Table of Contents
Contraceptive Methods
Overview of Contraception
World Contraception Day
It’s your life, It’s your future
Contraceptives









- Correct use of effective methods of contraception can prevent most unintended pregnancies.
- Unintended pregnancies lead to
delayed or no antenatal care
Abortion attempt.

Importance of Contraception
Over 200 million women worldwide would like to avoid a pregnancy, but are not using an effective method of contraception.
This is due to:
- a lack of supplies.
- cultural.
- political barriers.
- poor quality of services.




Contraceptive Targets in Female Reproductive Tract
- No methods are 100% effective at preventing pregnancy.
- The effectiveness of a method depends on
- mechanism of action.
- correct and consistent use.
- Compliance depends on:
- acceptability of the method.
- and tolerability (S/E).
Ideal Contraceptive
- Safe
- Effective
- acceptable
- reversible
- inexpensive
- long lasting
- require no or little medical supervision
Factors Influencing Contraceptive Choice
- A woman’s choice of contraception is just as likely to be based upon information from:
- media.
- friends.
- family,
- Health care professional.
Major factors that limit their uptake.
- Myths
- misconceptions : among women and health providers.
Characteristics of the User determining risk of pregnancy
- Compliance.
- age (reducing fertility in late 30s).
- and frequency of intercourse.
Determinants of Contraceptive Method Acceptability
- Personal characteristics (e.g. age).
- Fertility intentions.
- Perceptions of effectiveness.
- Perceptions of safety.
- Fear of side-effects.
- Familiarity.
- Experience of others.
- Ease of use and of access.
- Need to see a health professional.
- Intrusiveness.
- Non-contraceptive benefits.
Practical Prescribing
- Women considering using a particular method of contraception require clear, accurate information
- What a woman needs to know before starting a method of contraception
- How to use the method (pill, patch or ring) and what to do when misused (e.g. missed pill)
- Typical failure rates
- Common side-effects
- Health benefits
- Fertility return on stopping
- When she requires review
Effectiveness of Contraceptive Methods
Percentage of Women Experiencing an Unintended Pregnancy Within the First Year of Use
| Method | Typical use % | Perfect use % |
|---|---|---|
| No method | 85 | 85 |
| Fertility awareness-based method | 24 | 0.4-0.5 |
| Male condom | 18 | 2 |
| Female diaphragm | 12 | 6 |
| Progesterone-only pills | 9 | 0.3 |
| Combined hormonal contraceptive | 9 | 0.3 |
| Progesterone-only injectable | 6 | 0.2 |
| Cu-IUD | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| LNG-IUS | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Progesterone-only implant | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Female sterilization | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Vasectomy | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Mechanism of ActionZ
The efficacy of a method depends on its mechanism of action
-
Prevent ovulation:
- Combined hormonal methods (pill, patch and vaginal ring).
- Progestogen-only injectables.
- Progestogen-only implant (Nexplanon®).
- Oral emergency contraception.
- Lactational amenorrhoea.
-
Prevent sperm reaching the oocyte:
- Female sterilization.
- Male sterilization (vasectomy).
-
Prevent an embryo implanting in the uterus:
- Cu-IUD (Intra Uterine Copper Device).
- LNG-IUS. (Mirena).
-
Allow sperm into the vagina but poison them: spermicides.
-
Allow sperm into the vagina but block further passage:
- Cervical diaphragm & cervical cap.
- One of the mechanisms of action of progestogens.
-
Prevent sperm entering the vagina:
- male and female condoms;
-
avoid sex during the fertile time of the cycle:
Route of Administration of Contraceptive & Duration
| Route of currently available contraceptive | Duration |
|---|---|
| Oral CHC and progesterone | 24 hours |
| Transdermal CHC | 7 days |
| Vaginal ring CHC | 21 days |
| Progesterone-only injectable | 14 days (or 3 months for depot medroxyprogesterone acetate) |
| Progesterone-only implant(sub cutaneous ) | 3 years |
| Cu-IUD(intrauterine). | 3 years , 5 years , 10 years or more . |
| LNG-IUD(intrauterine). | 3 years , 5 years or more |
Non-Contraceptive Health Benefits of Contraceptives
| Method | Benefit against |
|---|---|
| Barrier methods (condoms) | protect against sexually transmitted infections |
| LNG-IUS (52 mg) | * Heavy menstrual bleeding * Endometriosis * Adenomyosis * Dysmenorrhoea * Endometrial protection * Simple hyperplasia |
| Combined hormonal contraception | * Heavy menstrual bleeding * Irregular menses * Hirsutism * Acne * Premenstrual syndrome * Reduces risk of ovarian cancer * Reduces risk of endometrial cancer |
| Progestogen-only injectable (depot medroxyprogesterone acetate) | * Heavy menstrual bleeding * Endometriosis * Dysmenorrhoea |
Methods of Contraception
Natural methods. Barrier methods Long acting reversable contraceptives :
- Implant
- Intra uterine device (IUD)
Hormonal contraceptives :
- Pill
- Depo Provera injection
Barrier methods : such as condoms Permanent contraceptives :
- Vasectomy
- Tubal ligation.
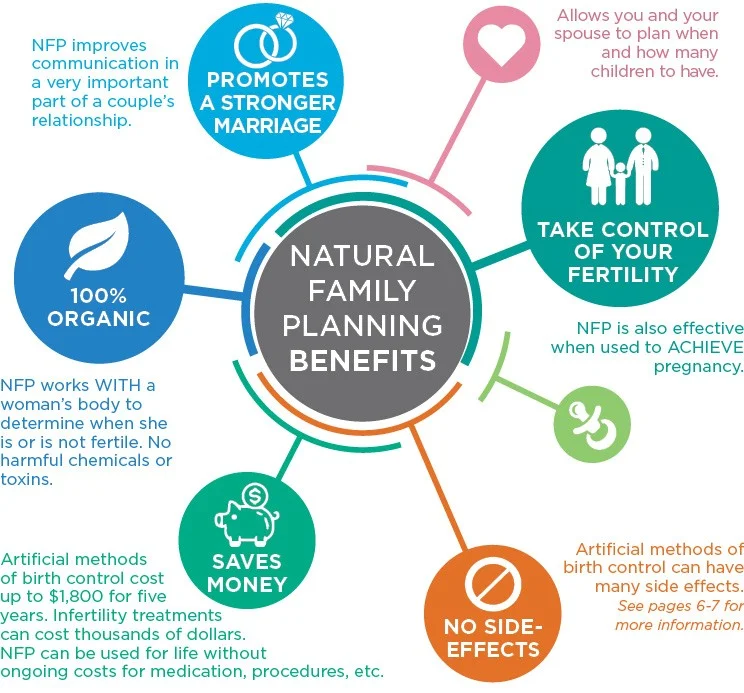
Natural Family Planning
- Calendar or rhythm method or safe period.
- Cervical mucus method
- Basal body temperature method.
- Breastfeeding is an effective (98%) temporary method of contraception only if :
- Lactational amenorrhoea
- & exclusive breastfeeding
- & infant is under 6 months old.