RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS
Definition
- Narrowing or complete stenosis of renal artery.
- It can affect one or both arteries.
What Happens due to stenosis
- Stenosis of renal artery renal ischemia
- Release of renin, angiotensin and then aldosterone all these substances cause vasoconstriction & raise the BP
ETIOLOGY OF R.A.S.
-
1) ATHEROSCLEROSIS:
- 85% of RAS cases. More in elderly
- Patient usually has atherosclerosis in other vessels also ( C.A.D. & PVD)
-
2) FIBROMUSCULAR DYSPLASIA:
- Thickening of the renal artery wall
- 10% -15% of cases. (females, young ppl)
WHEN TO SUSPECT
-
- BP not controlled even with 3 medicines
-
- Occurrence of “ flash pulmonary edema” w/out any cardiac disease
-
- Abdominal bruit on auscultation
-
- Affected kidney is smaller than the other
-
- HTN in a young person
-
- Severe worsening of serum creatinine after starting ACE or ARB
IMAGING FOR R.A.S.
- Doppler u/s :
- Initial test * Non-invasive
-
- MRA/CT: (magnetic resonance angiogram)
- More clear images * done if u/s doppler not clear * MRA is also non-invasive like Doppler
-
- Angiogram: z
- Gold standard, but invasive
- Not the first step test
- Done if noninvasive tests are inconclusive.
Angiogram showing renal art. stenosis

ANGIOGRAM
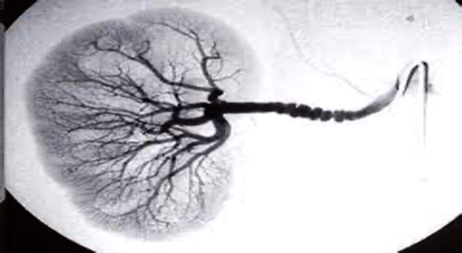 “String of beads” appearance of renal artery in fibromuscular dysplasia
“String of beads” appearance of renal artery in fibromuscular dysplasia
TREATMENT OF R.A.S.
- ***Atherosclerotic RAS: ***
- BP control w/ meds. * No ACEI & ARB
- Treatment to lower the cholesterol ( because it is due to atherosclerosis)
- Usually, no surgery or angioplasty ( done only if severe stenosis)
- Fibromuscular Dysplasia:
- Dilation of the stenosis by angioplasty wth. or without stent