Spondylosis
Clinical Features
- Age group: Patients >60 years (or younger with mechanical stress)
- Symptoms:
- Recurrent attacks of back pain related to activity or prolonged sitting
- Pain relieved by lying down
- Catching (locking) sensation
- Root irritation symptoms from facet joint osteophytes
- Physical findings:
- Localized back tenderness
- Paravertebral muscle spasm (±)
- Limitation of lumbar spine movement
- Pain on extremes of movement
- Typical feature: Difficulty in straightening up from forward bend position
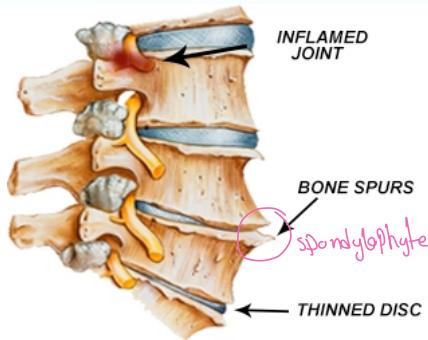
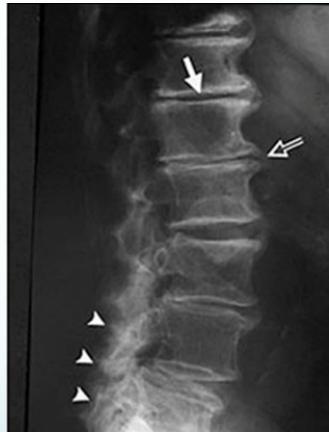
Radiographic Findings
- Narrowing of disc space
- Marginal bony spurs (Osteophytes)
- Osteoarthritic changes in facet joints
Treatment
Conservative Management:
- Intermittent lumbar corset
- Local heat pack
- NSAIDs
- Physiotherapy & manipulation
- Modified activities & isometric exercises
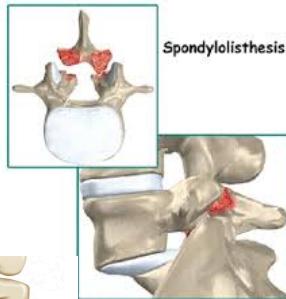
Spondylolisthesis
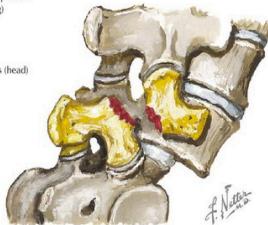
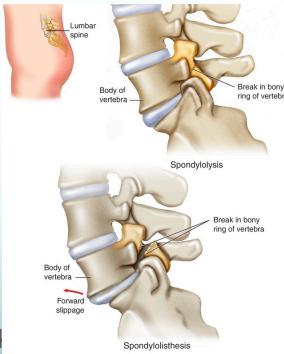
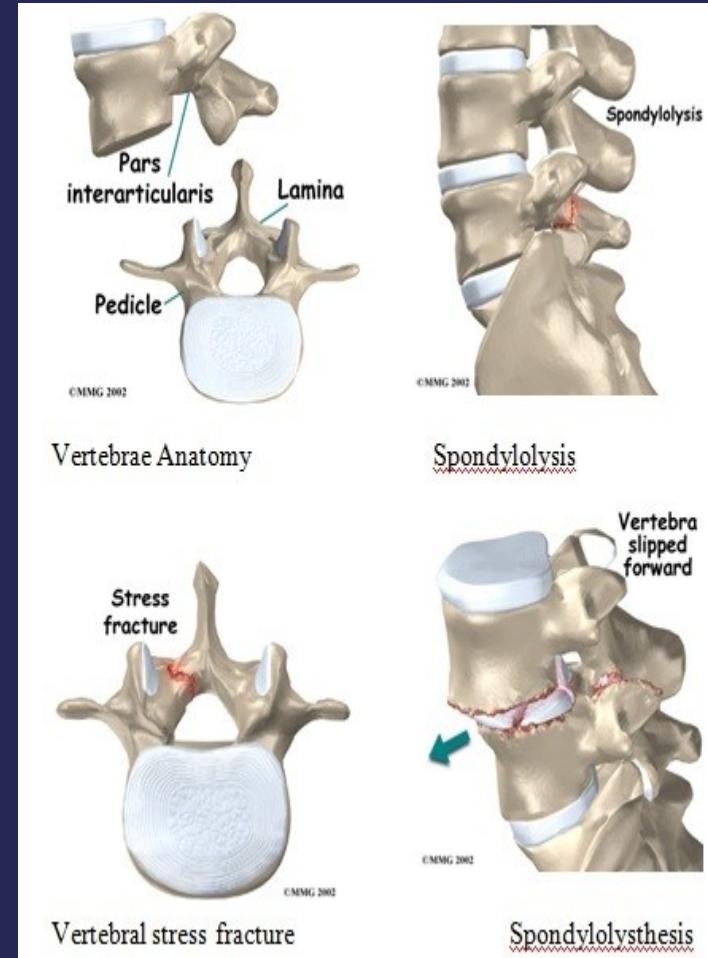
Definition: One vertebra moves over another (انترلاق فقرى)
Pathophysiology
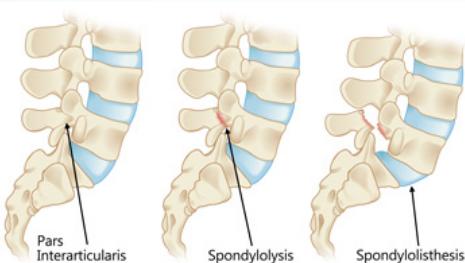
Normal anatomy: Lamina and facets constitute a locking mechanism preventing anterior displacement
Progression:
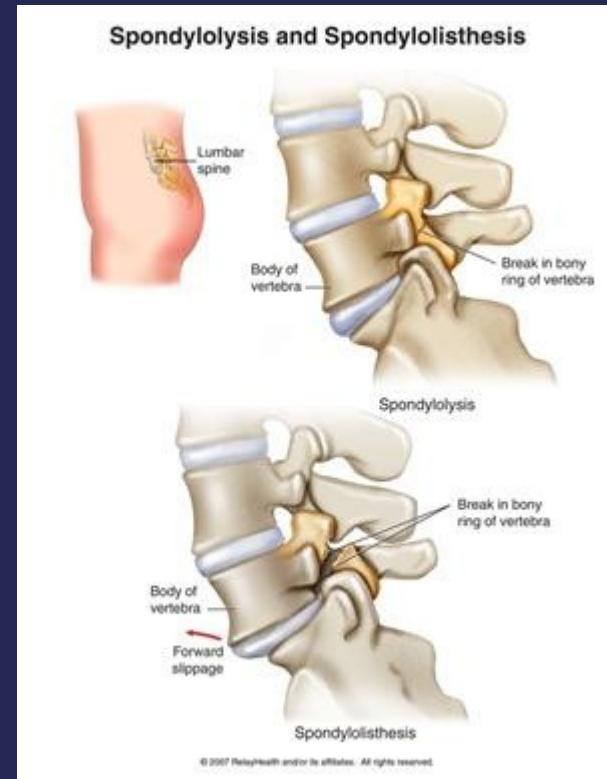
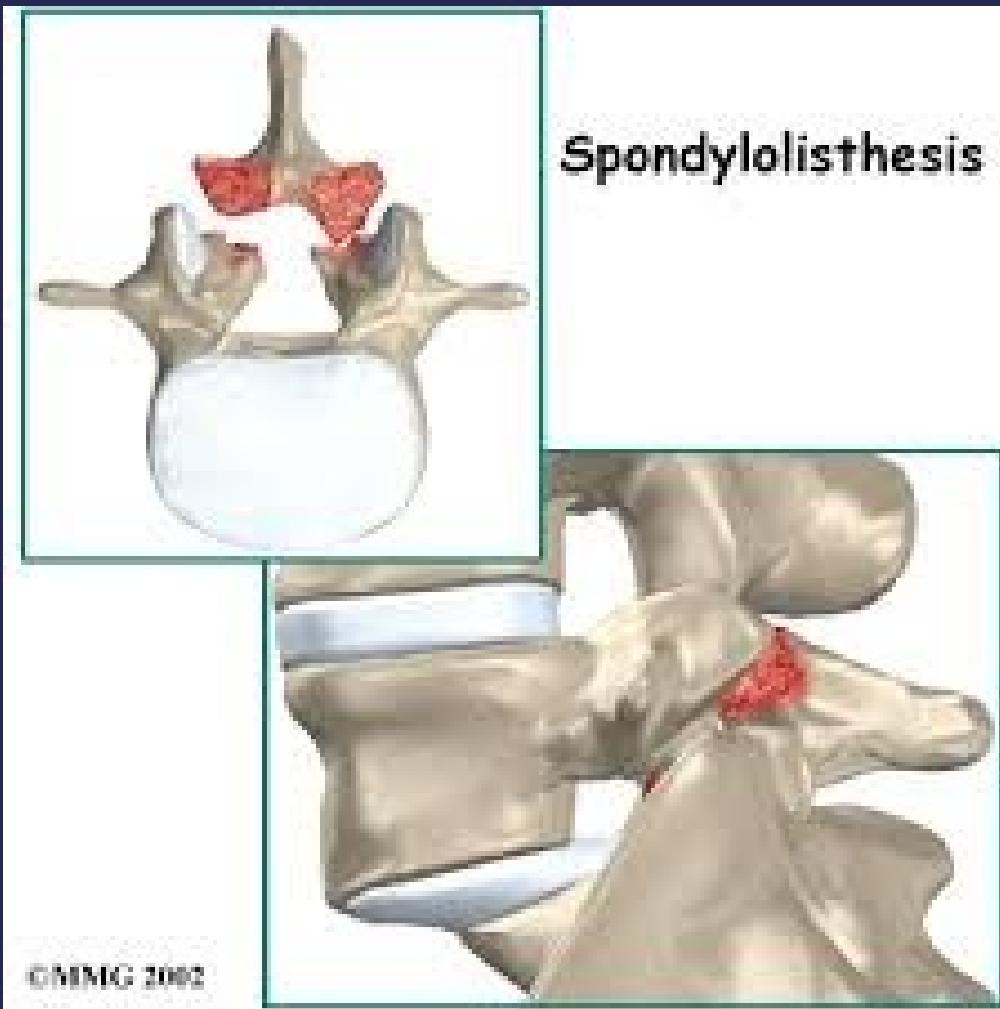
- Spondylolysis: Defect in pars interarticularis (no movement yet)
- Patient complains only of pain
- Spondylolisthesis: Anterior vertebral displacement
- Pain and nerve root compression
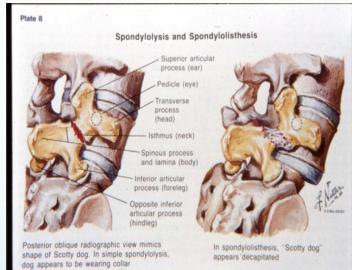
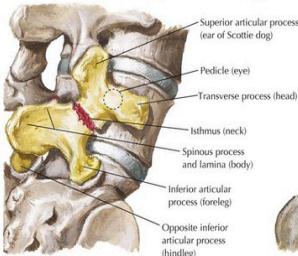
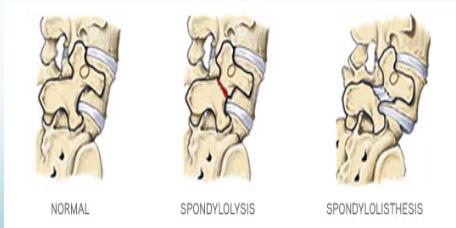
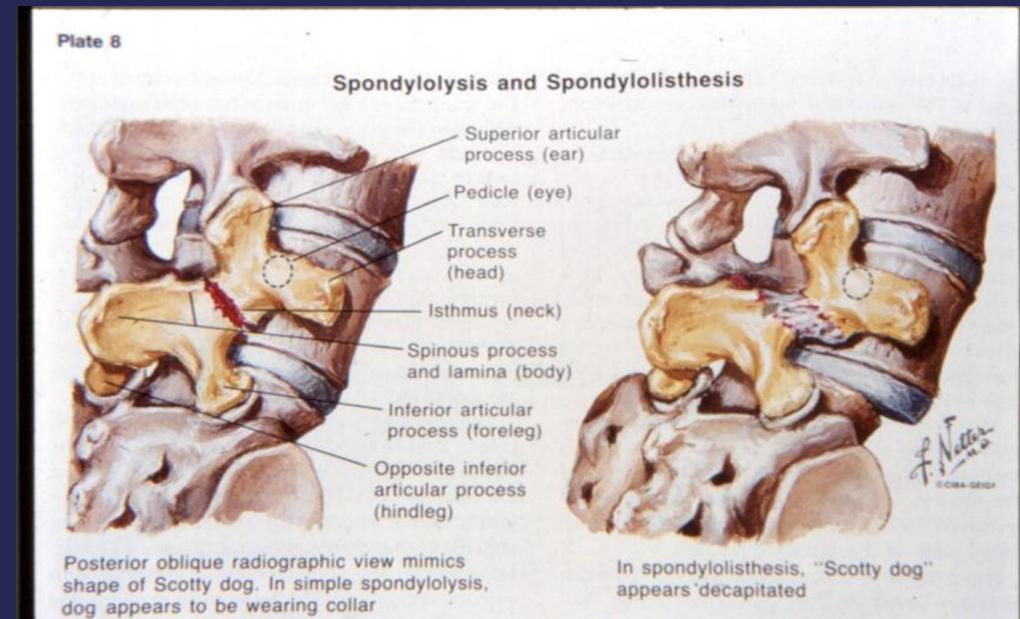
Radiographic “Scottie Dog” Sign
Posterior oblique views show:
- Normal: Scottie dog profile in yellow
- Spondylolysis: Scottie dog appears to be wearing a collar
- Spondylolisthesis: Scottie dog appears decapitated

Types and Clinical Features
| Type | Age Group | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Dysplastic | Children | Painless, protruding lower abdomen, tip-toe walking with flexed knees |
| Degenerative | >40 years, female > male | Chronic backache, spinal stenosis symptoms |
| Destructive | Any age | Secondary to trauma, TB, tumor |
| Spondylolytic | Adults | Backache after activity, flat buttock, step sign at back |
Diagnostic Imaging
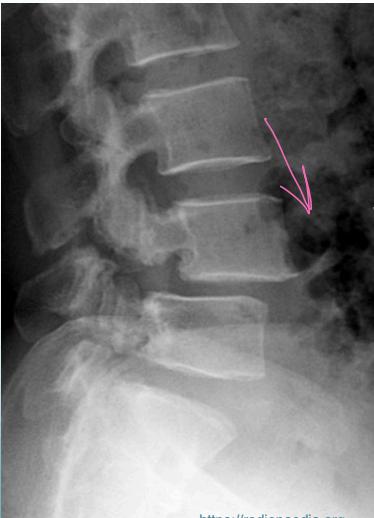
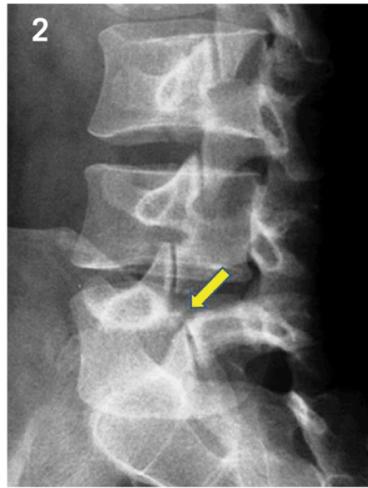
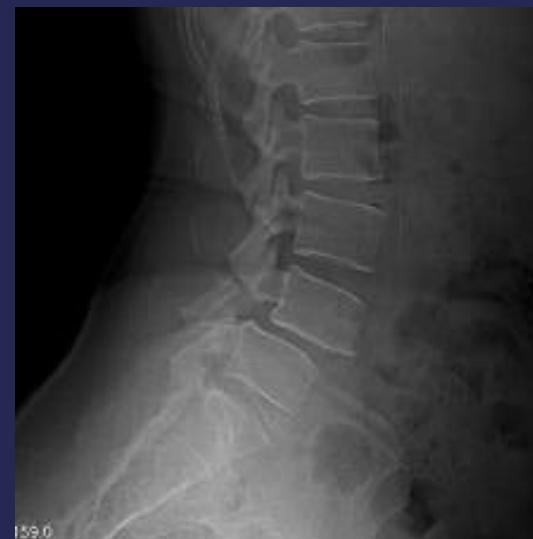
- Lateral view: Shows vertebral slip
- Oblique view: Shows decapitated Scottie dog

Treatment
Conservative:
- Older patients with mild symptoms
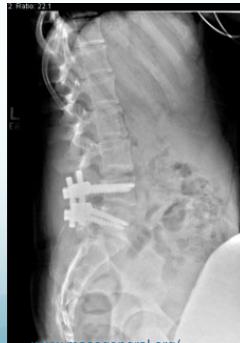
Operative (Spinal Fusion):
- Young patients with severe symptoms
- Neurological symptoms present
COMBINE BELOW
Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis
Definitions
- Spondylolisthesis: Anterior vertebral displacement
- Spondylolysis: Defect in the pars interarticularis
Normal Anatomy
- Lamina and facets normally prevent anterior displacement
Causes of Spondylolisthesis
- Dysplasia
- Spondylolysis
- Degenerative
- Destruction by trauma, TB, tumor
Clinical Features
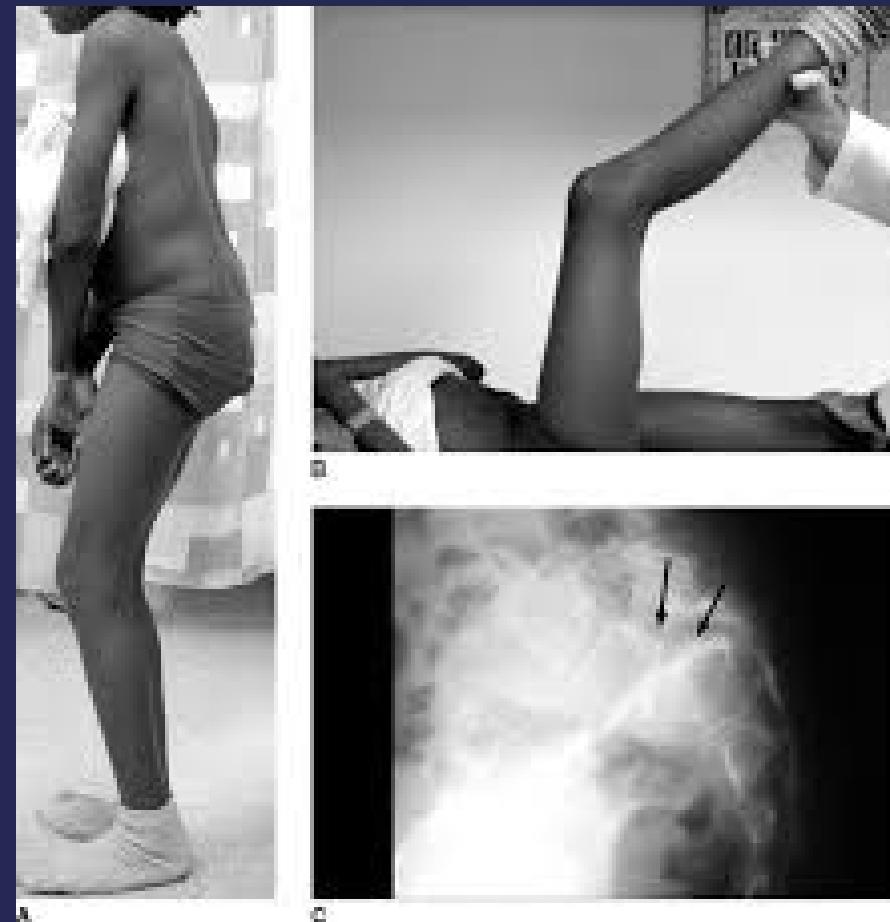
Dysplastic Type
- Children
- Painless
Postural Problems
- Protruding lower abdomen
- Tip-toe walking with flexed knees
Spondylolytic Type
- Adults (most common type)
- Backache after exercise
- Flat buttock
- Step sign
Degenerative Type
- Female > male
- Age > 40 years
- Chronic back pain
- Spinal stenosis symptoms
