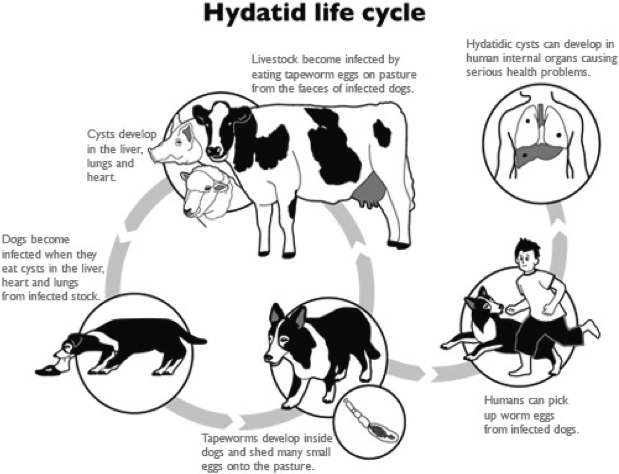
This infestation is caused in humans by one of two forms of tapeworm:
- Echinococcus granulosus
- Echinococcus multilocularis
Life cycle of echinococcus granulosus
- The adult tapeworm lives in the intestine of the dogs, from which the ova passed in the stool
- Sheep and goats serve as the intermediate host by ingesting the ova, whereas humans are accidental host.
- Ingested ova hatch in the duodenum and the embryos pass to the liver through the portal venous system.
- The hydatid cyst forms in the liver
Clinical features
Symptoms:
- The disease my be symptomless
- Chronic right upper quadrant abdominal pain is the commonest presentation
signs: Enlarged liver
Complications due to rupture of the cyst into:
- biliary system which can cause obstructive jaundice
- peritoneal cavity causing peritonitis and anaphylactic shock
- pericardium causing cardiac tamponade
- pleural cavity causing effusion and chest symptoms
Investigations
Laboratory tests: can show eosinophilia and serological tests, such as compliment fixation test to detect the foreign protein of hydatid cyst.
Imaging:
-
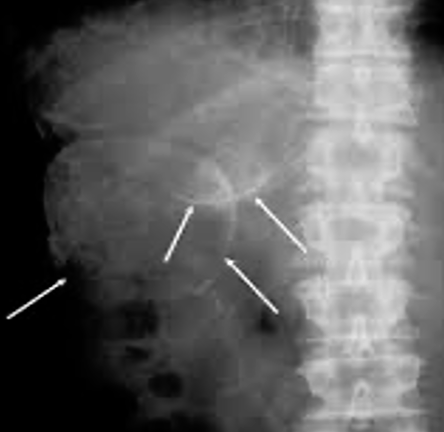
plain x-ray can show the calcification in the wall of the cyst
-
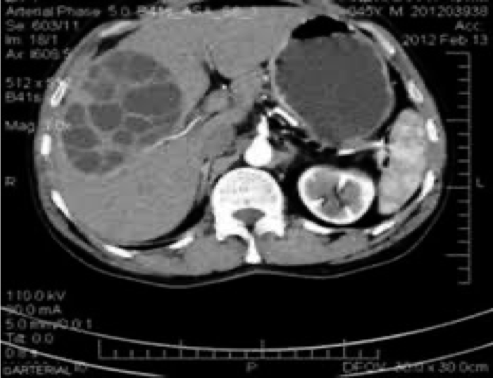
ultrasound and CT scan can show the site, size and daughter cyst in the liver
Calcification in the wall of the hydatid cyst in the right lobe of the liver
Hydatid cyst (multiple daughter cyst) in the right lobe of the liver
Treatment
-
In asymptomatic patient, small calcified cyst my require no treatment
-
Patient can be treated successfully with albendazole or mebendazole but this may be prolonged
-
Surgery is the most effective treatment: a) Deroofing and complete excision of the endocyst b) Complete excision of the cyst (pericystectomy)
-
Selected patients with central liver cyst may be suitable for puncture – aspiration-injection-re-aspiration (PAIR)