Common Chronic Shoulder Disorders
Objectives
-
Revision of anatomy
-
Discuss common disorders
- Shoulder instability
- Rotator cuff (impingement) syndrome
- Supraspinatus tendinitis
- Biceps tendinitis
- Adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
- Shoulder arthritis
- Scapular winging
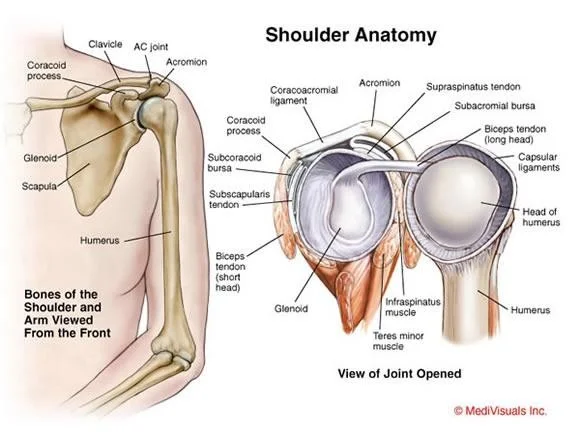
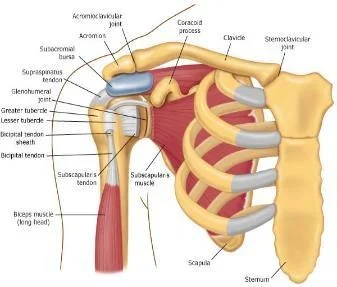
Anatomy
- Glenohumeral Joint
- Sternoclavicular Joint
- Acromioclavicular Joint
- Scapulothoracic Joint
Common Shoulder Complaints
- Pain
- Localized
- Generalized
- Painful arc
- Loss / limitation of function
- Stiffness
- Painful
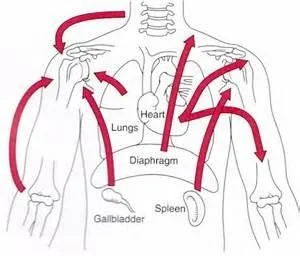
Shoulder Pain
- INTRINSIC
- Due to causes in the shoulder region
- EXTRINSIC
- Due to referred pain from outside the shoulder
Shoulder Instability
-
Shoulder (glenohumeral) joint is the most commonly dislocated joint of body
-
Instability means
- Excessive movement of humeral head on the glenoid during active shoulder movement
- May lead to recurrent dislocation
Shoulder Restraints Z
- Static:
- Glenoid labrum
- Capsule
- Ligaments around capsule
- Dynamic:
- Rotator cuff muscles
- stabilize the humeral head within the glenoid
Types of Instability
According to Direction
- Anterior
- The commonest
- Following acute traumatic dislocation
- Posterior
- Due to a violent jerk in an unusual position
- Multi-directional
- Ligament laxity
Classification Systems
- TUBS
- Traumatic
- Unilateral
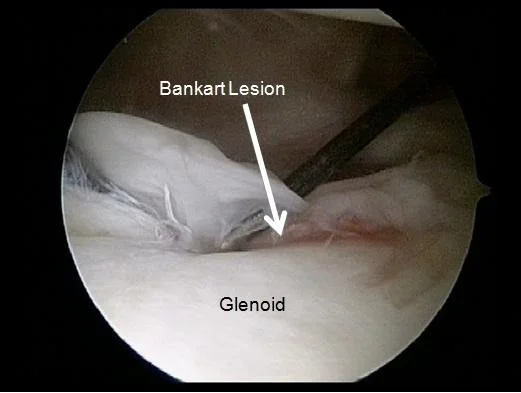
- Bankarts lesion
- Surgery
- AMBRI
- Atraumatic
- Multidirectional
- Bilateral
- Rehabilitation or Inferior capsular shift
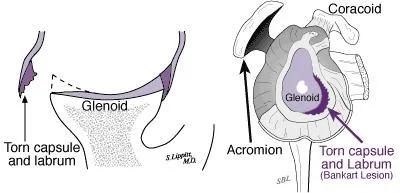
Traumatic – Soft Bankart
- No bony lesion seen on x-ray
- A tear in the labrum and capsule
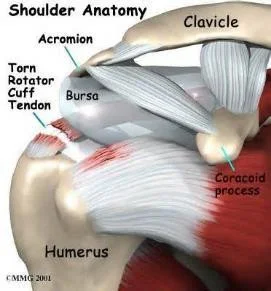
Rotator Cuff Disorders
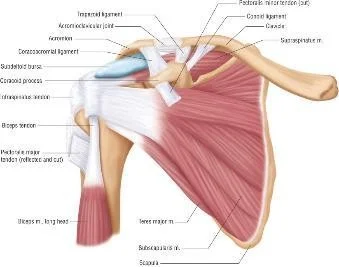
- Anatomy:
- Originate from the scapula
- Pass under coraco-acromial arch
- Insert in the Greater & Lesser tuberosities
- Separate from the ligament by bursa
| insertion | Position | Muscle |
|---|---|---|
| G tuberosity | above | Supraspinatus |
| G tuberosity | behind | Infraspinatus |
| G tuberosity | behind | Teres minor |
| L tuberosity | In front | Subscapularis |
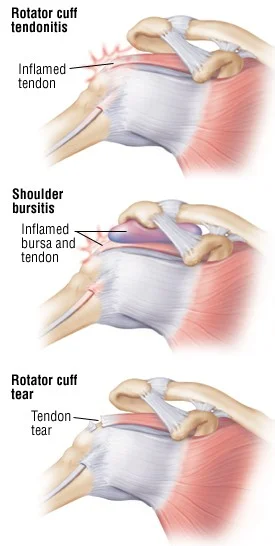
- Rotator cuff syndrome - which comprises several conditions with distinct clinical features and natural history:
- Acute tendinitis (painful arc syndrome)
- Chronic tendinitis (impingement syndrome)
- Rotator cuff tears
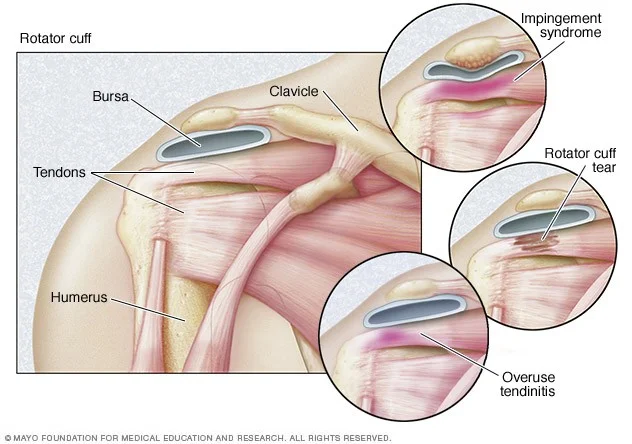
R.C.D - Acute Tendinitis
- Supraspinatus tendinitis
- The supraspinatus is the most commonly injured rotator cuff M
- Clinical features:
- Young adult
- Sever Pain, tenderness
- painful initiation of abduction
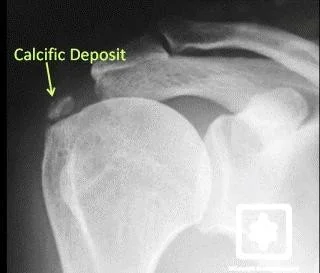
- X-ray:
- Normal
- Area of calcification
Supraspinatus Tendinitis
- Treatment:
- Rest
- NSAIDS
- Physiotherapy
- Local steroid injection
- Surgery: (acromioplasty, decompress the rotator cuff) If symptoms do not subside after 3 months of conservative treatment, or if they recur persistently after each period of treatment
R.C.D - Impingement Syndrome
- Chronic tendinitis
- Causes
- Over-use / Minor tears
- Impingement under the coracoacromial arch
- Osteophytes in under surface of acromioclavicular joint
- Curved acromion
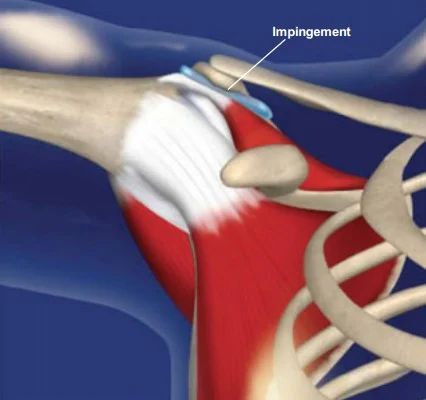
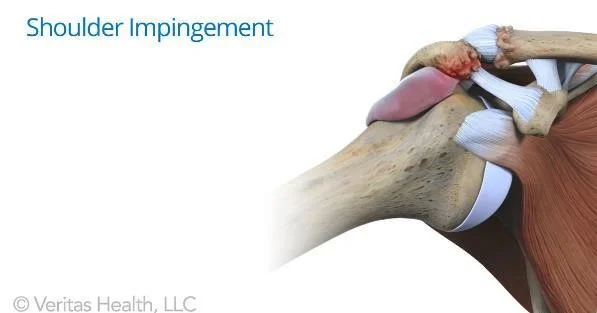
- Clinical features
- Age 40-60 years
- Pain
- Shoulder looks normal or wasted
- Tenderness
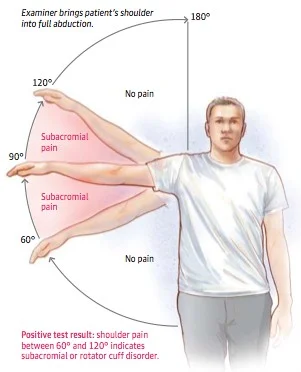
- Painful abduction arch (60° To 120°)
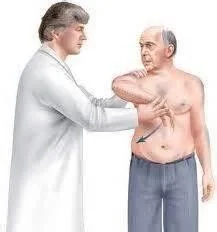
- Neer’s test (+ve)
- Hawkin’s test (+ve)

- X-ray:
- Calcification
- Degenerated AC jt.
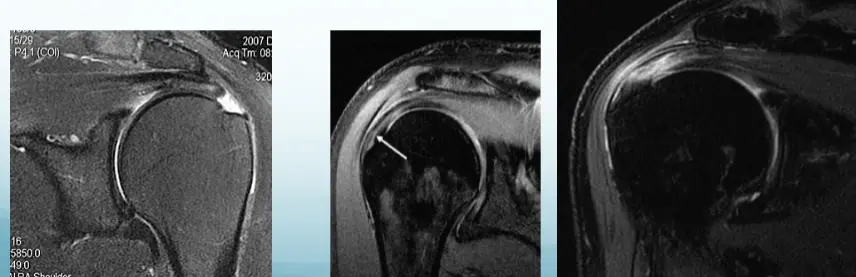
- MRI:
- Bursitis / Thickening of tendon
Treatment
-
Non-operative:
- Activity modification
- Sub-acromial steroid injection
- NSAIDS
- Rotator cuff and scapular stabilizing exercises
-
Surgery:
- Arthroscopic
- Acromioplasty
- Rotator cuff repair
- Arthroscopic
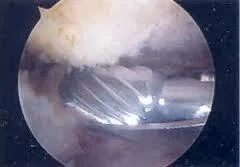
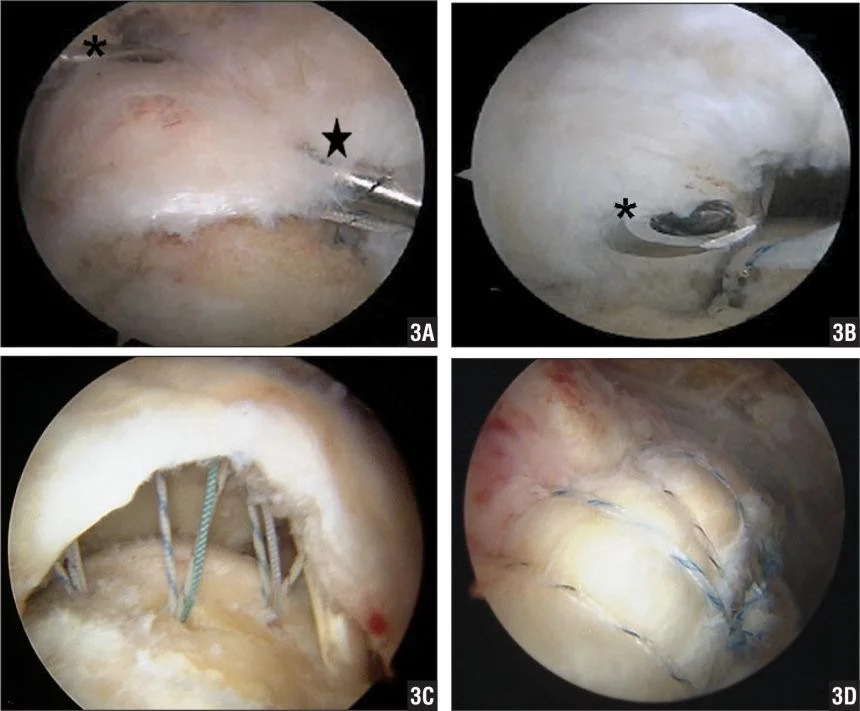
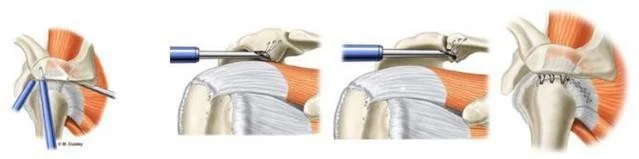
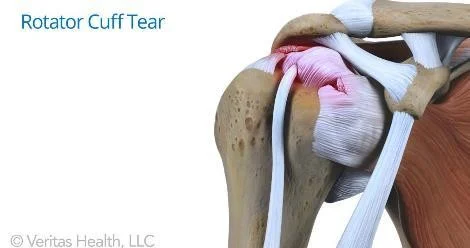
R.C.D - Tears- Predisposing factors
-
Degeneration (middle age)
-
Chronic irritation by osteophyte
-
Underlying disease, e.g., Rheumatoid
-
Precipitating factor: trauma
-
Types
- Incomplete
- Complete
-
Clinical picture
-
Typical presentation: trauma, pain, limited abduction
-
Early stage – normal appearance; late stage – wasting of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles
-
Tenderness over the greater tuberosity
-
After a few weeks
- Incomplete tear: pain and range of motion improve
- Complete tear: pain improves, but active range of motion decreases; passive motion remains painless and the drop‑arm sign may appear
-
-
Imaging
- X‑ray: early – normal; late – degenerative changes
- MRI – image of choice
-
Treatment
- Incomplete tear: physiotherapy, NSAIDs
- Complete tear: surgical repair
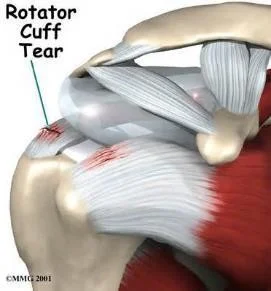

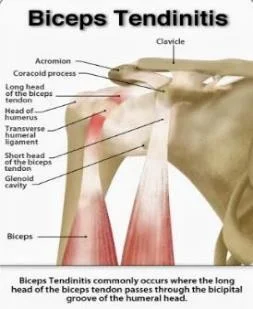
Biceps Tendon Disorders
- Tendinitis:
- Often associated with impingement
- Pain
- Tenderness: Bicepital groove
- Painful forward flexion
- Speed/Yergason test
- Treatment:
- NSAID
- Local steroid injection
- Surgery
- Tenotomy / Tenodesis
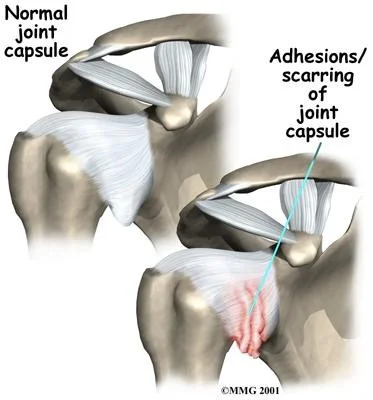
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)
- Presentation
- Pain and restriction of movements
- Causes
- Trauma, breast surgery, diabetes & immobilization
- Self-limiting with 3 stages
- Painful stage
- Stiff stage
- Thawing stage: The range of motion of shoulder begins to improve
Treatment
- Conservative
- Intra-articular injection
- Physiotherapy
- Surgical
- Manipulation under anesthesia
- Arthroscopic release of adhesions
Acromioclavicular Arthritis
- Clinical Features
- Pain, localized tenderness
- Pain on abduction above shoulder level

Shoulder Summary
- Common Symptoms
- Pain
- Loss of Function
- Stiffness
- Instability
- Common Disorders
- Shoulder instability
- Rotator cuff (impingement) syndrome
- Supraspinatus tendinitis
- Biceps tendinitis
- Adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
- Diagnostic Approach
- History
- Clinical examination
- Imaging investigations