APA SYNDROME
Some patients with SLE have a condition called Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome ( APA syndrome, APLS)
Definition of APA syndrome:
It is an autoimmune condition where there are some abnormal antibodies in the blood, which cause thrombosis in blood vessels. Thrombosis can occur anywhere in the body (arteries or veins)
TYPES OF APA SYNDROME
- Primary: no known cause
- Secondary APA: Secondary to some other disease eg SLE
Signs & symptoms:
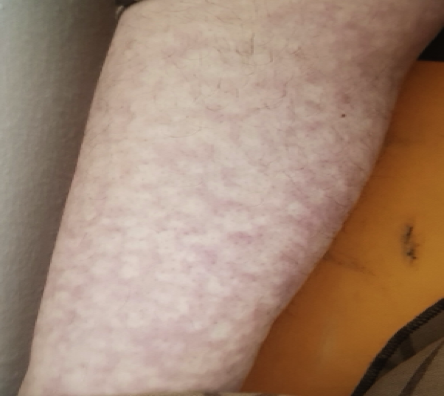
a) Venous thrombosis (eg DVT in the legs) b) Arterial thrombosis eg stroke, MI c) Pregnancy complications: recurrent miscarriage, still birth, intrauterine fetal death (females with recurrent abortions should always be screened for APA) d) Skin discoloration called “livedo reticularis”: this is a net like appearance of the skin
Livedo reticulitis
WHEN TO SUSPECT APA syndrome
- Arterial thrombosis
- Recurrent DVT
- Thrombosis in unusual sites eg. : portal vein, hepatic veins, intracranial veins
- Female with recurrent abortions, intrauterine fetal death
Blood tests:
- Antiphopspholipid antibodies (3 types)
A) lupus anti-coagulant
B) anticardio-lipin antibody
C) antibody to β2 glycoprotein - Thrombocytopenia
- High PTT ( ? Very strange, right?)
HOW TO DIAGNOSE
- Signs and symptoms(arterial or venous thrombosis PLUS
- Positive antibodies ( do twice, 12 weeks apart)
-
Diagnosis requires both 1 & 2
-
Either all 3 or just one or two antibodies may be present
If antibodies are present but no history of thrombosis, it is not APA syndrome
TREATMENT
-
For acute thrombosis: Heparin (i.v. or LMWH) then
-
For long term secondary prophylaxis: Oral anticoagulants( warfarin, apixaban) LMWH (second choice)
VERY IMPORTANT
If a lady with APA syndrome, who was taking warfarin, now becomes pregnant ⇒ stop warfarin & give LMWH.
- Warfarin is contraindicated in pregnancy
- Apixaban etc are category C drugs ( possible teratogenic but may be used if strongly needed)
RAPID FIRE QUESTIONS
-
How many types of APA syndrome?
- Two types: Primary and Secondary.
-
What happens in APA?
- Autoimmune disorder causing blood clots (thrombosis) and pregnancy complications.
-
Name the 3 antibodies?
- Lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies, and anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies.
-
How to diagnose APA syndrome?
- Clinical criteria (thrombosis or pregnancy complications) plus laboratory tests showing persistent presence of antiphospholipid antibodies.
-
What happens to the PTT?
- Prolonged PTT (Partial Thromboplastin Time).
-
What skin lesion is seen?
- Livedo reticularis.
-
Name some unusual sites of thrombosis?
- Cerebral veins, hepatic veins, and renal veins.
-
Treatment of APA syndrome?
- Long-term anticoagulation therapy (e.g., warfarin), and management of risk factors.