Surgery
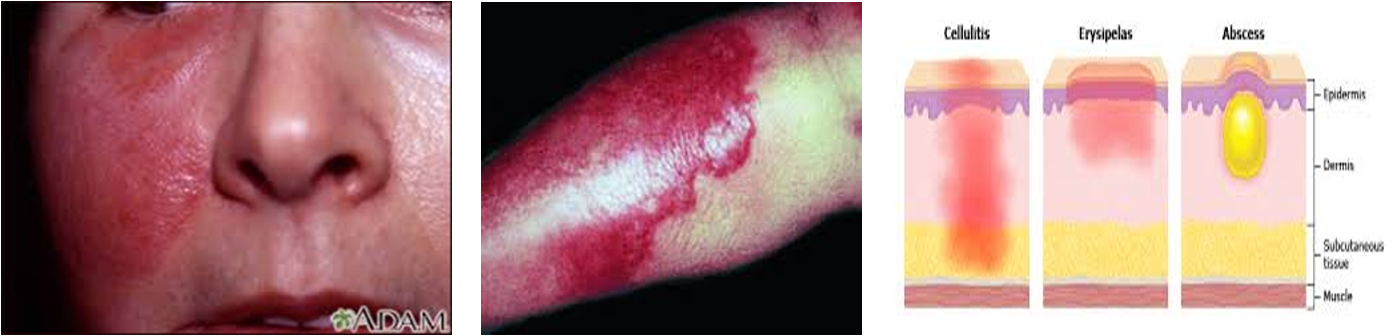
Erysipelas:
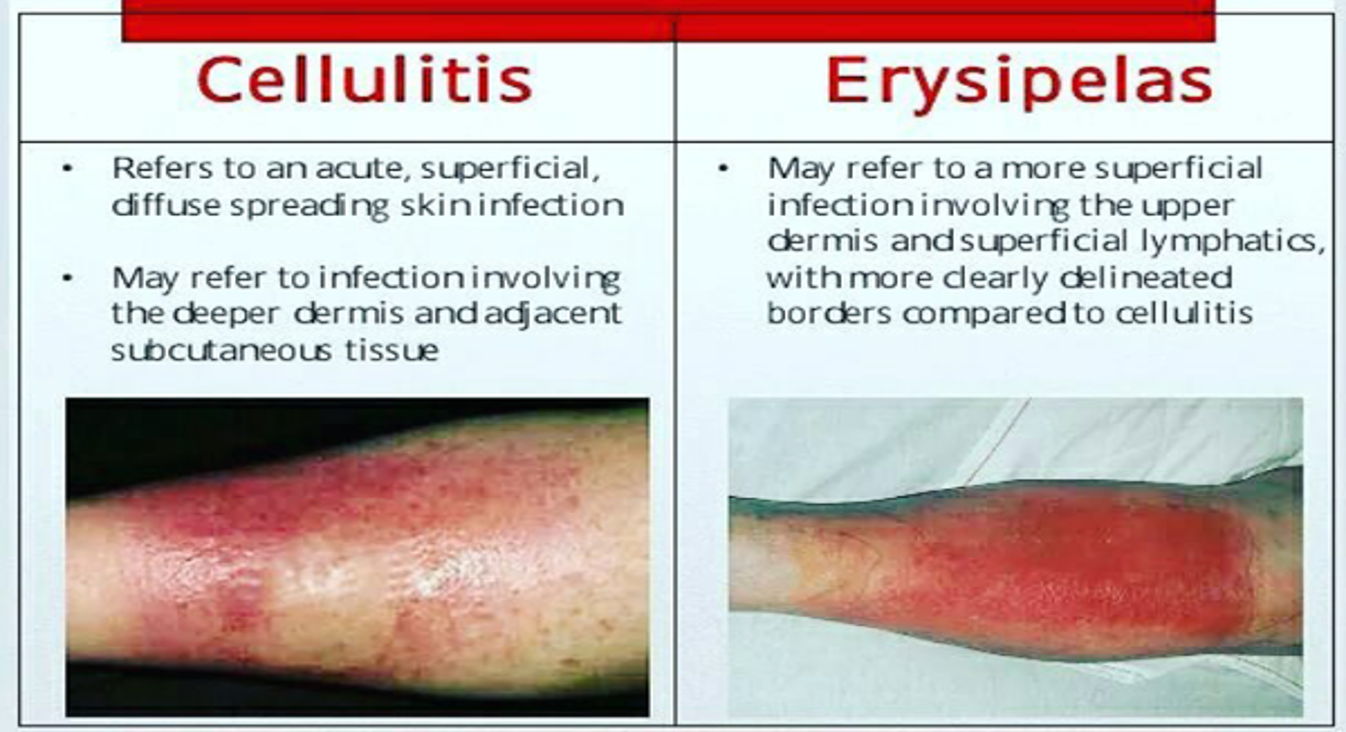
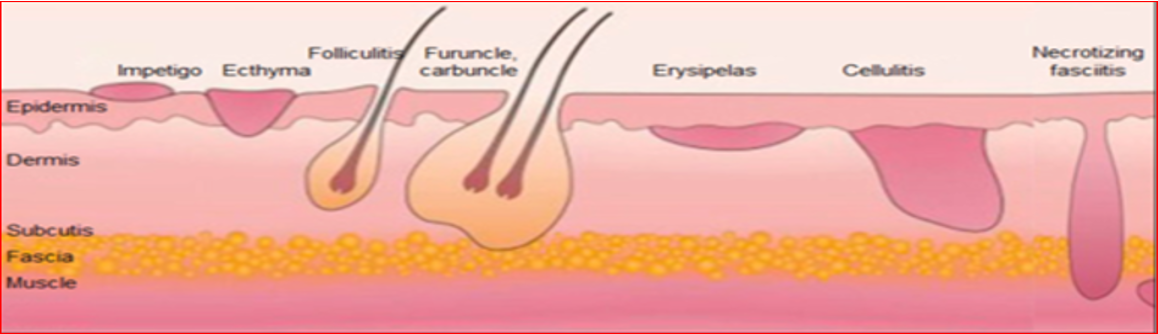
- It is infection of the upper layers of the skin (superficial)
- while cellulitis affects the deeper tissues.
The most common cause is group A streptococcal bacteria, especially Strep. pyogenes.
Erysipelas characterized by - hot, edematous, erythematous plaques with well-defined, raised edges with vesicles and bullae. While in cellulitis, the Reddened skin is less clearly defined, dark-red or slightly purplish.
C/Features: Fever, malaise and lymphadenopathy accompany cutaneous infection.
Treatment: Sensitive to Penicillin & Erythromycin
Dermatology
Erysipelas
- Erysipelas is a superficial cellulitis with marked dermal lymphatic involvement (causing the skin to be edematous or raised)
- Main pathogen is group A streptococcus
- Usually affects the lower extremities and the face
- Presents with pain, superficial erythema, and plaque-like edema with a sharply defined margin to normal tissue
- Plaques may develop overlying blisters (bullae)
- May be associated with a high white count (>20,000/mcL)
- May be preceded by chills, fever, headache, vomiting, and joint pain
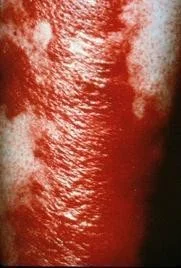
Example
Large, shiny erythematous plaque with sharply demarcated borders located on the leg
Treatment
- Immediate empiric antibiotic therapy should be started (cover most common pathogen - Streptococcus)
- Elevation of the involved area
Erysipelas
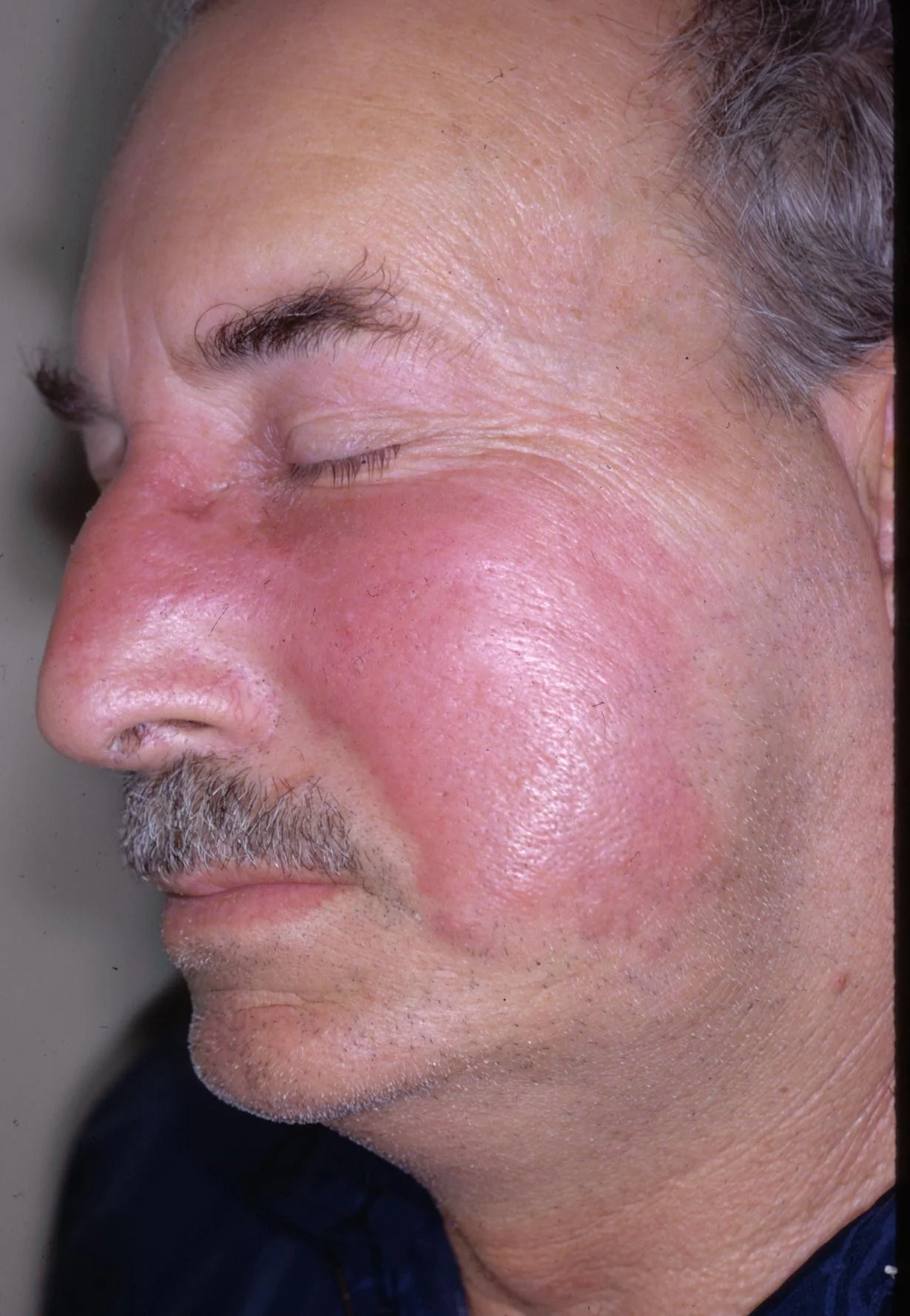
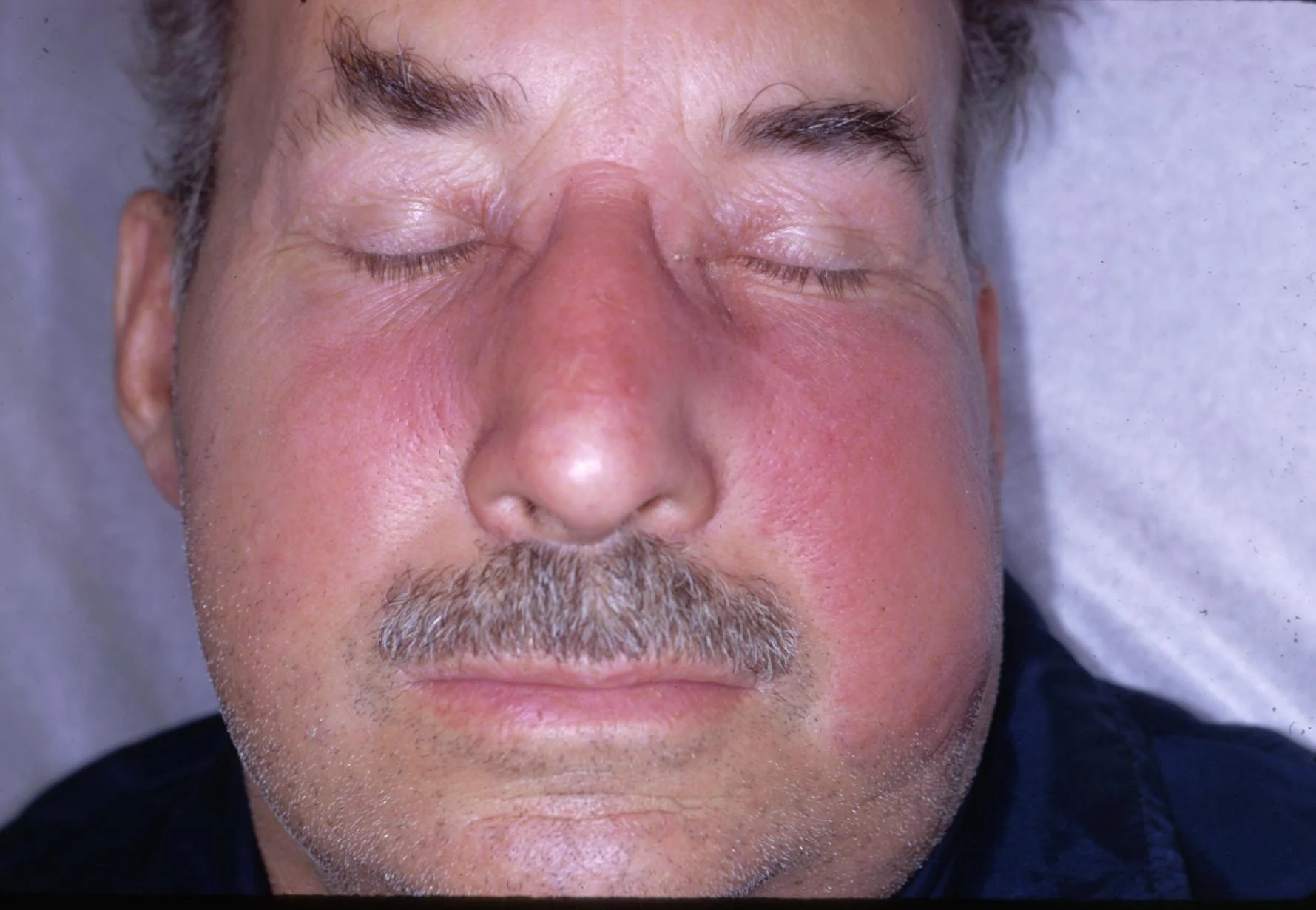
Question 1
What does this person have?
 A skin infection called Erysipelas
A skin infection called Erysipelas
Erysipelas - Description
- Erysipelas is a superficial cellulitis with marked dermal lymphatic involvement (causing the skin to be edematous or raised)
- Main pathogen is group A streptococcus
- Usually affects the lower extremities and the face
- Presents with pain, superficial erythema, and plaque-like edema with a sharply defined margin to normal tissue
- Plaques may develop overlying blisters (bullae)
- May be associated with a high white count (>20,000/mcL)
- May be preceded by chills, fever, headache, vomiting, and joint pain
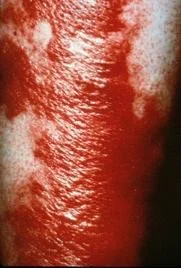
Example of Erysipelas
Large, shiny erythematous plaque with sharply demarcated borders located on the leg
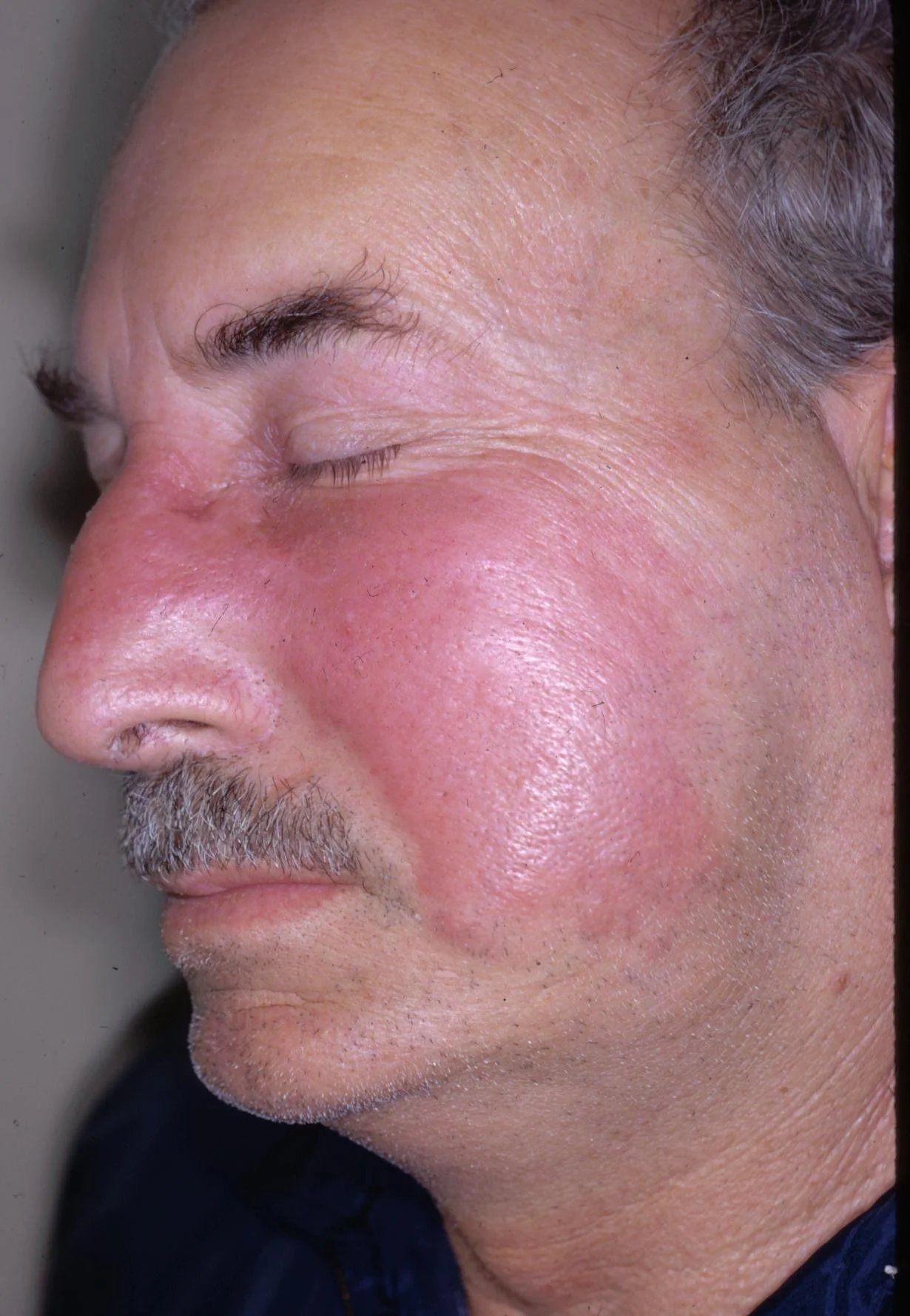
Question 2
- What is the most appropriate treatment? a. Oral antibiotics b. Oral steroids c. Topical antibiotics d. Topical moisturizers e. Topical steroids
Question 2 - Answer
Answer: a
- What is the most appropriate treatment? a. Oral antibiotics b. Oral steroids c. Topical antibiotics d. Topical moisturizers e. Topical steroids
Oral antibiotics are the most appropriate therapy in uncomplicated erysipelas.
Erysipelas: Treatment
- Immediate empiric antibiotic therapy should be started (cover most common pathogen - Streptococcus)
- Monitor patients closely and revise therapy if there is a poor response to initial treatment
- Elevation of the involved area