Protocol for Management of Infertile Couple
- History taking and examination of the wife.
- History taking and examination of the husband.
- Investigating the husband starting with semen analysis.
- Investigation of the wife:
- Evaluation of ovulation: day 3 FSH, LH, E2, DAY 21 PROGESTERONE, urinary LH, BIPHASIC basal body temperature chart, PROLACTIN, TFT, Testosterone.
- Uterine factor investigation: pelvic US, sonohystrogram, and hysteroscopy (if needed).
- Evaluation of tubal patency: HSG, laparoscopy (if needed).
- Cervical factor investigation. PCT if needed.
- Treatment started only after complete investigation and actual diagnosis of the cause(s).
Summary of Investigation
- Semen analysis
- Day 3 FSH, LH, E2, DAY 21 PROGESTERONE, PROLACTIN, TFT, androgen profile if hyperandrogenism.
- PELVIC US / SONOHYSTROGRAM (IF NEEDED)
- HSG
- POSTCOITAL TEST IF NEEDED
- LAPAROSCOPY / HYSTEROSCOPY IF NEEDED
Assisted Reproductive Technologies

A.R.T = Assisted Reproductive Technology
Types:
- Intrauterine Insemination = IUI: cannula is used to deliver sperm into the endometrial cavity after either spontaneous or induced ovulation with ovulation trigger.
- In vitro fertilization and embryo transfer = I.V.F-E.T i.e., the embryo resulted after fertilization by 2-3 days is transferred in the uterine cavity.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection = ICSI
Indications:
- Male factors of infertility: low sperm count, low sperm motility, and abnormal morphology associated with reduction in fertilizing ability.
- Tubal causes or peritoneal: e.g., moderate to severe endometriosis.
- Unexplained infertility.
- Immunologic infertility or genetic disorders.
- Ovulatory dysfunction not responding to ovulatory drugs.
- Couples seeking preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
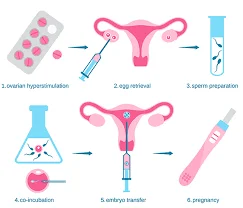
Steps of IVF-ET Cycle: Y
- Initial consultation and assessment.
- Controlled induction ovulation and ovulation trigger.
- Trans-vaginal oocyte retrieval.
- In vitro fertilization of the ova.
- Embryo culture till blastocyst stages and then embryo transfer in the uterine cavity.
- Excess embryos not used for transfer can be cryopreserved for an unlimited period.
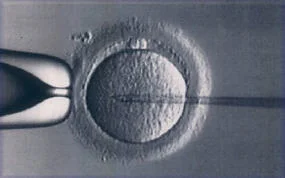
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection: Z
- SAME IVF STEP EXCEPT
- In ICSI, a single spermatozoon is injected microscopically into each oocyte, and the resulting embryos are transferred into the uterus.
- Indications: For infertility refractory to IUI/IVF, Severe abnormal semen analysis OR if PGD NEEDED.
Z IVF
Z ICSI
Z IUI

Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis
- The process of PGD proceeds by biopsy and genetic analysis of either oocyte or embryo.
- Indications Of PGD
- Single-Gene Disorders: As cystic fibrosis.
- Aneuploidy Testing of women who are of advanced reproductive age, have a history of recurrent pregnancy losses, or have undergone multiple failed IVF cycles.
- Sex Selection: medically for X-linked disorder (e.g., muscular dystrophy) or non-medical use (has limited application).
Case Study
45.A 28-year-old woman has a 3-year history of primary infertility. She presents with increasing symptoms of steady, aching lower abdominal pain at the time of menses. The pain persists throughout menstruation and often after and radiates into the rectum. Tender nodules in the uterosacral ligaments are noted in pelvic examination. Which one of the following would be the most contributory investigation?
a) Postcoital test b) Diagnostic laparoscopy c) Hysterosalpingogram on day 9 of her cycle d) Endometrial biopsy on day 26 of her cycle e) Basal body temperature charting