اللهم يا معلّم موسى علّمني، ويا مفهم سليمان فهّمني، ويا مؤتي لقمان الحكمة وفصل الخطاب آتني الحكمة وفصل الخطاب اللهم اجعل ألستنا عامرة بذكرك، وقلوبنا بخشيتك، وأسرارنا بطاعتك، إنك على كل شيء قدير، حسبنا الله ونعم الوكيل
Updates through https://medatlax.com/Clinical/Level-11/GYN/Topics/OSPE-GYN/OSPE-GYN - will be highlighted yellow
Radiology is excluded, MAIN & Operations are from current year’s, Secondary is from previous years
OSPE GYN Main
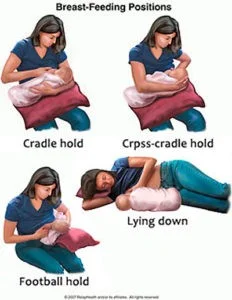
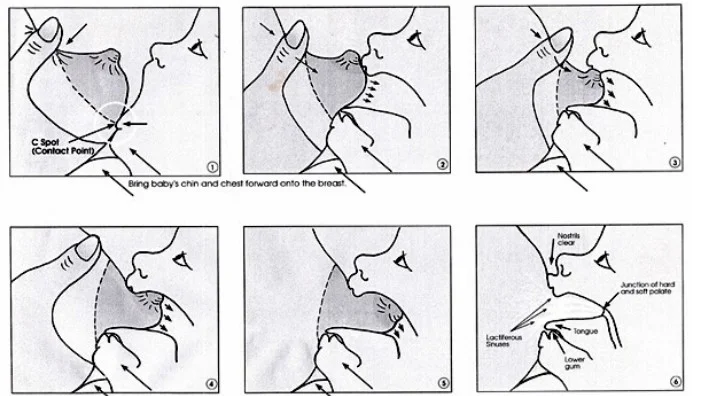
The Right Technique for Breastfeeding
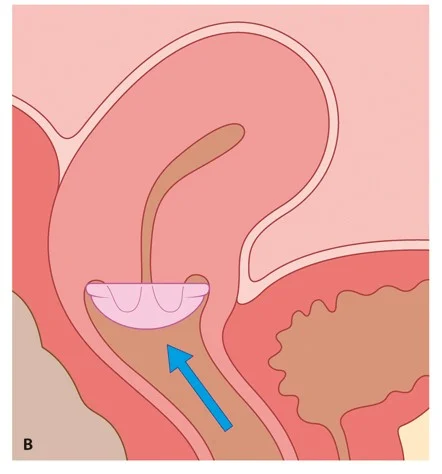
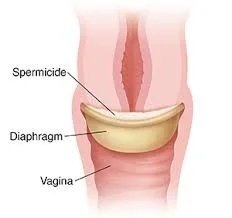
Diaphragm and Cap
- These are latex or non-latex devices that are
- inserted into the vagina to prevent passage of
- sperm to the cervix .
- Caps fit over the cervix.
- They are often used in with a spermicide.
Disadvantages
- women need to be taught how to insert and remove.
- High failure rate.
- May be associated with increased vaginal discharge
- Associated urinary tract infections.

Doyen Retractor
Identify this structure
- Doyen retractor
What are the uses?
- Retract the urinary bladder in CS
- Retract tissues in C-section
- Retract the uterus and abdominal wall in abdominal and pelvic surgery

Cesarean section set.
Name two complications of the procedure?
- Anaesthetic compilations.
- Fetal depression / headach / Pain (back)
- Technical complications.
- Bowel injury / uterus injury / Bleeding
- Postoperative short complication.
- wound infection, urin retention
- Long term postoperative.
- wound adhisions, Bowel adhisions
Give example or two for each.

Green Armytage forceps
Identify this structure
- Green Armytage forceps
What are the uses?
- Control bleeding from the incision edges
- Help in suturing incision

Short curved or Wrigley’s forceps (Outlet forceps)
Identify this structure
- Short curved or Wrigley’s forceps (Outlet forceps)
What are other types?
- Long curved or Simpson’s forceps (mid-cavity traction)
- Long straight or Kielland’s forceps (rotation & traction)
- Piper forceps: for after-coming head in vaginal breech
Forceps delivery: indications
Maternal:
- Dangers for the mother (prophylactic forceps): e.g., pre-eclampsia/eclampsia; associated disease (diabetes, heart, lung)
- Maternal distress
Fetal:
- Prophylactic forceps (dangers for the fetus), e.g., cord prolapse
- Abnormal presentations/position: occipito-posterior, deep transverse arrest, face presentation, after-coming head
- Fetal distress or impending fetal compromise
- Prolonged second stage of labor
Forceps delivery: complications
Maternal:
- Trauma to lower uterine segment, cervix, vagina, perineum
- Sepsis
- Obstetric shock
- Pelvic injuries: symphysis and sacro-iliac joint injury; fracture of coccyx
- Postpartum haemorrhage (traumatic or atonic)
- Vesico-vaginal fistula and stress incontinence
Fetal:
- Soft tissue compression
- Cranial injury
Contraindication
- Cephalo-pelvic disproportion

Vacuum (Kiwi) delivery
Identify this structure
- Kiwi vacuum
Types
- Two Metal cup ventouse
- Plastic cup ventouse (Kiwi is plastic)
Prerequisites:
- Clinically adequate pelvis
- Experienced operator
- Cervix fully dilated
- Engaged fetal head
- Cephalic presentation
- Ruptured membranes
- Empty bladder
- Gestational age > 34 weeks
- For forceps add anaesthesia and episiotomy
Vacuum: contraindications and complications
Contraindications (mention 2):
- Face, breech and transverse presentations or after-coming head
- Premature babies
- Moderate or severe cephalo-pelvic disproportion
- Fetal or maternal distress requiring rapid delivery
Complications:
- Increased risk of cervical incompetence
- Vaginal laceration
- Fetal skull injuries: cephalohematoma
- Intracranial haemorrhage
- Scalp lacerations, necrosis and alopecia
B 
Couvelaire uterus
What can you see in the picture?
- Couvelaire uterus (bleeding into uterine myometrium)
What is the cause?
- DIC due to abruptio placentae
How to treat?
- Evacuate uterus and give oxytocin; if failed, hysterectomy (definitive)

Bimanual removal of the placenta
Name this procedure
- Bimanual removal of the placenta
Give two complications
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Uterine inversion
- Uterine rupture

Artificial rupture of membranes (ARM, amniotomy)
Name this procedure
- ARM (Artificial Rupture of Membranes) / Amniotomy
Indications
- Induction of labour
- Acceleration of labour
Give two complications
- Injury to the fetus
- Injury to surrounding tissues
- Bleeding due to disruption of placenta previa
- Non-reassuring fetal testing
- Cord prolapse
- Infection (due to prolonged rupture of membranes)

Manual reposition of the uterus
Name this procedure
- Manual reposition of the uterus
Give two possible risk factors for inversion
- Macrosomia
- Rapid delivery
- Prolonged labour
- Short umbilical cord
- Hasty cord traction before separation
- Use of uterine relaxants
- Uterine anomalies
- Retained placenta
- Placenta accreta

Uterine balloon tamponade (Bakri balloon)
Identify this instrument
- Uterine balloon tamponade (Bakri balloon)
Indication
- Control postpartum haemorrhage (PPH)
Contraindications (mention 2)
- Suspected ruptured uterus
- If hysterectomy is indicated
- DIC

B-Lynch uterine compression suture
Name this procedure
- B-Lynch
Indication
- To stop PPH due to uterine atony

Abdominal ultrasound
Name this procedure
- Abdominal ultrasound
Indications
- Obstetrical:
- Determining gestational age
- Number of fetuses
- Placental location
- Amount of amniotic fluid
- Gynaecological:
- Ovarian pathologies
- IVF
- Folliculometry
- Fibroid diagnosis
- Early pregnancy bleeding diagnosis
 
Cardiotocography (CTG)
What is the indication?
- Alterations in fetal heart rate on auscultation
- High-risk delivery
- Induced and/or stimulated labor
- Auscultation cannot be performed (maternal habitus or other reasons)
Alternatives
- Pinard stethoscope
- Sonic aid
- Stethoscope
- Doppler ultrasound
- Fetoscope
- Naked ear
Fetal heart assessment: non-CTG devices
- Pinard stethoscope
- Stethoscope
- Sonic aid
- Doppler ultrasound
- Fetoscope
- Naked ear  sonic aid doppler
 

Physiological skin changes in pregnancy
What do you see?
- Right: Chloasma
- Left: Linea nigra
Cause
- Hyperpigmentation (melanin deposition) due to pregnancy

Striae gravidarum
What do you see?
- Striae gravidarum
Cause
- Skin overstretching due to rapid increase in size (pregnancy)
- Replacement of elastic tissue by fibrous tissue

Partogram
What is this slide?
- Partogram
Purpose of use
- Chart the progress of labour
- Chart important events during labour
- Chart maternal and fetal condition
- Early detection of abnormal progress of labour
- Recognition of CPD
- Allow further management of labour
- Detect complications

Fundal height measurement with tape
Name the procedure
- Measuring fundal height with tape
Use
- Detect duration of pregnancy
- Assess fetal growth / dating of pregnancy

First fundal grip (Leopold’s maneuvers)
What is this maneuver?
- First fundal grip (measuring fundal height)
Indication
- Detecting gestational age
Causes of fundal level more than dates
- Wrong dates
- Polyhydramnios
- Macrosomia
- Multiple pregnancy
- Placenta previa
- Tumours
- Hydrocephalus
- Molar pregnancy
Causes of fundal height less than dates
- Wrong dates
- Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
- Missed abortion
- Intrauterine death (IUD)
- Transverse lie
- Deep engagement
- Oligohydramnios

Cord prolapse case
A patient admitted 2 hours ago; cervix 4 cm dilated. Membranes ruptured spontaneously one minute ago. PV: cervix 6 cm; CTG: FHR 170 bpm.
Diagnosis
- Cord prolapse
Mode of delivery
- Emergency caesarean section
Mention two risk factors
- Breech presentation
- Multiple pregnancy
- Prematurity
- Obstetrical interventions (ARM; artificial rupture of membrane, ECV; external cephalic version, IOL; induction of labor)
- High head
- High parity
- CPD (Cephalopelvic disproportion)
- Polyhydramnios

Macrosomia
Diagnosis
- Macrosomia
Give two possible causes
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
- Excessive weight gain during pregnancy
- History of previous macrosomia
- Familial
- Male fetus
- Post-dates
- Maternal obesity
Give two possible complications
- Labor problems (shoulder dystocia, birth injuries, need for instruments or C-section)
- Genital tract lacerations
- Uterine rupture
- PPH
B 
McRoberts maneuver and suprapubic pressure
Indication
- Release of impacted shoulder in shoulder dystocia
Complications
- Maternal:
- Increased perineal trauma (3rd/4th degree tears)
- Postpartum haemorrhage
- Psychological trauma
- Fetal:
- Brachial plexus injury
- Fractured clavicle or humerus
- Hypoxic brain injury
How to prevent (mention 2)
- Diagnosis and anticipation
- Optimal control of gestational and insulin-dependent diabetes
- Reduction of maternal obesity
- Careful plan for mode of delivery in women with previous shoulder dystocia
Risk factors (give two)
- Macrosomia
- Poorly controlled diabetes (GDM or pregestational)
- Maternal obesity
- Previous shoulder dystocia
- Instrumental delivery

Footling breech
Diagnosis
- Footling breech
Mode of delivery
- Caesarean section
Two possible complications of breech delivery
- Head entrapment
- Cord prolapse
- Intracranial haemorrhage
- Spinal cord injury
- Limb fracture
- Nuchal arm


External cephalic version (ECV)
Name the procedure
- External cephalic version (ECV)
Contraindications (mention 2)
- Any contraindication to vaginal birth (e.g., placenta previa)
- Clinically inadequate pelvis
- Footling breech
- Macrosomia
- IUGR
- Hyperextended fetal neck in labour
- Lack of trained personnel
- Previous caesarean section
ECV: complications
Give two possible complications
- Placental abruption
- Uterine rupture
- Fetomaternal haemorrhage
- Emergency caesarean section
- Fetal bradycardia
- Cord accident
- PPROM
- Iatrogenic breech
- Failure of procedure

Caput succedaneum
Identify the abnormality
- Caput succedaneum
Possible causes
- Prolonged labor
- Obstructed labor
- Early pushing
- Use of vacuum/forceps
- PPROM

Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
Diagnosis
- IUGR
Possible causes
- Maternal:
- Chronic maternal disease (hypertension, cardiac disease, chronic renal failure)
- Substance abuse (alcohol, recreational drugs, smoking)
- Autoimmune disease (e.g., antiphospholipid syndrome)
- Genetic disorders (e.g., phenylketonuria)
- Poor nutrition
- Low socioeconomic status
- Placental (placental insufficiency):
- Abnormal trophoblast invasion
- Pre-eclampsia
- Placenta accreta
- Abruption
- Placenta praevia
- Fetal:
- Genetic abnormalities (trisomy 13/18/21, Turner’s)
- Congenital abnormalities (cardiac, gastroschisis)
- Congenital infection (CMV, Rubella, Toxoplasmosis)
- Multiple pregnancy
Management note
- Mild IUGR: consider delivery around 37 weeks
Give two possible complications
- Increased perinatal mortality
- Cerebral palsy
- Stillbirth (IUFD)
- Delayed milestones
- Short stature
- Intrapartum fetal distress and asphyxia
- Meconium aspiration
- Emergency caesarean section
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Hypoglycaemia and hypocalcaemia
- Later risk of CVD and diabetes
Treatment:
-
Depends on severity
-
Severe ‘abnormal doppler’: Immediate delivery by Cesarean Section (CS) regardless of the Gestational Age (GA).
-
Moderate: Follow up by Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) flow on Doppler.
-
Mild: Wait, but deliver her before 37 weeks (e.g., in the 36th week).

Preterm baby
Diagnosis
- Preterm baby
Give two risk factors
- Previous preterm birth
- Multiple pregnancy
- Cervical surgery
- Uterine anomalies
- Medical conditions (renal disease, diabetes)
- Pre-eclampsia and IUGR (spontaneous or iatrogenic)
- Infections
- Stress
Short-term complications
- ARDS
- PDA and other heart problems
- Intraventricular haemorrhage
- Hypothermia
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Anaemia
- Neonatal jaundice
- Hypoglycaemia
- Infection and feeding problems
Long-term complications
- Cerebral palsy
- Learning disabilities
- Vision problems
- Hearing problems
- Dental problems
- Behavioural and psychological problems
- Asthma

Down’s syndrome
Diagnosis
- Down’s syndrome
Give two possible findings
- Typical appearance: flat nasal bridge, epicanthic folds, single palmar crease
- Intellectual impairment
- Congenital malformations:
- Cardiac abnormalities (VSD, ASD, Tetralogy of Fallot)
- Gastrointestinal atresias (e.g., duodenal atresia)
- Increased risk of other medical conditions (leukaemia, thyroid disorders, epilepsy)
Give two investigations
- First trimester:
- Blood test: PAPP-A
- Ultrasound: nuchal translucency
- Second trimester (quad screen):
- AFP, Estriol, hCG, Inhibin A
B 
Gastroschisis
Diagnosis
- Gastroschisis
Possible causes
- Unknown; associated with very young mothers
Possible association in pregnancy
- Polyhydramnios
Two possible complications
- Difficulty expanding the lungs leading to breathing problems
- Intestinal complications: atresia, stenosis, sepsis, NEC

Exomphalos (omphalocele)
- Failure of gut to return into the abdominal cavity after embryological extrusion and rotation
- Bowel (and sometimes other viscera) contained within a sac
- Associated with chromosomal abnormalities
- Requires referral to fetal medicine and postnatal surgery
- Not an indication for CS
Gastroschisis vs. Omphalocele
- Gastroschisis: protrusion of gut through anterior abdominal wall defect; bowel not covered by sac; floats freely; usually in very young women; no chromosomal abnormalities; GI tract may become obstructed or atretic; refer to fetal medicine; vaginal delivery not contraindicated
- Omphalocele: bowel within a covering sac; associated with chromosomal abnormalities; refer to fetal medicine; postnatal surgery

 

Late decelerations
Shape
- Has the same shape and depth (uniform)
Causes (reduced uteroplacental blood flow)
- Maternal hypotension
- Pre-eclampsia
- Uterine hyperstimulation

Variable decelerations
Shape
- Multiple decelerations with different depth and shape (not identical)
Main cause
- Umbilical cord compression
Due to
- Fetal hypoxia
- Short cord
- Prolapsed cord
- Decreased amniotic fluid
- Fetal descent

Reduced variability
Finding
- Variability present but reduced (zigzag-like)
Causes
- Fetal sleeping
- Fetal acidosis due to hypoxia
- Fetal tachycardia
- Drugs (opiates, benzodiazepines)
- Prematurity
- Congenital heart abnormalities
     
Prolonged deceleration
Shape
- Very wide deceleration
Causes
- Uterine hyperstimulation
- Supine hypotension
- Post-epidural insertion
- Placental abruption
- Ruptured uterus
 
Sinusoidal pattern
Shape
- Smooth, regular, wave-like pattern
- Frequency around 2–5 cycles per minute
- Stable baseline 120–160 bpm
- No variability
Causes
- Fetal hypoxia
- Fetal anaemia
- Fetal/maternal haemorrhage

D&C set
What is this set?
- D&C set
Give two complications
- Cervical lacerations
- Cervical incompetence (recurrent miscarriage)
- Asherman’s syndrome (infertility)
- Uterine perforation
- Infection
- Haemorrhage
- Risk of anaesthesia
- Risk of blood transfusion
 
Tenaculum / Vulsellum
Identify this structure
- Tenaculum / Vulsellum
Give two indications
- Grasp anterior lip of the cervix
- Vaginal operations (e.g., D&C)
- Myomectomy
- Hysterectomy
Give two complications
- Laceration of the cervix
- Infection
- Bleeding
Give two contraindications
- Soft pregnant cervix
- Infection

Uterine sound
Identify this structure
- Uterine sound
Indications
- Determine size, direction, and length of uterus
- Differentiate uterine inversion from submucous fibroid/polyp
- Primary dysmenorrhea assessment
Complications
- Perforation
- Infection
Contraindications
- Suspicion of pregnancy
- Soft uterus (malignancy, infection, molar pregnancy)

Ovum forceps
Identify this structure
- Ovum forceps
Give two indications
- Remove intact separated ovum
- Evacuate uterine contents in D&C
- Remove IUCD and products of conception

Hegar’s dilators
Identify this structure
- Hegar’s dilators
Indications
- Diagnostic:
- Assess cervical incompetence
- Diagnose intrauterine lesions and septa
- Diagnose spasmodic dysmenorrhea
- Therapeutic:
- Cervical stenosis
- Dysmenorrhea
- Drain hematometra or pyometra
- As a step in other operations:
- D&C or evacuation
- Vaginal hysterectomy
- Before insertion/removal of some contraceptive devices
Complications
- Perforation
- Cervical incompetence
- Ascending infection
- Cervical laceration
Contraindications
- Infection
- Viable pregnancy

Cusco’s speculum (Duck’s speculum)
Identify the instrument
- Cusco’s speculum (self-retaining)
Give two indications of usage
- Expose the cervix
- Expose vaginal walls
- Allow application of instruments to the cervix
- Obtain swabs
- Introduce uterine sound
- Insert IUD
- Perform HSG
- Take premenstrual endometrial biopsy
- Take cervical biopsy
One advantage
- Easy to introduce
- Self-retaining
- Adjustable to size of vagina

Anterior vaginal wall retractor
Identify this structure
- Retractor for anterior vaginal wall
Uses
- Exposes the anterior vaginal wall
- Grooved blade directs blood or urine
- Provides space for operative work
Disadvantages
- Assistance is required
- With cystocele, exposure of the cervix is often difficult

Uterine curette
Identify this structure
- Uterine curette
Indications
- Diagnostic curettage:
- Abnormal bleeding (DUB, malignancy)
- Secondary bleeding
- Cervical polyps
- TB endometrium
- Sterility workup (anovulation, non-responsive endometrium)
- Amenorrhea (atrophic endometrium, PCO)
- Therapeutic curettage:
- Non-malignant uterine bleeding
- Dysmenorrhea
- Removal of endometrial polyps
Complications
- Sepsis
- Perforation
- Asherman’s syndrome
- Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Peritonitis

Laparoscopy
What is this procedure?
- Laparoscopy
Give two complications
- Bowel perforation
- Bladder perforation
- Cardiac arrest by fluid overload
- Hyperkalaemia
- Hydrothorax
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Risk of anaesthesia

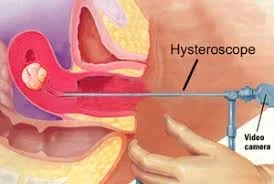
Hysteroscopy
Identify this structure
- Hysteroscope
Give two indications
- Abnormal premenopausal bleeding
- Removal of foreign body (IUD, retained fetal bone)
- Confirmation of abnormal ultrasound findings
- Suspected Müllerian anomalies

Complete molar pregnancy
What do you see?
- Complete mole
Give two complications
- Excessive intraoperative bleeding
- Perforation or atony (possible hysterectomy)
- Persistent trophoblastic disease
- Pulmonary oedema secondary to heart failure (preeclampsia, hyperthyroidism, anaemia, fluid overload)
- Trophoblastic embolus
- DIC
- ARDS
Other tests
- Blood tests: Serum β-hCG, FBC, RFT/electrolytes, LFT, TFT
- Chest X-ray
- Group and save
Management
- Suction evacuation by experienced hands
- Serial β-hCG until negative
- Avoid pregnancy at least 6 months after last negative β-hCG
- Contraception (avoid COCP and IUCD)
Follow-up
- Serial β-hCG for at least 6 months after evacuation
- Pregnancy only after last undetectable β-hCG
- Contraception (avoid COCP)
- After any pregnancy, follow β-hCG

Partial molar pregnancy
Diagnosis
- Partial mole
Note
- Same investigations, management, and follow-up as complete mole

Polycystic ovary (ultrasound appearance)
What do you see?
- Polycystic ovary (not PCOS)
Two other clinical findings
- Obesity
- Infertility
- Hirsutism
- Acne
How to treat (overview)
- Reduce weight; treat acne, hirsutism, and infertility

Cervical cerclage (McDonald)
What is this procedure?
- Cervical cerclage
Give two possible contraindications
- Uterine contractions
- Uterine bleeding
- Chorioamnionitis
- Premature rupture of membranes
- Fetal anomaly incompatible with life
B 
Myomectomy
What is this procedure?
- Myomectomy
Indication
- Removal of symptomatic fibroid in those who have not completed their families
Give two complications
- Bleeding
- Hysterectomy
- Adhesions
- Recurrence
- Infection
- Injury to adjacent tissues
- Anaesthesia complications

Torsion ovarian cyst
What do you see?
- Torsion of ovarian cyst
How to treat
- Laparotomy to reduce torsion or cystectomy

Cystectomy and ovarian cyst complications
Identify this procedure
- Cystectomy
Complications of ovarian cyst
- Torsion
- Bleeding
- Rupture
- Infection (sepsis/peritonitis)
- Pseudomyxoma peritonei
- Malignancy
- Adhesions & intestinal obstruction (and injury)
- Bladder injury

Subdermal implant (Implanon)
Identify this structure
- Subdermal implant (Implanon)
Uses
- Contraception
- DUB
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
- Dysmenorrhoea
- PMS

Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA, Depo-Provera)
Identify this structure
- Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate)
Uses
- Contraception
- DUB
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
- Dysmenorrhoea
- PMS
Give two possible complications
- Weight gain
- Bleeding disturbances
- Mood swings
- Delay in return to fertility
- Breast tenderness
- Acne

Levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG-IUS, Mirena)
Identify this structure
- Mirena (progestogen-releasing intrauterine system; LNG-IUS)
Mention two side effects
- Hormonal: acne, breast tenderness, mood disturbance, headaches
- Others: perforation, expulsion, difficult removal
Benefits / indications
- Contraception
- Reducing heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB)
- Dysmenorrhoea
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
- Protect endometrium against hyperplasia

Intra-abdominal IUD
What do you see?
- Intra-abdominal IUD
Cause
- Perforation
If no device on ultrasound, next step to confirm site
- X-ray

Copper intrauterine device (Cu-IUD)Z
Identify this structure
- Copper IUD
Give two indications
- Contraception
- Dysmenorrhoea
- DUB
- PMS
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
Give two contraindications
- Pregnancy
- DUB (as a contraindication to insertion in evaluation phase)
- PID
- Cervical cancer
- Endometrial cancer
Give two complications of copper IUD
- Pregnancy (failure)
- Pain
- Bleeding
- PID (increased vaginal discharge)
- Perforation
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Expulsion
- Difficult removal
- Actinomyces-like organisms (ALOs)
What do missing threads indicate?
- Pregnancy
- Expulsion
- Perforation

Hirsutism and acne
What do you see?
- Hirsutism and acne
Most likely diagnosis
- PCOS
If she has infertility, how to treat?
- Weight reduction
- Induction of ovulation
Gynaecological Operations
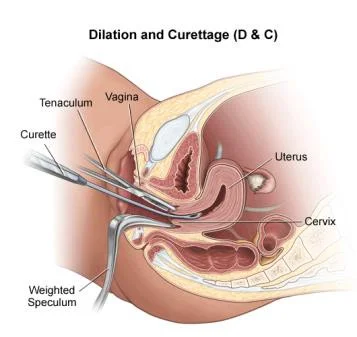
Dilatation And Curettage (D&C)
Indication:
- Miscarriage.
- Endometrial sample.
- Assessment of ovulation.
- IUCD removal.
Instrument:
- Uterine curette
- Uterine sound
- Sims speculum.
- Hegar dilators.
- Tenaculum.
Instruments Used in Gynaecological Examinations

- Metallic Catheter
- Cusco’s Speculum (Duck’s Speculum)
- Sim’s Speculum
- Sim’s Uterine Sound
- Tenaculum
- Hegar’s Uterine Dilator
- Uterine Curette
Steps Involved in Dilatation and Curettage
The technique is outlined in a numbered list:
- Evacuate the bladder
- Anesthesia
- Vaginal speculum & grasp the cervix
- Sounding
- Dilate the cervix
- Curette
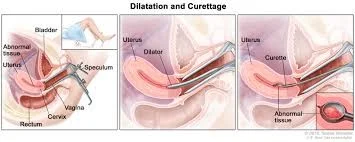
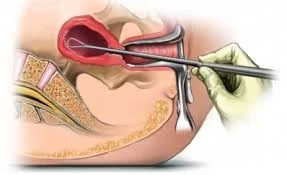
Complications of D&C
-
Cervical lacerations.
-
Cervical incompetence (recurrent miscarriage).
-
Asherman’s syndrome (infertility).
-
Uterine perforation.
-
Infections.
-
Haemorrhage.
-
Risk of anaesthesia.
-
Risk of blood transfusion.
-
Metallic catheter insertion
- For urinary drainage (urine).
-
Speculum insertion (OSCE)
- Technique: insert with blades closed, twist while advancing until fully inserted, then open gently until the cervix is visualized.
- Use a controlled, gentle motion; lubricate if indicated.
-
Tenaculum
- Apply to hold the cervix steady when required (eg. for sounding, instrumentation).
-
Uterine sound
- Purpose: measure the length and direction of the uterus.
- Insert slowly and gently; confirm direction before advancing other instruments.
-
Hegar dilators (progressive dilatation)
- Insert sequentially from smaller to larger sizes to achieve the required dilatation.
- Purpose: allow passage of instruments or evacuation; proceed gradually to reduce cervical trauma.
-
Ovum forceps
- Used to grasp tissue (eg. products of conception or retained material) or remove specimens as indicated.
- Apply gently and confirm secure hold before traction.
-
Curettage (uterine curretage)
- Systematic scraping: anterior wall → lateral walls → posterior wall → contralateral lateral wall.
- Continue until the desired clinical endpoint is reached (eg. bleeding reduces or tissue removal is adequate).
- Perform cautiously to minimize trauma and monitor bleeding.
remove all instruments and unbind speculum
finally send products to histopathology
complications
- perforation
- lacerations
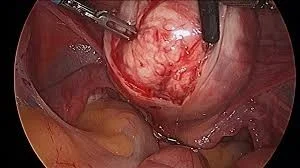
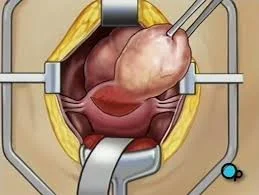
Myomectomy
-
Indications: Removal of symptomatic fibroid in those who do not complete their families.
-
Types:
- Abdominal
- Vaginal
- Hysteroscopic: submucous <5cm
- Laparoscopic: Pedunculated subserous
- Complications:
- Bleeding.
- Hysterectomy.
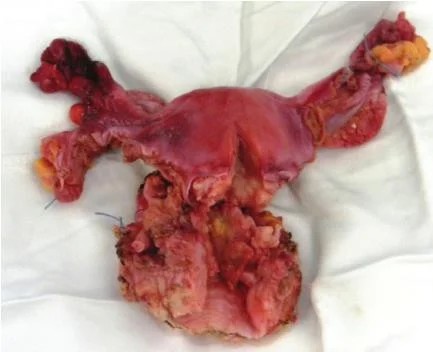
Hysterectomy
Removal of uterus.
Complication:
- Infertility.
- Depression.
Gynaecological Indications for Hysterectomy
- Fibroid.
- Advanced endometriosis.
- Adenomyosis.
- Malignant tumors of the cervix, body, tubes or ovary.
- Recurrent DUB not responding to conservative treatment.
- Prolapse.
- Postmenopausal bleeding.
- Sterilization.
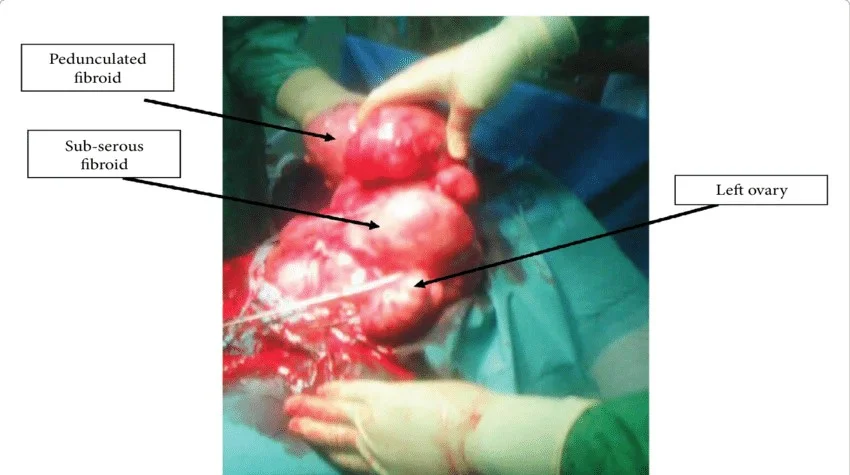
Obstetric Indications for Hysterectomy
- Uncontrolled postpartum haemorrhage.
- Rupture uterus.
- Placenta accreta.
- Invasive mole.
- Couvelaire uterus.
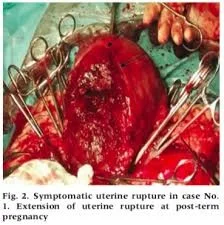
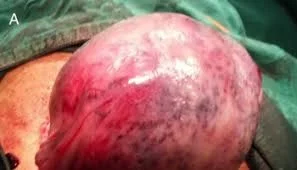
Types of Hysterectomy
- Abdominal
- Vaginal
- Laparoscopic
- Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy (vaginal + laparoscope).
- Caesarean hysterectomy.
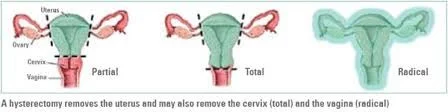 Types of Abdominal Hysterectomy
Types of Abdominal Hysterectomy
- Subtotal: removal of the uterus with preservation of the cervix
- Total: removal of the uterus & cervix
- Radical: removal of the uterus, cervix, parametrial tissue, endopelvic fascia, uterosacral ligaments & pelvic lymph nodes
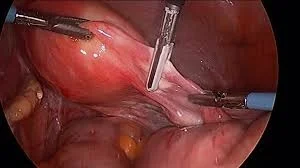
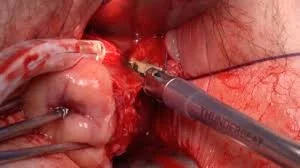 Caesarean Hysterectomy
Removal of the uterus after C.S due to
Caesarean Hysterectomy
Removal of the uterus after C.S due to
- Atonic uterus.
- Postpartum haemorrhage.
- Placenta accreta.
Cervical Cerclage
 Indications
Indications
- (1) Prophylactic (elective). Suspected cervical incompetence. Cerclage at 14 weeks {early miscarriage caused by other factors}.
- (2) Urgent (therapeutic) Asymptomatic women with sonographic evidence of cervical shortening and/or funnelling.
Contraindications
- Uterine contractions.
- Uterine bleeding
- Chorioamnionitis
- Premature rupture of membranes
- Fetal anomaly incompatible with life
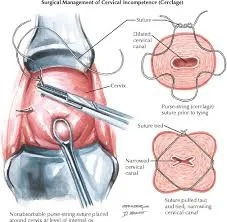
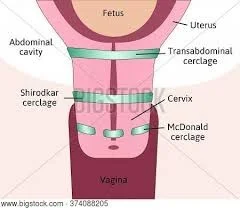
Types of Cervical Cerclage
Mc Donald. Shirodkar. Transabdominal.
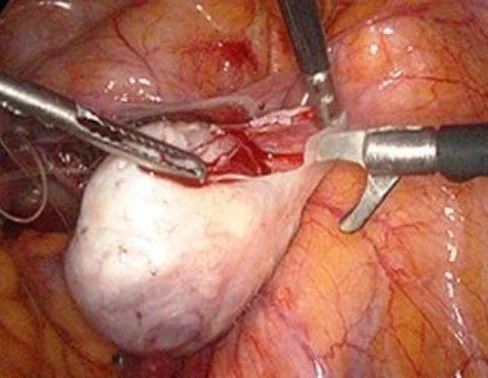
Ovarian Cystectomy
-
Indication:
- Ovarian cyst.
-
Complication:
- Rupture of ovarian cyst.
- Bleeding.
- Adhesion.
- Bladder injury.
- Bowel injury.
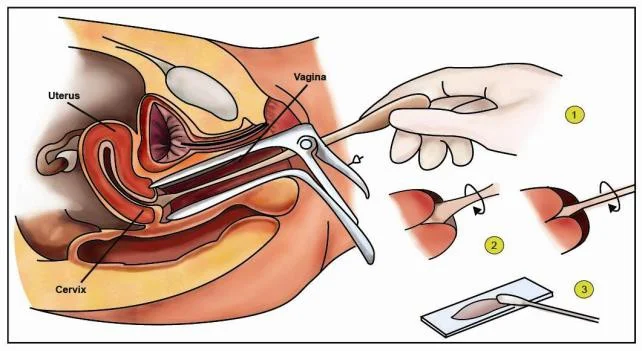
Pap Smear
- Indication: Screening for cervical cancer.
- Complication:
- Infection.
- Failure.
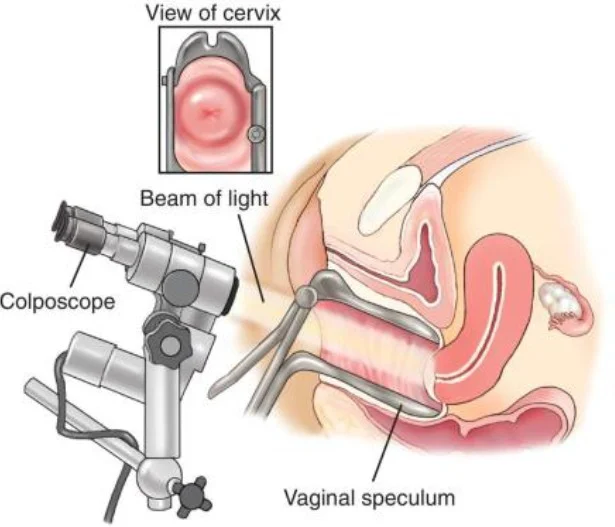
Colposcopy
Indication:
- Abnormal pap smear
- Punch biopsy.
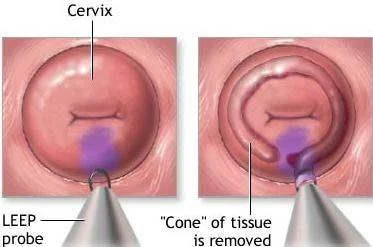
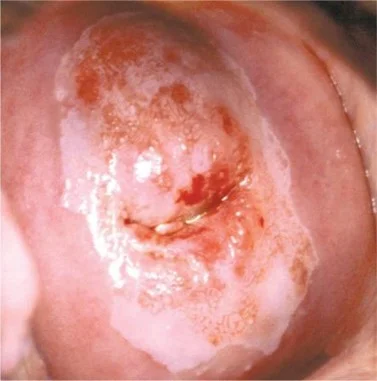
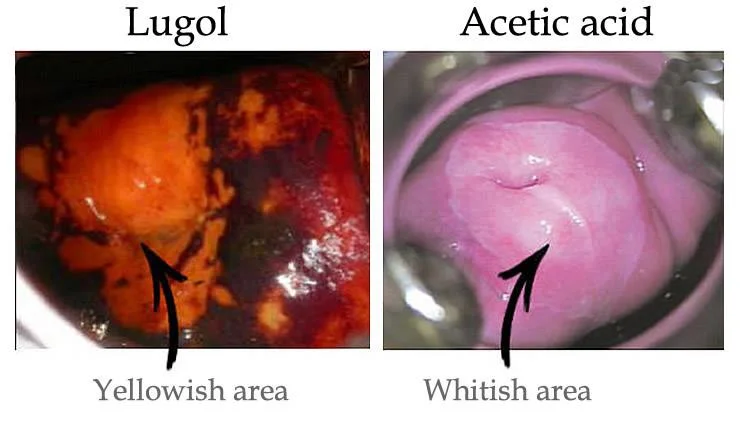
Cone Biopsy
Indication:
- CIN
Under anaesthesia The dye we use in biopsy:
- Acetowhite test:
Acetic acid, abnormal cell will absorb so take the biopsy from the white cell. - Iodine test:
Lugol solution normal cell absorb and become brown because it contains glycogen so take biopsy from non-absorbed cells.
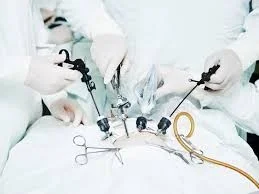
Laparoscopy
- Minimal invasive procedure.
- Diagnostic or therapeutic.
Complications of Laparoscopic ProceduresZ
- Bowel perforation.
- Bladder perforation.
- Cardiac arrest by fluid overload.
- Hyperkalaemia.
- Hydrothorax.
- Bleeding
- Infection.
- Risk of anaesthesia.
Laparoscopic Procedures
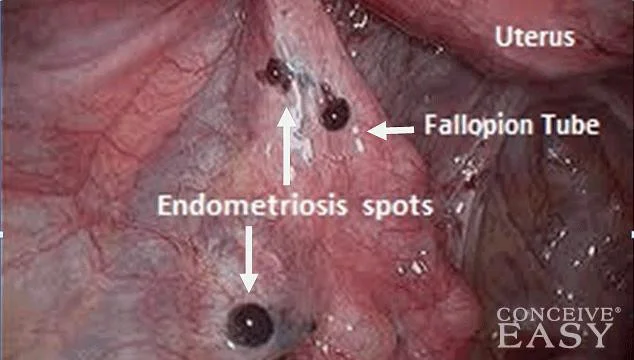 Diagnostic for endometroisis
Diagnostic for endometroisis
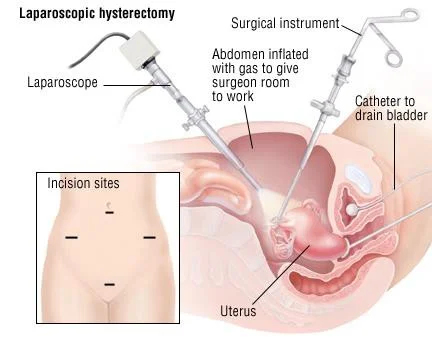 Laparoscopic hysterectomy
Laparoscopic hysterectomy
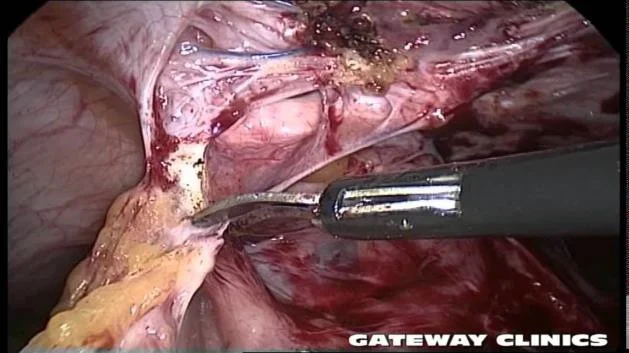 Laprascopic Adhesiolysis
Laprascopic Adhesiolysis
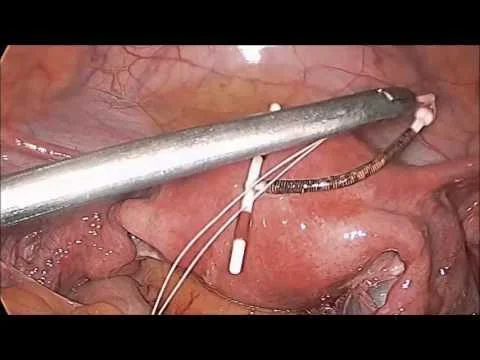 Laparoscopic removal of IUCD
Laparoscopic removal of IUCD
Additional Laparoscopic Procedures
- Laparoscopic ovarian hysterectomy.
- Laparoscopic removal of ectopic pregnancy.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy.
- Laparoscopic drilling for PCOS.
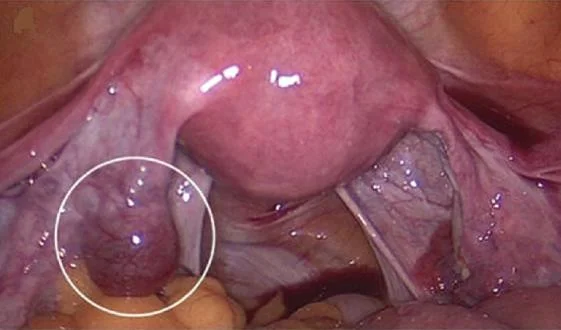 laparoscopic ovarian hysterectomy. laparoscopic removal of ectopic pregnancy
laparoscopic ovarian hysterectomy. laparoscopic removal of ectopic pregnancy
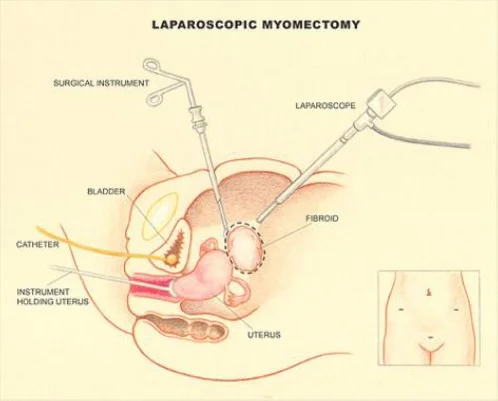 laparoscopic myomectomy
laparoscopic myomectomy
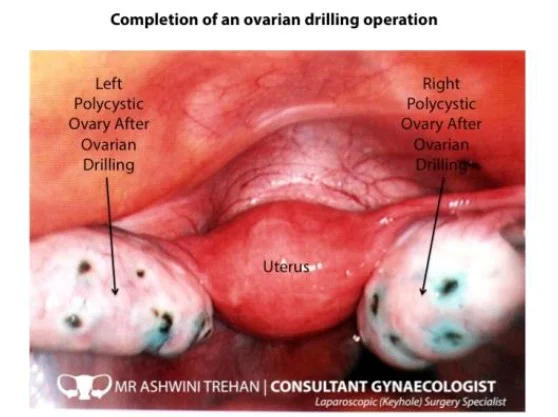 Laparoscopic drilling. PCOS
Laparoscopic drilling. PCOS
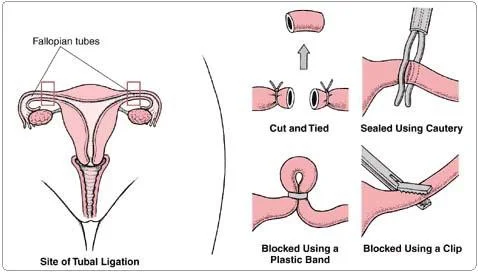
Bilateral Tubal Ligation
Indication: Family planning. Routes:
- Laparotomy
- Laparoscopy
- Hysteroscopic.
Complication:
- Failure.
- Risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Secondary OSPE - OLD
   
Placental Abruption (Abruptio Placentae)
What is this condition?
- Placental Abruption (Abruptio Placentae)
What are the types?
- Concealed
- Revealed
What is the common clinical presentation?
- Painful pervaginal bleeding
What are the causes or risk factors?
- Polyhydramnios
- Previous Abruptio placenta
- Preeclampsia
- Smoking
- Trauma
- Multiple pregnancy
- Hypertension
- Medical disease
What are the complications?
- Maternal: Shock, Death, DIC, Anemia, Risk for surgery, hysterectomy, Risk for blood transfusion
- Fetal: IUGR, IUFD, Cerebral palsy
 
Macrosomia / Preterm Baby
What is this condition?
- Preterm Baby
- Macrosomia
What are the complications to the baby?
- Respiratory distress syndrome
- Jaundice
- Hypothermia
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Shoulder dystocia and nerve injury
- Neonatal hypoglycaemia
- Hyperbilirubinemia
- Hypocalcaemia
- Perinatal asphyxia
What is the most likely disease that complicated the mother during pregnancy?
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
  
Breech Presentation
What is this presentation?
- Breech Presentation (Extended, Flexed, Footling)
What is the absolute indication for Cesarean section?
- Footling Breech (3)
 
Bimanual/Manual Removal of Placenta
What is this procedure?
- Bimanual/Manual Removal of Placenta
If you try it and fail how will you manage?
- Leave it or you may need hysterectomy
 
Pinard Stethoscope/Fetoscope
What is this instrument?
- Pinard Stethoscope/Fetoscope
What are the alternatives?
- Fetoscope
- Cardiotocography (CTG)
- Doppler ultrasound (Sonic aid)
- Naked Ear

Tenaculum Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Tenaculum Forceps
What are the uses?
- To hold fibroid during myomectomy
- To hold cervix for: laparoscopy, hysterosalpingogram, D&C, endometrial sample, IUCD insertion, anterior or posterior repair
- To hold uterus during hysterectomy
What are the complications?
- Injury (cervix, uterus, bladder, vagina, ureter)
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Laceration of the cervix


Intrauterine Device (IUD) / Mirena
What is this instrument/device?
- Intrauterine Device (IUD) / Mirena (hormonal loaded intrauterine device)
Mention two non-contraceptive uses/benefits:
- Treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB)
- Treatment of dysmenorrhea
- Pain associated with endometriosis
- Adenomyosis pain
- Protecting against endometrial hyperplasia
- Conservative management in endometrial carcinoma
What are the complications?
- Failure to fix in place (Expulsion)
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Pregnancy (failure)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Perforation
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Difficult removal
- Actinomyces-like organisms (ALOs)
- ‘Missing’ threads

Ventouse Delivery
What is this procedure?
- Ventouse Delivery
What are the prerequisites?
- Fully dilated cervix
- Ruptured membranes
- Cephalic Presentation
-
36 weeks “term babies”
- Abdomen <1/5th palpable
- Position should be known
- Mother (consent, analgesia, empty bladder, catheter deflated “removed”)
- Trained operator
- Adequate facilities
- Back-up plan
- Anticipate complications
- Someone trained in neonatal resuscitation
What are the complications?
- Trauma of birth canal
- Hematoma
- Caput succedaneum
- Scalp injury/laceration
- Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)
- Mother infection
What are the contraindications?
- Presence of active infection
- Face presentation
What is the flexion point?
- 3 cm anterior to posterior fontanel
    
Twins (Types, Complications)
Name the type of twins for each
- 1: Monochorionic diamniotic
- 2: Monochorionic monoamniotic
- 3: Conjoint twin
What is the mode of delivery for number 3?
- Cesarean section
What is the zygosity of conjoined twins?
- Monozygotic
Basic Types:
- Monozygotic (identical): 1 ovum + 1 sperm
- Division before chorion forms: resembles dizygotic pattern.
- Division after chorion forms: monochorionic diamniotic.
- Division after chorion and amnion form: monochorionic monoamniotic.
- Late division: conjoined twins.
- Dizygotic (fraternal): 2 ova + 2 sperm
- Typically: dichorionic diamniotic.
Complications:
- Twin to twin transfusion syndrome
- Abortion
- Congenital anomaly
- Malpresentation/Malposition
- IUGR/IUFD
- Polyhydramnios
- Maternal: Preeclampsia, Placenta previa, DM, Antepartum hemorrhage, Risk of CS, Risk of post partum hemorrhage

Herpes Simplex Lesion / Genital Herpes
Name of organism causing this lesion:
- Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) or type 2 (HSV-2)
Effect on baby / Neonatal complications:
- Spread of infection to baby
- Eye infection
- Disseminated disease with involvement of multiple major organs
- Central nervous system disease with encephalitis
- Skin, eye, or mouth infection with localized involvement
 

Ectopic Pregnancy
What is this condition?
- Ectopic Pregnancy
How to Manage or treat?
- Medical (methotrexate)
- Surgical (salpingectomy, laparotomy or laparoscopy, salpingostomy)
- Conservative
What are the symptoms?
- Abdominal pain and headache
- Vaginal bleeding
- Nausea, vomiting
- Internal bleeding, hemorrhage
- Shock
- Amenorrhea
 
Lower Limb Edema / Pitting Edema
What you can see:
- Lower Limb Edema / Pitting Edema
Causes in pregnancy:
- Heart Failure
- Preeclampsia (PIH)
- Infection
- Long standing
- Renal diseases
- Liver diseases
 
Lateral Grip (Leopold II)
What is this procedure/manoeuvre?
- Lateral Grip (Leopold II)
What are the uses?
- To identify fetal lie and back
- To detect the fetal back

Tubal Ligation
What is this procedure?
- Tubal Ligation
Mention other types of irreversible or permanent contraception:
- Salpingectomy
- Hysterectomy
- Vasectomy
 
Hydatidiform Mole / Molar Pregnancy
Identify the picture/diagnosis?
- Hydatidiform mole / Partial molar pregnancy
What is the finding on Pelvic US?
- Snow storm appearance
Mention two possible complications?
- Excessive intraoperative bleeding (Perforation or atony)
- Hysterectomy
- Persistent trophoblastic disease
- Pulmonary oedema 2ry to heart failure
- Associated preeclampsia
- Associated Hyperthyroidism
- Associated anaemia
- Trophoblastic embolus (DIC or ARDS)
How are you going to follow the patient?
- Follow up with quantitative beta HCG for 1 year.
- Effective contraception.
What is the first site for metastasis?
- Lung

Amniocentesis
Identify the procedure?
- Amniocentesis
Give indications for this procedure:
- Karyotyping (Fetal karyotyping)
- Amnioreduction
- TORCH screen
- Diagnosis of congenital abnormality/genetic disease
- Assess of lung maturity and RH isoimmunization
- Therapeutic for polyhydramnios
What are the risks/complications?
- Abortion if done early
- Injury to fetus
- Infection
- RH isoimmunization
- Preterm labour
- Rupture membrane
- Abruptio placenta

Nitrazine Test
Name this test?
- Nitrazine test (Nitrazine blue)
Used for?
- To detect Premature Rupture of Membranes (PROM)
What is a positive result?
- Blue color (PH > 6 “alkaline”) indicating amniotic fluid.
 
Ducks/Cusco’s/Couscous Vaginal Speculum
Name this instrument?
- Ducks/Cusco’s/Couscous speculum
Give two indications/uses?
- Pap smear
- Visualize cervix and vagina
- Insertion/removal of IUD
- Endometrial sample
- Colposcopy
Advantages:
- Self retain
Disadvantages:
- Discomfort
- Can’t assess anterior & posterior vaginal wall

Multiple Pregnancy
Give the diagnosis of this US?
- Multiple pregnancy

Uterine Curette
Name the instrument?
- Uterine curette
Give uses:
- Uterine sample
- Evacuation of abortion, molar or remaining placenta
Give complications/side effects:
- Uterine perforation
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Asherman syndrome (complication of D&C)
 
Name the abnormality?
Give one complication?

Cesarean Section
Name the procedure?
- Cesarean section
Give two complications?
- Heavy bleeding
- Infection

Cystectomy
Name the procedure?
- Cystectomy
Give two complications?
- Torsion
- Infection
 
Cervical Cerclage
Name the procedure?
- Cervical cerclage
Give three contraindications?
- PROM
- Uterine bleeding
- Uterine contractions
 
Laparoscopy with fibroid
Name this procedure?
- Laparoscopy
Give one indication?
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Uterine fibroid
 
Artificial Rupture of Membrane (ARM)
Name this procedure?
- Artificial rupture of membrane (ARM)
Give two complications?
- Injury to the fetus
- Bleeding
- Cord prolapse
- Infection

CTG (Cardiotocography) - Variable Decelerations
What is the finding of this CTG?
- Variable decelerations
What is the cause?
- Cord compression

Striae Gravidarum (Stretching Marks)
What you see in the picture?
- Striae gravidarum (Stretching marks)
What is the cause?
- Over-stretching of the abdomen
What are other physiological skin changes?
- Chloasma
- Linea nigra

Removal of Implanon
What you see in this picture?
- Removal of implanon
 
Strawberry Cervix
What do we name this finding?
- Strawberry cervix
What is the causative organism?
- Trichomonas vaginalis

Premature Baby
What is your diagnosis?
- Premature baby
Give two possible complications
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
- Jaundice
- Hypothermia
- ICH (Intracranial Hemorrhage)
Give one important cause
- Overdistention of uterus
- Infections
- Cervical incontinence
 
Outlet/Forceps Delivery
What is the name of the above procedure?
- Outlet forceps / Forceps delivery
Mention prerequisites?
- Full dilated cx
- Empty bladder
- Cephalic presentation
- Anaesthesia
- Expertise person
- Fully dilated and effaced cervix
What is the most common indication for this procedure?
- Abnormal fetal CTG
 
Unicornuate Uterus
What is the uterine abnormality in this picture?
- Unicornuate uterus
What is the commonest complication of this anomaly?
- Miscarriage / Recurrent pregnancy loss (Abortion)
- Premature delivery
- Infertility
- Placenta previa
- Abnormal presentation/lie
- IUGR
Cause of this anomaly?
- During development, one of the mullerian ducts doesn’t form
 
Perineal Tear
What is the degree of this tear?
- Second degree / Third degree
What muscles are involved in a second degree tear?
- Bulbospongiosus
- Transverse perineal muscle
What examination is needed after repair of a third degree tear?
- PR (Per Rectal) examination
How to prevent it?
- Moisturizers
- Controlled weight gain
- By squeezing the perineum during crowning

Hirsutism
What is the diagnosis?
- Hirsutism
What is the treatment?
- Treat the cause, hair removal
  
Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
What is this set/procedure?
- Dilation and curettage (D&C) set
What are two complications?
- Perforation
- Cervical incompetence
- Infection
- Bleeding
What are the indications?
- Evacuation of abortion
- Endometrial sample

Abdominal/Pelvic Ultrasound
What is this test?
- Abdominal/Pelvic ultrasound
What are the uses?
- Estimate gestational age
- Diagnose ovarian pathologies
- Know where is the pregnancy
- Viability of pregnancy
- Multiple or single pregnancy
- Monitoring for growth
- Assessment of gestational age
- For placental location
- For amniotic fluid

Caput Succedaneum
What is the diagnosis?
- Caput succedaneum
What are two causes?
- Obstructed labor
- Ventouse delivery

Laparoscopic Set
What is this set?
- Laparoscopic set
What are two complications?
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Bowel injury

Polycystic Ovary (PCO) / Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
What is the diagnosis?
- Polycystic ovary / Polycystic ovary syndrome
What are two symptoms?
- Hirsutism
- Acne
- Obesity / Weight gain
- Infertility
- Irregular menstruation
- Amenorrhea
- Risk of diabetes
Mention 1 option of treatment?
- Combined oral contraceptive pills
- Ovarian drilling (it is out of mode now)
- Laparoscopic ovarian drilling

Fundal Height Measurement
What is this procedure?
- Fundal height measurement with tape
What is the purpose?
- As a step in examination of pregnant female to confirm if the fundal height meet the period of amenorrhea
  
Umbilical Cord Prolapse
What is the diagnosis/condition?
- Umbilical cord prolapse
What is the treatment?
- Emergency cesarean section
- Knee-chest position maybe considered
What are the causes?
- Fetal: cord abnormalities, prematurely
- Pregnancy: PPROM, multiparity
- Malpresentation
- High head
- Cephalopelvic disproportion
- Rupture membrane
- Polyhydramnios
- Multiple pregnancy
- Abnormal lie

Down Syndrome
What is the diagnosis?
- Down syndrome trisomy 21
What are two screening tests?
- Nuchal translucency by US
- Triple or quadrable test
What is a diagnostic test for this trisomy?
- Amniocentesis

Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome
What is this sign?
- T sign (amniotic membrane)
What is the associated condition?
- Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (more in mono chorionic mono amniotic twins)


Uterine Fibroids
What is the location of these fibroids?
- Intramural
In general, which of the following is NOT a common symptom of uterine fibroids?
- Amenorrhea
 
Endometriosis
The diagnosis is:
- Endometriosis
One option of its treatment is:
- Combined oral contraceptives
- Surgical cauterization
- Danazol
What is the characteristic feature?
- Chronic abdominal pain

Rectocele
The diagnosis is:
- Rectocele
One option of its treatment is:
- Posterior Repair
 
Montgomery’s Gland
The breast nodule represents the following:
- Montgomery’s gland
It is used to:
- Reassuring
What is its cause?
- Normal physiological changes of the areola in pregnancy

Mayo scissor
This device is:
- Mayo scissor
It is used for:
- Cutting through tissues like rectus sheath
Side effects:
- Blood vessels injury
- Bladder or bowel injury
- Infection
- Bleeding

Late Decelerations
This cardiotocography shows the following decelerations:
- Early decelerations
The cause of these decelerations is:
- Head Compression

Granulosa Cell Tumor
This histopathology shows the following:
- psamomma body
The appropriate diagnosis is:
- Serous cyst adenocarcinoma of the ovary

Fetal scalp electrode
This device is:
- Fetal scalp electrode
It is used to:
- Monitor fetal Heart rate during labor
Side effects:
- Fetal injury
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Maternal injury to cervix
Prerequisites:
- Cephalic presentation
- Rupture of membrane
- Cervix dilated


Uterine sound
This device is:
- Uterine sound
It is used for:
- Uterine cavity measurement
- To asses direction for uterus (whether uterus anteverted or retroverted)
Side effects:
- Uterine perforation
- Bleeding
- Infection

Hysterosalpingogram
This radiological test is known as:
- Hysterosalpingogram
This radiological test shows:
- Unicornuate uterus with patent fallopian tube

Monopolar Cautery
What is this instrument?
- Monopolar Cautery
What are the uses?
- To control small bleeding
- To cut
What are the side effects?
- Bladder and bowel burn injury

Sims Vaginal Speculum
What is this instrument?
- Sims Vaginal Speculum
What are the uses?
- For prolapse
- Exposure for vagina for: cerclage, hysteroscopy
What are the advantages?
- Assist ant and post vaginal tissue
- Less discomfort in comparison with cusco’s spec
What are the disadvantages?
- Not self retain

Chorionic Villus Sampling
What is this procedure?
- Chorionic villus sampling
What are the uses?
- Fetal karyotype
- Fetal genetic study
What are the complications?
- Infection
- Abortion
- Bleeding
 
Spina Bifida
What is this condition?
- Spina bifida
What are the causes?
- Folic acid deficiency
What is the treatment?
- Surgical repair
If this baby has hydrocephaly what are the usual ultrasound features of the brain?
- Banana sign
- Enlarged ventricular system

Laprascopic Ovarian Cystectomy
What is the indication for this procedure?
- Ovarian cyst
  
Turner Syndrome
What is this syndrome?
- Turner syndrome
What are the features?
- Webbed neck
- Short stature
What is the chromosomal abnormality?
- 45XO
What is the phenotype?
- Female

Needle Holder
What is this instrument?
- Needle Holder
What are the uses?
- To hold needle for suturing
What are the side effects?
- Infection
- Injury to bladder or rectum

Bandage Scissors
What is this instrument?
- Bandage Scissors
What are the uses?
- To cut lower uterine segment during C-section
- To cut episiotomy
What are the side effects?
- Fetal injury
- Anal sphincter injury
- Blood vessels injury
- Bladder and bowel injury

Metzenbaum Scissors
What is this instrument?
- Metzenbaum Scissors
What is the use?
- To cut soft tissue: peritoneum & thin adhesions
What are the side effects?
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Injury to adjacent: artery, ureter

Suture Removal Scissors
What is this instrument?
- Suture Removal Scissors
What are the uses?
- For cutting the suture
What are the side effects?
- Infection
- Bleeding

Ovum Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Ovum Forceps (Tissue Forceps)
What are the uses?
- Evacuation of tissue
- Holding it with gauze to clean bleeding
- Disinfection the abdomen with iodine in surgery
What are the side effects?
- Risk for uterine perforation
- Bleeding
- Infection

Artery Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Artery forceps
What are the uses?
- For controlling bleeding and for the retraction of tissues, skin
What are the side effects?
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Injury to blood vessels, bowel or bladder
 
Tooth Tissue Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Tooth Tissue Forceps
What is the use?
- To hold tough tissue: skin, rectus sheaths, ligaments
What are the side effects?
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Injury to blood vessels, bowel or bladder

Non Tooth Tissue Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Non Tooth Tissue Forceps
What are the uses?
- For holding soft tissue like blood vessels, fascia
What are the side effects?
- Infection
- Injury to blood vessels or bowel or bladder

Vulsellum Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Vulsellum Forceps
What are the uses?
- To hold the cervix during vaginal hysterectomy, evacuation
What are the side effects?
- Injury to cervix or bladder
- Infection

Allis Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Allis Forceps
What are the uses?
- To hold tough tissue like vaginal vault during hysterectomy
What are the side effects?
- Injury to bladder or bowel
- Infection

Kockers Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Kockers Forceps
What is the use?
- To hold tough tissue: rectus sheath during CS, TAH, any laparotomy (Not use for holding thick lig and thick adhesion; causes tear in ligaments)
What are the side effects?
- Injury to bladder, ureter, bowel
- Infection
- Bleeding

Green Armytage
What is this instrument?
- Green Armytage
What are the uses?
- To hold lower uterine segment during uterine suture in CS
- Or control uterine bleeding
What are the side effects?
- Bladder or bowel injury
Note: Ovum and Allis and Tenaculum forceps have the same use:
- Hold ant lip of cervix for evacuation (abortion)
- IUCD insertion
- Laparoscopy
- During anterior repair
- During Post repair
- Vaginal hysterectomy
- To hold fibroid, Or hold uterus during hysterectomy
Extra use for Ovum forceps:
- Use for evacuation of fetal tissue (abortion) or to clean bleeding of surgical field or area of surgery
**Complications:
-
**
-
Cervical Injury
-
Bladder injury
-
Abdominal wall injury
-
Blood vessels injury
-
Uterine perforation

Hegars Dilator
What is this instrument?
- Hegars Dilator
What are the uses?
- To dilate cervix for laparoscopy
- Hysteroscopy
- Uterine sample
- D&C
What are the side effects?
- Uterine perforation
- Cervical injury
- Infection
- Bleeding

Metal Catheter
What is this instrument?
- Metal Catheter
What are the uses?
- To empty bladder (single use in OR)
What are the side effects?
- Urethral injury
- Infection
- Bladder injury

Amniohook
What is this instrument?
- Amniohook
What are the uses?
- To rupture the amniotic membrane during labor
What are the side effects?
- Baby injury

Obstetric Forceps
What is this instrument?
- Obstetric Forceps
Indications:
- Failure to advance in second stage
- Maternal conditions where prolonged expulsive efforts may be detrimental
- Fetal distress in the second stage
- Prolapse of the cord in the second stage
Uses:
- Vaginal delivery
- Cesarean section
Side effects:
- Facial palsy
- Post partum hemorrhage
- Infection

Bipolar Cautery
What is this instrument?
- Bipolar Cautery
What are the uses?
- To control bleeding during surgery
- For tubal ligation during sterilization
Advantage:
- Safer than monopolar
Side effects:
- Bladder and bowel burn injury

Foley’s Catheter
What is this instrument?
- Foley’s Catheter
What are the uses?
- Used for long standing evacuation
- Empty bladder
- Monitor input & output
Side effects:
- Ureter injury
- UTI

Sonicaid Doppler
What is this instrument?
- Sonicaid Doppler (US Doppler)
What are the uses?
- To check Fetal heart In OPD
Advantages:
- Safe
- Easy

Vaginal Contraceptive Ring
What is the name of this instrument?
- Vaginal contraceptive ring
Write one uses and one disadvantage for it?
- Use: As hormonal barrier contraceptive for family planning
- Disadvantage: Vaginal discomfort or irritation
 
Genital Warts
What is the name of this lesion?
- Genital warts
What is the cause?
- Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
Treatment?
- Podophyllin (contraindicated in pregnancy)
- Or surgical excision

Face Presentation
What is the name of this presentation?
- Face presentation
Write one of its causes and one of its complication?
- Causes: Grand multiparity, Multiple gestations, Fetal malformations, Prematurity or low birth weight, Cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD), Macrosomia, Multiple nuchal cords, Contracted maternal pelvis, Previous C-section
- Complications: Facial and skull trauma and swelling, prolonged labor, fetal compromise, abnormal fetal heart rate patterns
 
Bicornuate Uterus
What is this anomaly?
- Bicornuate uterus
Write two pregnancy complications?
- Abortion
- Preterm labor
- Infertility
- Obstetric complication
- Recurrent abortion
- Placenta previa
- Abnormal presentation/lie
- IUGR

Omphalocele
What is the diagnosis?
- Omphalocele
Write the site and the treatment?
- Site: Umbilicus
- Treatment: Surgical repair

Dichorionic diamniotic twins with blighted ovum
Description:
- One started to grow and the other is a blighted ovum.

Missed IUD
Name this test?
- Pelvic X ray
What did you see?
- Missed IUCD (Uterine perforation)
How are you going to remove it?
- Surgery either open or laparoscopy
 
Didelphys Uterus
Name this test?
- Hysterosalpingogram
What are the findings?
- Double uterus
- Double cervix
- Blocked RT tube
- Patent LT tube
What is the diagnosis?
- Didelphys and blocked RT tube
Mention 2 presentations of this patient?
- Infertility and recurrent abortion
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Preterm labour
- IUGR
- Placenta previa
- Malpresentation and malposition

Arcuate Uterus
Name this test?
- Hysterosalpingogram
What is the finding?
- Arcuate uterus and Bilateral tubal block
What is the characteristic symptom or the complaint patient comes with?
- Infertility

Calcified Fibroid
What is this?
- Pelvic X ray
What is finding?
- Prosthetic hip replacement
- Calcified fibroid

Multiple Subserosal Fibroid
Name this procedure?
- Laparoscopy
What is the diagnosis?
- Multiple subserosal fibroid
Mention 2 options of treatment?
- Myomectomy or hysterectomy
- Uterine embolization
Mention 2 symptoms she may present with?
- Menorrhagia
- Abdominal pain
- Abnormal irregular menstruation
- Infertility
- Recurrent abortion
- Placenta previa
- Abnormal presentation/lie (Breech)
- Pressure symptoms (urine retention and incontinence, bowel constipation)

Simple Ovarian Cyst
What is this?
- Simple ovarian cyst
Treatment?
- Ovarian cystectomy (abdominal or laparoscopy)

Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst
This?
- Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Complications?
- Rupture
- Torsion
Treatment?
- Ovarian cystectomy (abdominal or laparoscopy)

Evacuation
Name this procedure?
- Evacuation
Mention 1 indication?
- Incomplete abortion
- Molar pregnancy
Mention 2 complications?
- Uterine perforation
- Infection
- Risk of anesthesia
- Risk for Asherman syndrome
 
Simple Follicle
What is this?
- Simple follicle
What is the cause?
- Ovulation
Treatment?
- Reassurance

4D US
This?
- 4D US

Cordiocentesis
Name this procedure?
- Cordiocentesis
Indication?
- Diagnosis of congenital abnormality
- Diagnosis of genetic disease
- Diagnosis of RH isoimmunization
- Diagnosis of infection to baby
- Diagnosis of anemia
The risk is?
- Injury to fetus
- Infection
- RH isoimmunization
- Preterm labour
- Rupture membrane
- Abruptio placenta
- Fetal distress
- Cord hematoma

Teratoma
This is?
- Teratoma

Pap Smear
This is?
- Pap smear
Indication?
- Screening for cervical cancer

Contraception
This?
- Contraception
Mention one use?
- Contraception
- Polycystic ovary
- Regulation of menstruation
- Treatment of fibroid
- Endometriosis
Complication?
- Acne
- Obesity
- Mood swing
- Nausea, vomiting
- Thromboembolism
- Breast cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Headache, migraine
- Irregular bleeding