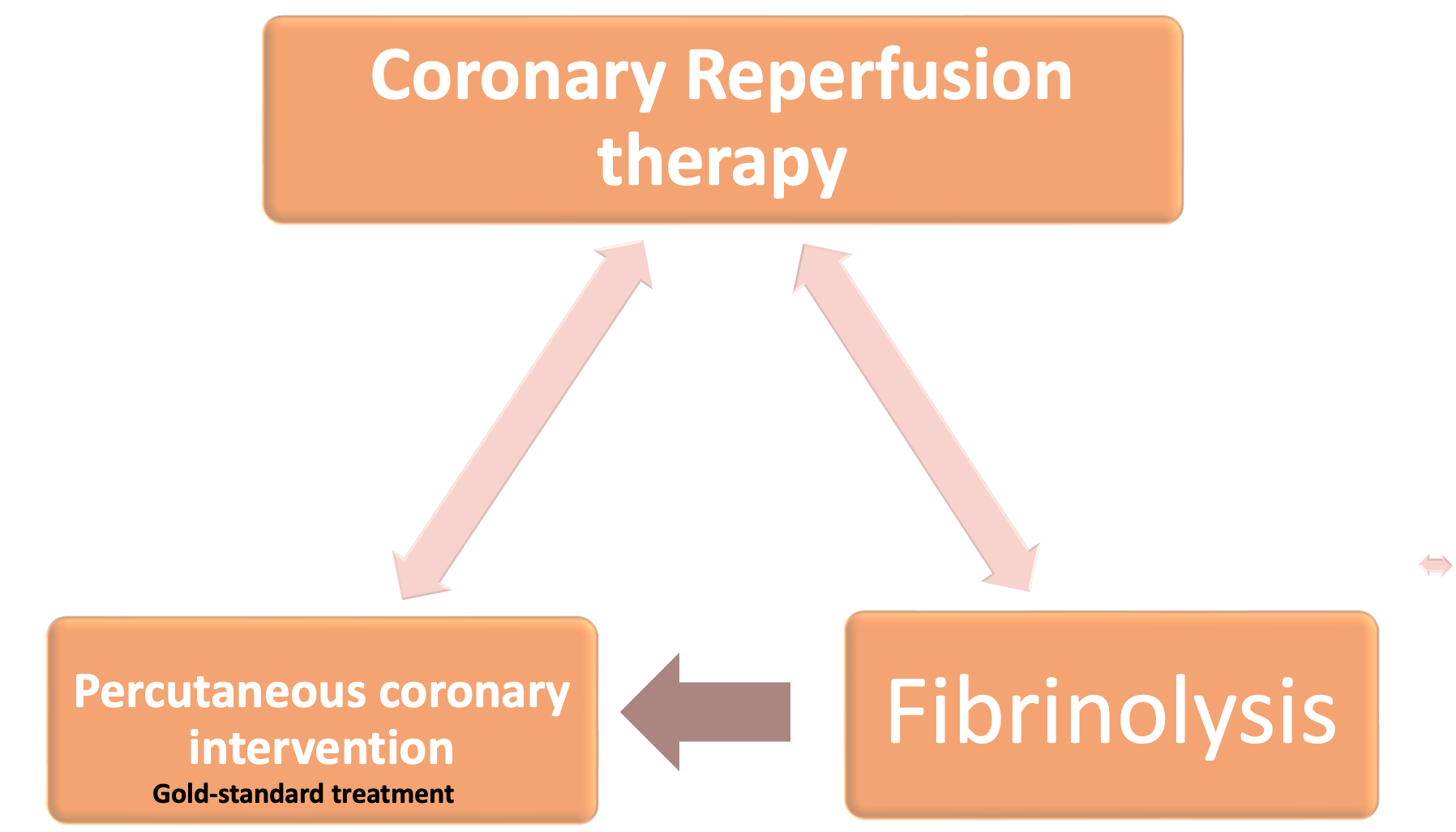
Gold-standard treatment
Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has emerged as the gold-standard treatment for STEMI but is not available in all centres. Thrombolysis should be performed in patients without access to primary PCI 18
Management options for STEMI
Immediate revascularization.
Diagnosis of STEMI should not be excluded based on a single ECG.
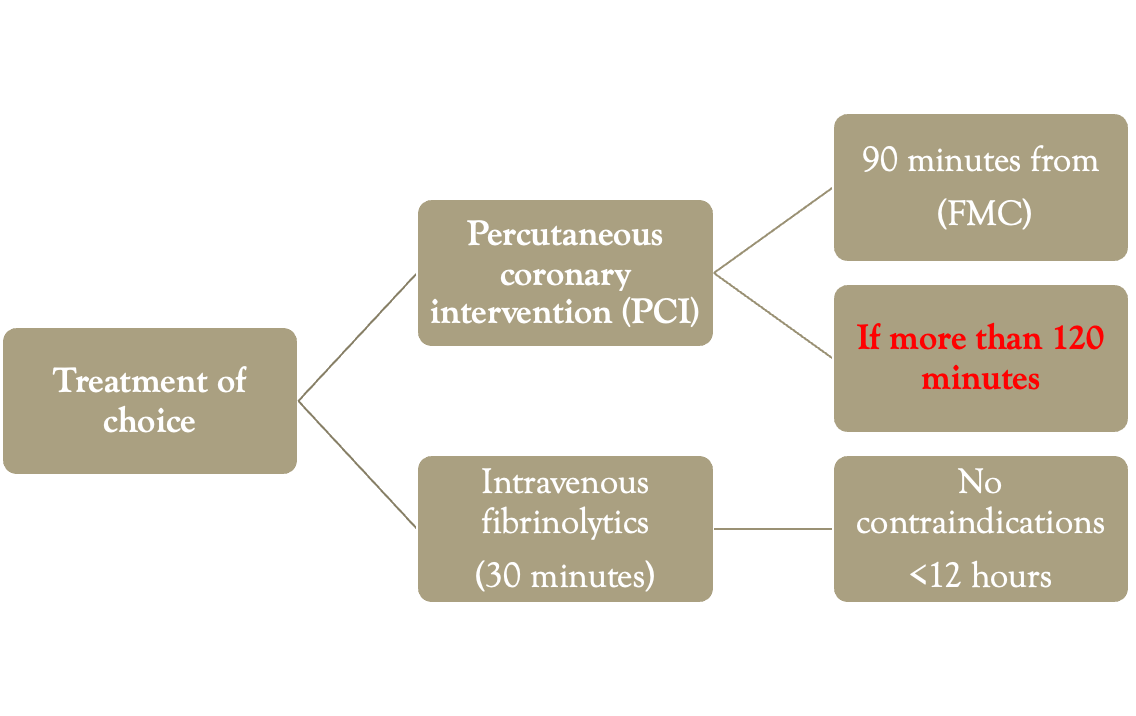
STEMI
PCI
PCI is advised within 90 min, where facilities are available when patient presented to hospital in 6 hours(up to 12 hours) of pain.
THROMBOLYSIS
- If PCI not available ( small hospital ) Fibrinolysis (Thrombolysis) is done within 6 hours
- ( Up to 12 hrs ) of STEMI
- Drugs used for Thrombolysis are Alteplase (human tissue plasminogen activator or tPA) Streptokinase
Contraindications for fibrinolysis SDL
Severe hypertension unresponsive to emergency therapy Presence of intracranial conditions that increase the risk of bleeding (e.g. arteriovenous malformation) Intracranial malignancy Additionally for streptokinase: previous exposure within 6 months (highly antigenic)
Medical Treatment ACS
- O2
- Morphine and anti emetic (IV morphine: ! vomit)
- Antiplatelets agent: Aspirin + // (Clopidrogrel / prasugrel/ ticagrelor)
- Antithrombin drugs: Enoxaprin- low molecular heparin/Bivalirudin / Fondaparinux / Rivaroxaban
- Glycoprotein IIB/IIIA inhibitors: Abciximab
- Beta blockers
- ACEIs
- Nitrates - nitrates & nitrites
- Statin eg lipitor
STEMI -COMPLICATIONS
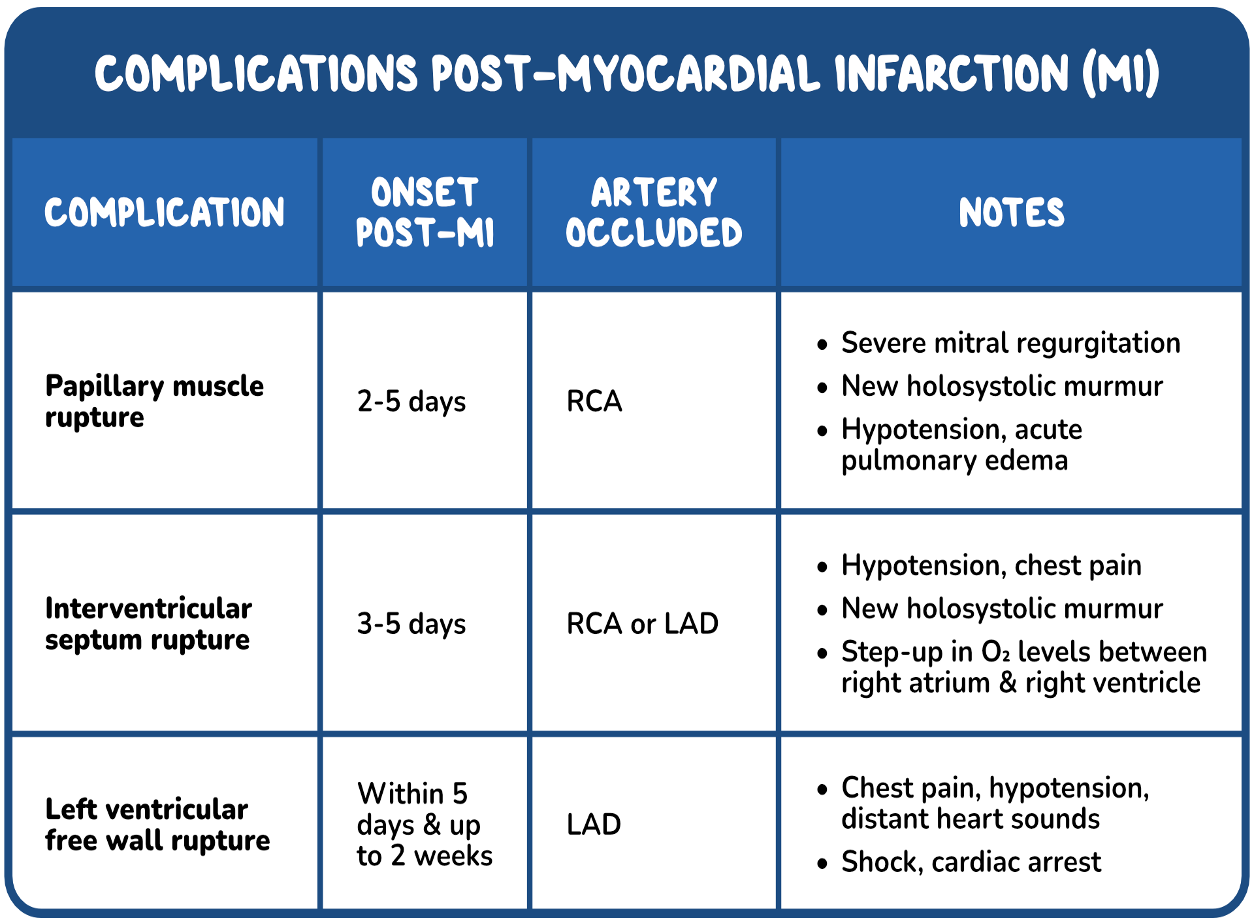 Heart failure: Killip - Pericarditis
Killip I – no crackles and no third heart sound
• Killip II – crackles in <50% of the lung fields or a third heart sound
• Killip III – crackles in >50% of the lung fields
• Killip IV – cardiogenic shock.
Heart failure: Killip - Pericarditis
Killip I – no crackles and no third heart sound
• Killip II – crackles in <50% of the lung fields or a third heart sound
• Killip III – crackles in >50% of the lung fields
• Killip IV – cardiogenic shock.
STEMI – CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Ventricular fibrillation ( C death )
- Cardiac arrest
- Atrial fibrillation
- Conduction defect - common with INFERIOR MI as Rt CA supplies SA & AV nodes
V fib is more dangerous than v tach
Post ACS Life-style modification
- Diet- Omega- 3 fatty acid from fish
- Daily walk 20- 30 min daily
- Stop smoking
- Maintain alcohol consumption in safe limits 21 units/ week
- If over-weight – reduce weight
- Control Hypertension less than 140/90 mmHg , DM: 130/ 90 mmHg
- Maintain Hb A1c less than 7% in Diabetic patient
FM
ST Segment Elevation
- A ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome is defined as the presence of one of the following on ECG, in combination with the patient’s clinical presentation:
- ≥ 1 mm ST elevation in at least two adjacent limb leads.
- ≥ 2 mm ST elevation in two contiguous precordial leads.
- New onset bundle branch block.
Localization of Ischemic Area STEMI
Leads and Affected Areas
| Leads | Affected Area | Occluded Artery |
|---|---|---|
| V1-V2 | Septal | Proximal LAD |
| V3-V4 | Anterior | LAD |
| V5-V6 | Apical | Distal LAD, LCx or RCA |
| 1, aVL | Lateral | LCx |
| 11, aVF, 111 | Inferior | 90% RCA, 10% LCx |
Myocardial Ischemia or Infarction
- Pressure-type of chest pain
- Generally involves central to left-sided pain with radiation to jaw or arms
- Exacerbated by activity, relieved with rest
- Relieved with nitro spray
- Associated with nausea, diaphoresis, syncope, shortness of breath
- Enquire about cardiac risk factors: age, sex, smoking history, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, previous myocardial infarction, and family history
Clinical Signs
- ↓BP indicates cardiogenic shock
- ↑JVP, pulsatile liver and peripheral edema seen in right-sided heart failure
- Oxygen desaturation, crackles, S3 seen in left-sided heart failure
- New murmurs: mitral regurgitation murmur in papillary muscle dysfunction
Management Strategy for STEMI
- MONA - Morphine, oxygen, nitro, aspirin
- Beta blockers, ACE inhibitors
- Early invasive strategy with either thrombolytic therapy or percutaneous coronary intervention (preferred)
STEMI Management
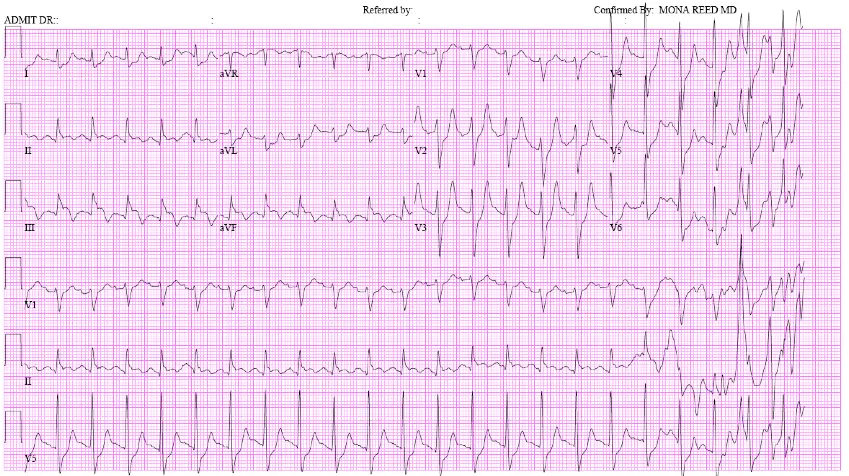
- ADMIT DR.:
- Referred by:
- Confirmed By: MONA REED MD
| I | aVR | V1 | V4 | ||
| II | aVL | V2 | V5 | ||
| III | aVF | V3 | V6 | ||
| V1 | |||||
| II | |||||
| V5 |