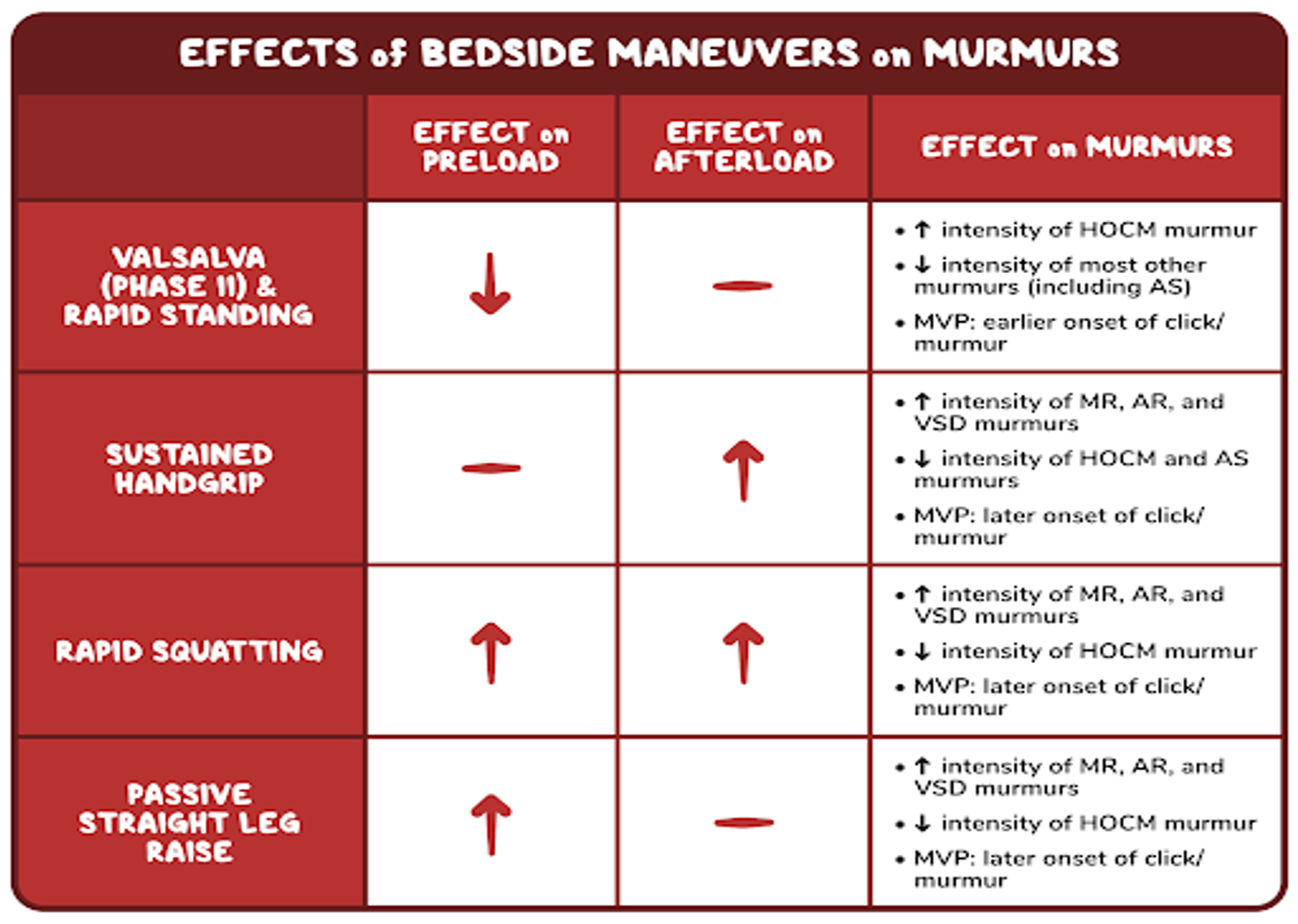
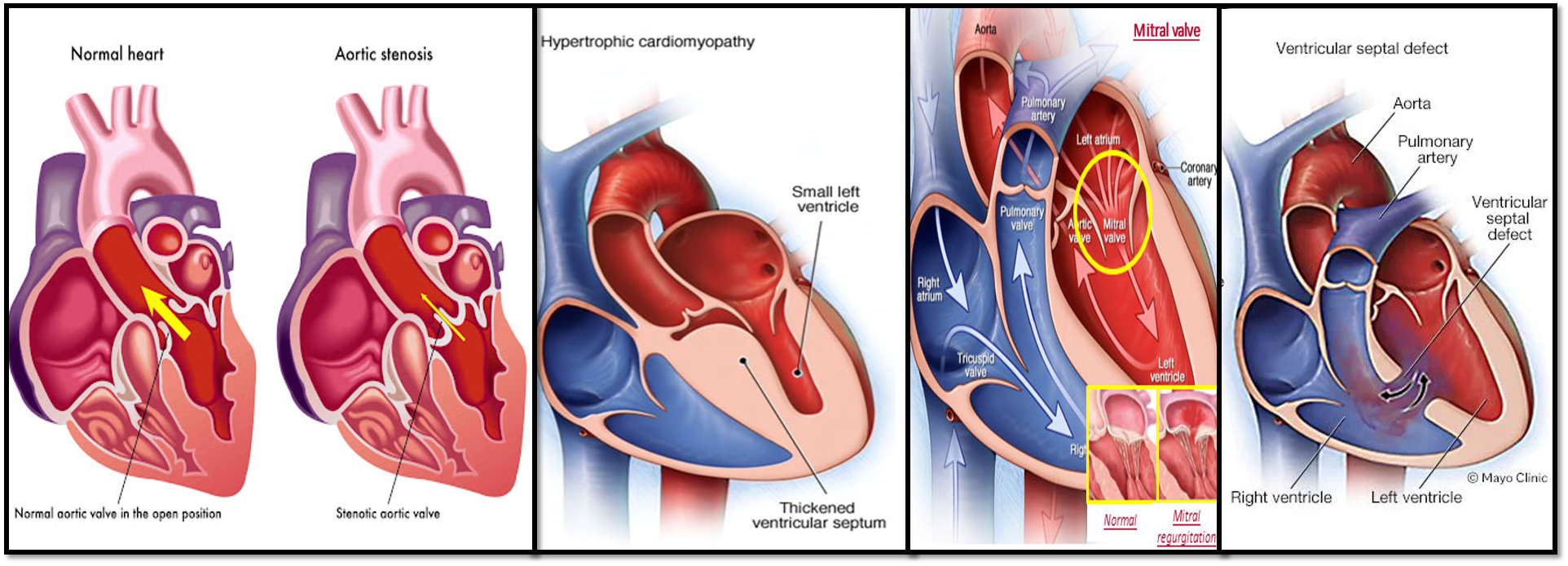
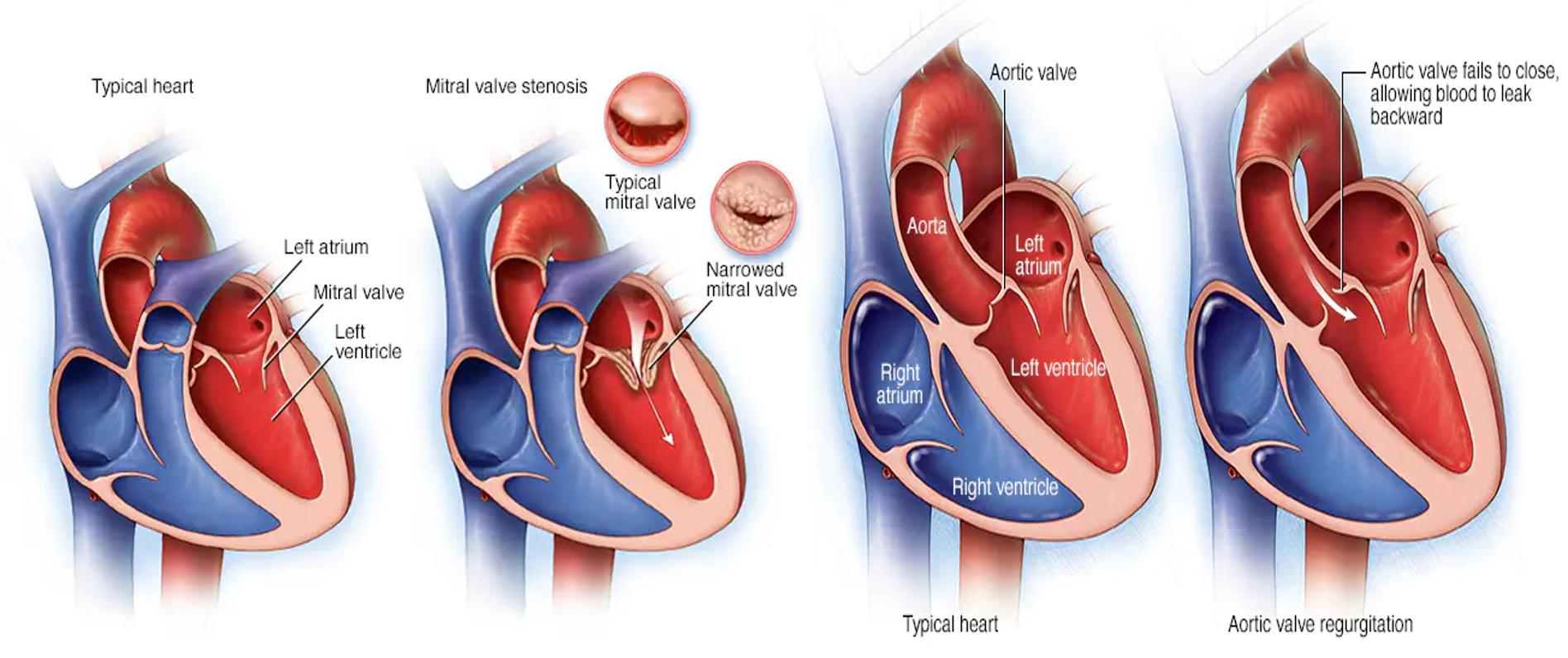
Valvular Heart Disease
Dr. nada
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this session, the student should be able to:
- Recognize the common etiologies of valvular stenosis and regurgitation.
- Recognize the signs and symptoms of severe valvular stenosis and regurgitation.
- Outline the management of different valvular lesions.
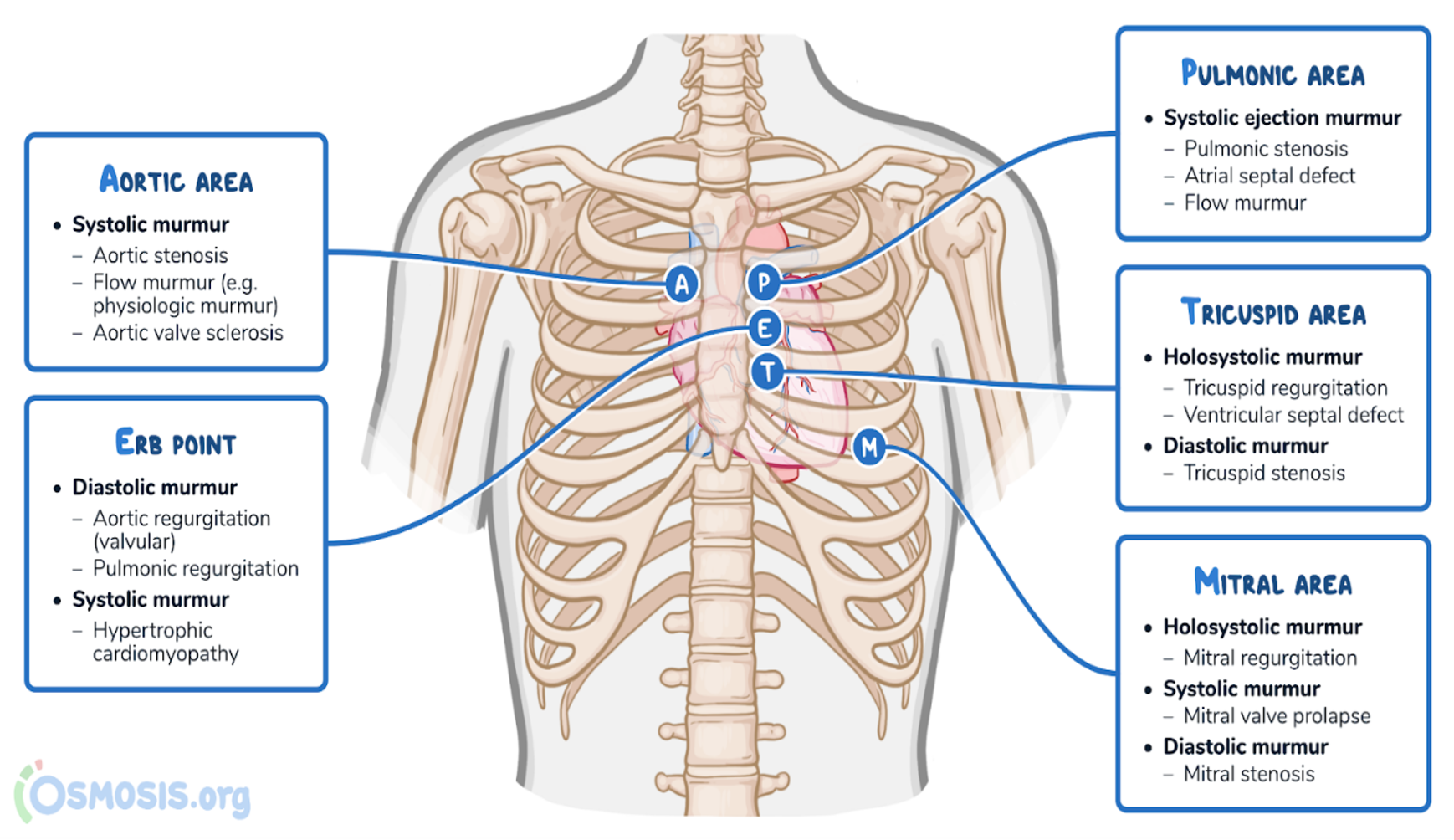
Aortic Presentation
| Systolic Murmurs - aorta open | Diastolic Murmurs/Sounds |
|---|---|
| (crescendo-decrescendo) AS = aortic stenosis & PS = pulmonary stenosis HCM = hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | (Early Diastolic/Decrescendo) AR = aortic regurgitation PR = pulmonary regurgitation |
| (Holosystolic/Pansystolic) MR = mitral regurgitation TR = tricuspid regurgitation VSD = ventricular septal defect | (Mid-late Diastolic/ decrescendo- crescendo) MS = mitral stenosis TR = tricuspid stenosis |
| I = innocent murmur | S3 = third heart sound |
| PDA = patent ductus arteriosus (continuous murmur) |
SDL
Basic Concept
Regurg/Insuff: Leaking (backflow) of blood across a closed valve.
Stenosis: Obstruction of (forward) flow across an opened valve.
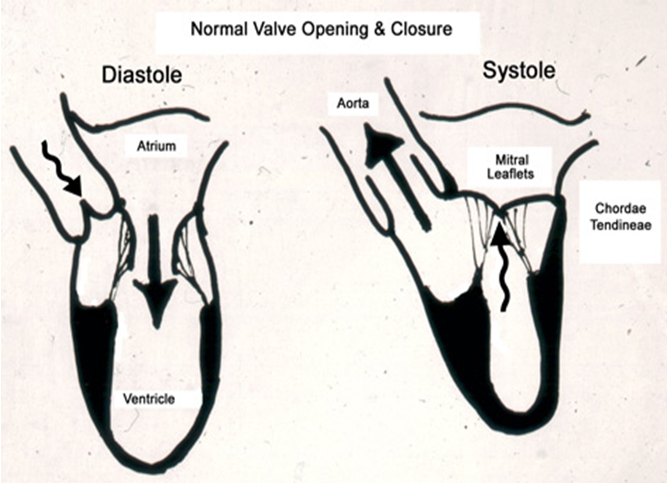
Systole:
- AV/PV – opens-------Aortic Stenosis
- S1-S2 – MV/TV – closes------Mitral Regurg
Diastole:
- AV/PV – closes------Aortic Regurg
- S2-S1 – MV/TV – opens-------Mitral Stenosis
These concepts are set in stone; it can’t occur any other way. It would be anatomically impossible.
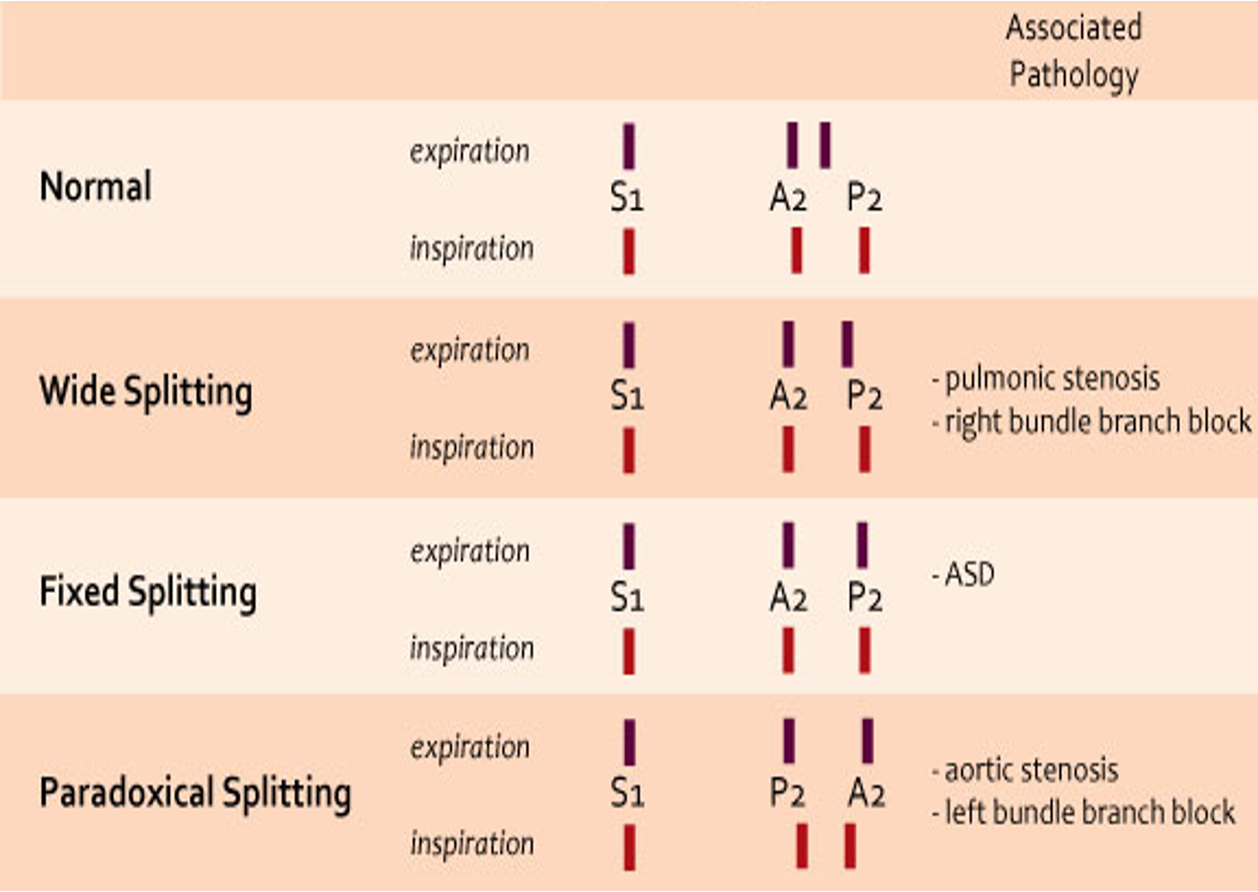
Normal Heart Sounds & S2 Splitting Z
Wide splitting - Pulmonic Stenosis & Right bundle branch block
Fixed Splitting - ASD
Paradoxical Splitting - Aortic Stenosis & Left bundle branch block
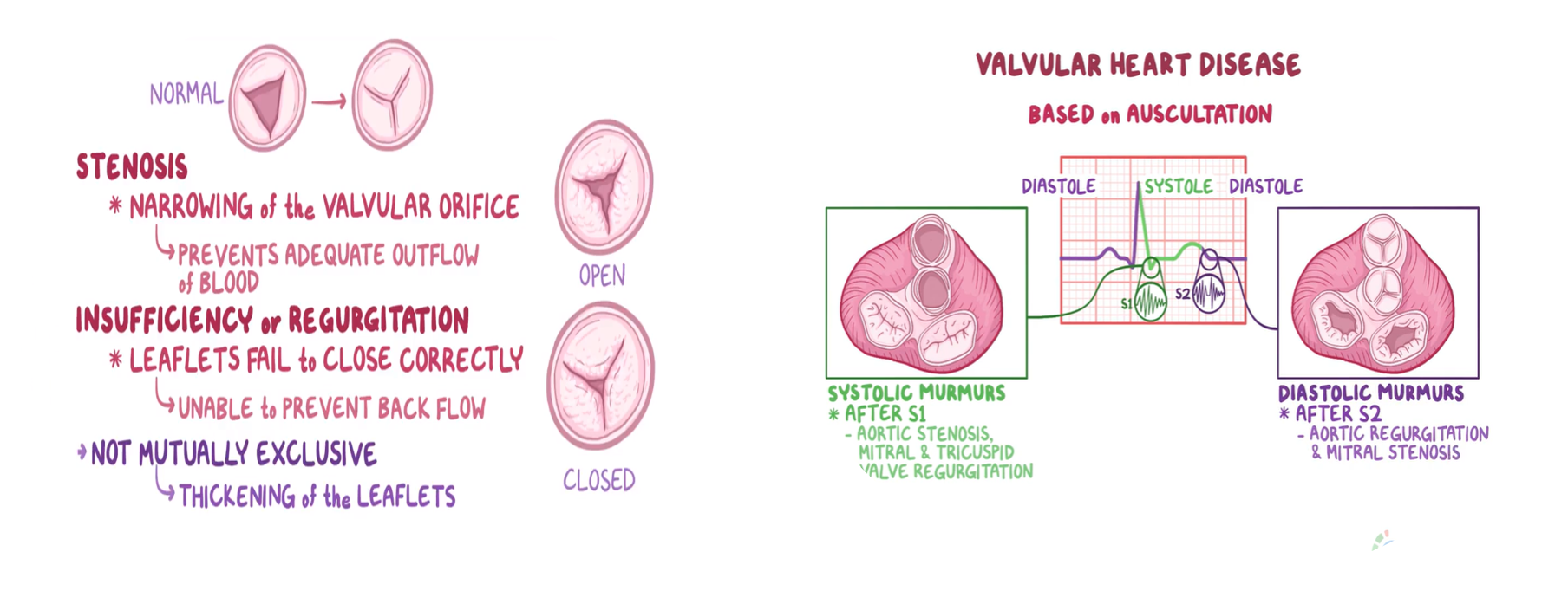
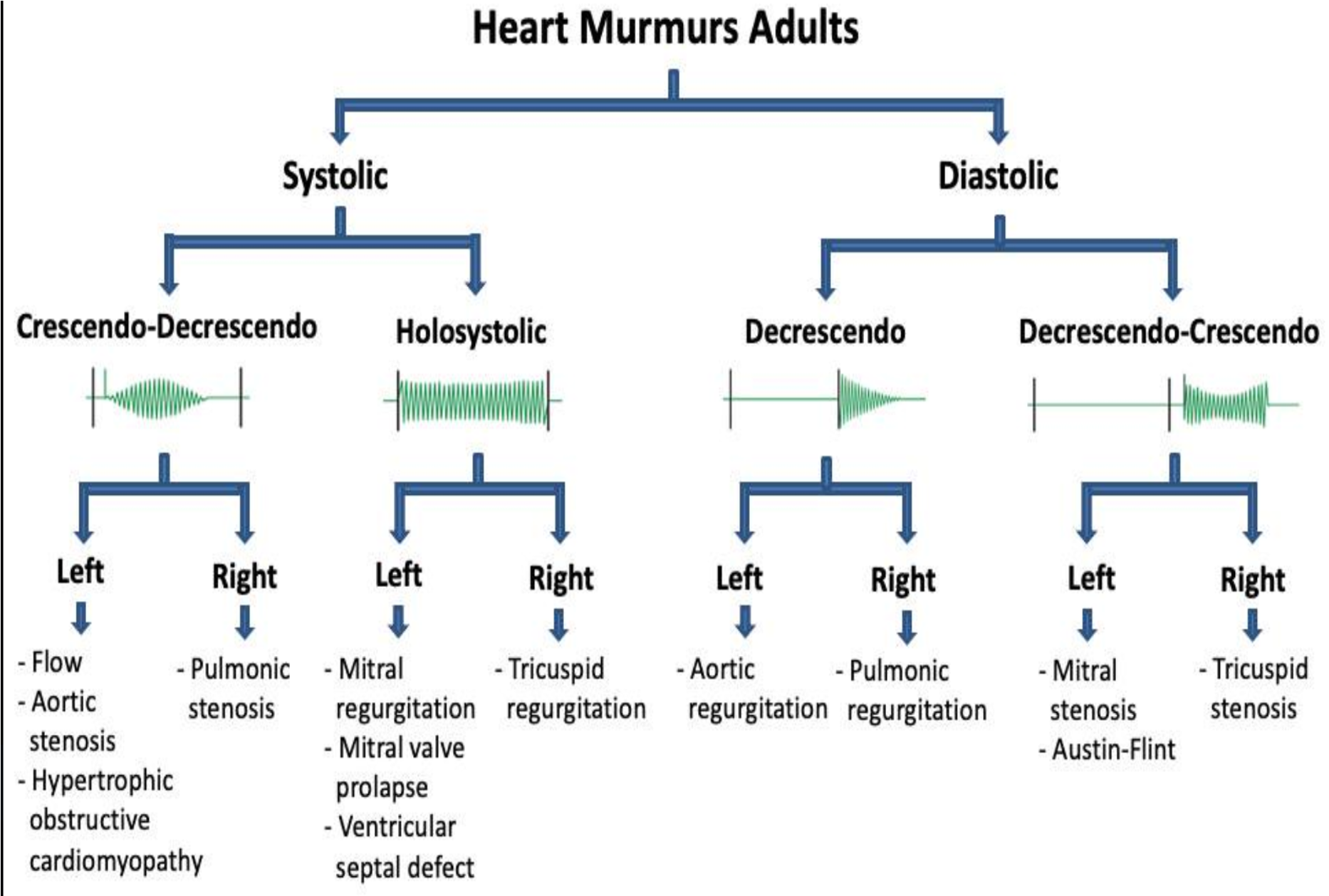 X - Y Crescendo-Decrescendo; LT flow, aortic stenosis, Hypertrohic obstructive Cardiomyopathy & RT Pulmonic Stenosis
X - Y Crescendo-Decrescendo; LT flow, aortic stenosis, Hypertrohic obstructive Cardiomyopathy & RT Pulmonic Stenosis
Holosystolic - Pansystolic