Orthopedics Case Scenarios: Emergency Cases
Dr. Tarif Al-Akhras
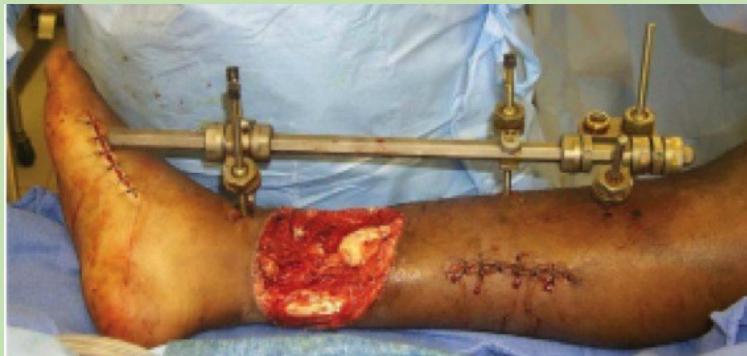
Case Scenario 1: Open Tibia Fracture
Patient Presentation:
- A 30-year-old man was involved in a car accident
- Brought to the emergency room unconscious
- Large wound at the anterior aspect of left leg with severe deformity and bone exposed
Clinical Task:
- Describe actions that you will take in the emergency management of this case
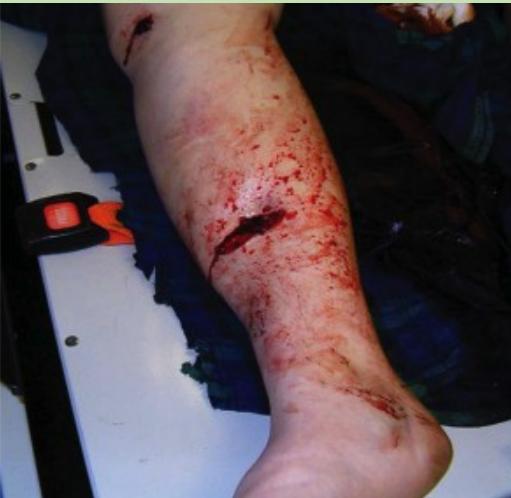
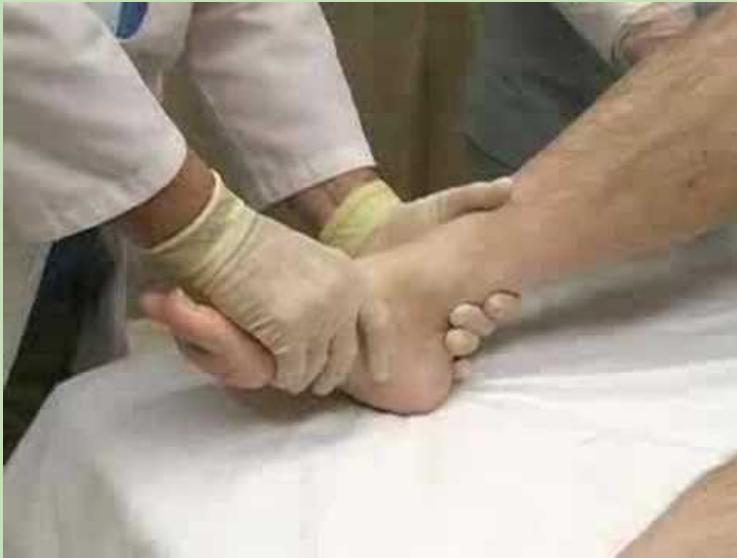
Immediate Actions in Emergency Room
Primary Assessment:
- ABCDE: save life, save limb, save function
- Cervical collar? (consider spinal injury)
- Cover wound with sterile dressing, Splint leg
- Take picture of wound before dressing
- Secondary survey
- Check distal pulses
- If no pulse, consider correcting major deformity by traction
Medical Management:
- IV Fluids: appropriate type and volume – request blood if needed
- Anti-Tetanus prophylaxis
- Antibiotics – appropriate broad-spectrum coverage
- Wound management:
- Clean major contamination, take picture, apply sterile dressing
Open Fracture Management
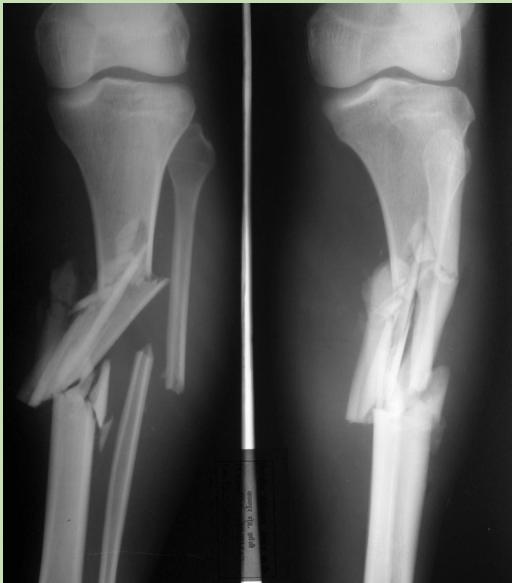
Detailed History Assessment
If possible, obtain further information:
Accident Details:
- Type of accident
- Mechanism of injury
- Place of injury
- Time since injury
- Pre-hospital management
Patient Information:
- Age, other diseases, medications
- Consciousness status and duration if lost
- Anti-Tetanus vaccination status
Treatment Protocol
- Admit to Operating Room for definitive management
- Apply Gustilo Classification for treatment planning
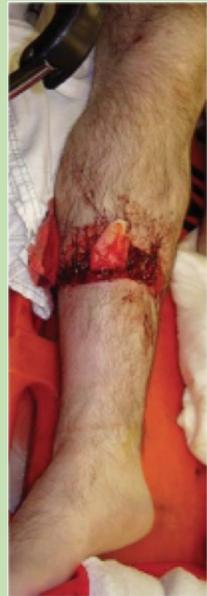
- Perform Surgical Debridement
Gustilo Classification of Open Fractures
Type I
- Wound < 1 cm long
- No evidence of contamination
- Minimal soft tissue injury
Type II
- Wound > 1 cm long
- No soft tissue stripped from bone
- Moderate soft tissue injury
Type IIIA
- Large wound with adequate soft tissue coverage of bone
- Severe soft tissue injury but still coverable
Type IIIB
- Large wound with periosteal stripping
- Bone exposed requiring soft tissue coverage procedures
- Often requires flap coverage
Type IIIC
- Large wound with significant arterial injury
- Requires vascular repair
- High risk of limb loss

Surgical Debridement Protocol
Immediate Prophylactic Measures:
- Tetanus serum given immediately
- Tissue and blood samples taken for culture
- Fluids and broad-spectrum antibiotics administered intravenously
- Wound pulse-irrigated thoroughly
Surgical Technique:
- All nonviable tissue thoroughly debrided
- Wound left open; external fixation device allows access to wound for dressing
- Device may be replaced with cast when infection clears
Complications:
- Despite proper management, chronic osteomyelitis may develop with sequestra and drainage
Key Principle: “Dilution is the solution to pollution”

Principles of Fracture Fixation
Fixation Options:
- Internal fixation (consider contamination and soft tissue status)
- External fixator (preferred for severe open fractures)
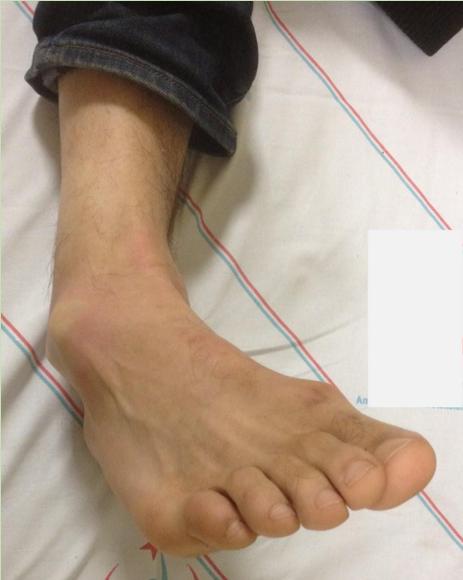
Case Scenario 2: Ankle Injury
Patient Presentation:
- 25-year-old man fell down on his right ankle
- What urgent management should you provide after ABC protocol was cleared?
Case Scenario 3: Additional Emergency Cases
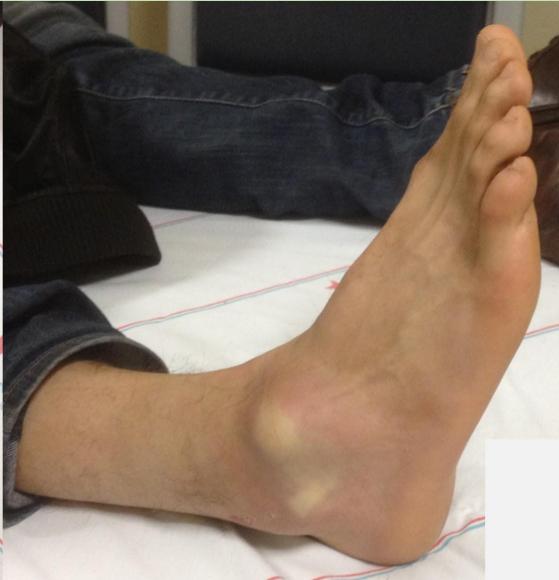
Case Scenario 4: