Gynaecological Operations
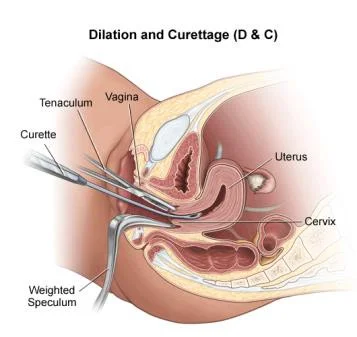
Dilatation And Curettage (D&C)
Indication:
- Miscarriage.
- Endometrial sample.
- Assessment of ovulation.
- IUCD removal.
Instrument:
- Uterine curette
- Uterine sound
- Sims speculum.
- Hegar dilators.
- Tenaculum.
Instruments Used in Gynaecological Examinations

- Metallic Catheter
- Cusco’s Speculum (Duck’s Speculum)
- Sim’s Speculum
- Sim’s Uterine Sound
- Tenaculum
- Hegar’s Uterine Dilator
- Uterine Curette
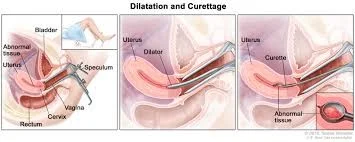
Steps Involved in Dilatation and Curettage
The technique is outlined in a numbered list:
- Evacuate the bladder
- Anesthesia
- Vaginal speculum & grasp the cervix
- Sounding
- Dilate the cervix
- Curette
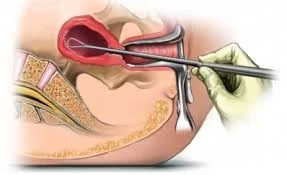
Complications of D&C
-
Cervical lacerations.
-
Cervical incompetence (recurrent miscarriage).
-
Asherman’s syndrome (infertility).
-
Uterine perforation.
-
Infections.
-
Haemorrhage.
-
Risk of anaesthesia.
-
Risk of blood transfusion.
-
Metallic catheter insertion
- For urinary drainage (urine).
-
Speculum insertion (OSCE)
- Technique: insert with blades closed, twist while advancing until fully inserted, then open gently until the cervix is visualized.
- Use a controlled, gentle motion; lubricate if indicated.
-
Tenaculum
- Apply to hold the cervix steady when required (eg. for sounding, instrumentation).
-
Uterine sound
- Purpose: measure the length and direction of the uterus.
- Insert slowly and gently; confirm direction before advancing other instruments.
-
Hegar dilators (progressive dilatation)
- Insert sequentially from smaller to larger sizes to achieve the required dilatation.
- Purpose: allow passage of instruments or evacuation; proceed gradually to reduce cervical trauma.
-
Ovum forceps
- Used to grasp tissue (eg. products of conception or retained material) or remove specimens as indicated.
- Apply gently and confirm secure hold before traction.
-
Curettage (uterine curretage)
- Systematic scraping: anterior wall → lateral walls → posterior wall → contralateral lateral wall.
- Continue until the desired clinical endpoint is reached (eg. bleeding reduces or tissue removal is adequate).
- Perform cautiously to minimize trauma and monitor bleeding.
remove all instruments and unbind speculum
finally send products to histopathology
complications
- perforation
- lacerations
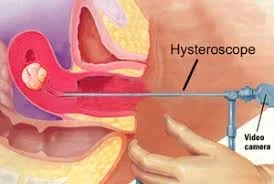
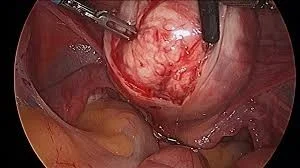
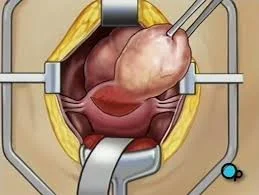
Myomectomy
-
Indications: Removal of symptomatic fibroid in those who do not complete their families.
-
Types:
- Abdominal
- Vaginal
- Hysteroscopic: submucous <5cm
- Laparoscopic: Pedunculated subserous
- Complications:
- Bleeding.
- Hysterectomy.
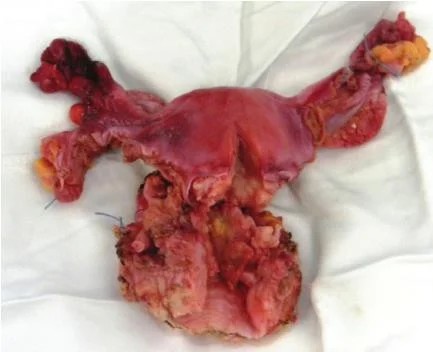
Hysterectomy
Removal of uterus.
Complication:
- Infertility.
- Depression.
Gynaecological Indications for Hysterectomy
- Fibroid.
- Advanced endometriosis.
- Adenomyosis.
- Malignant tumors of the cervix, body, tubes or ovary.
- Recurrent DUB not responding to conservative treatment.
- Prolapse.
- Postmenopausal bleeding.
- Sterilization.
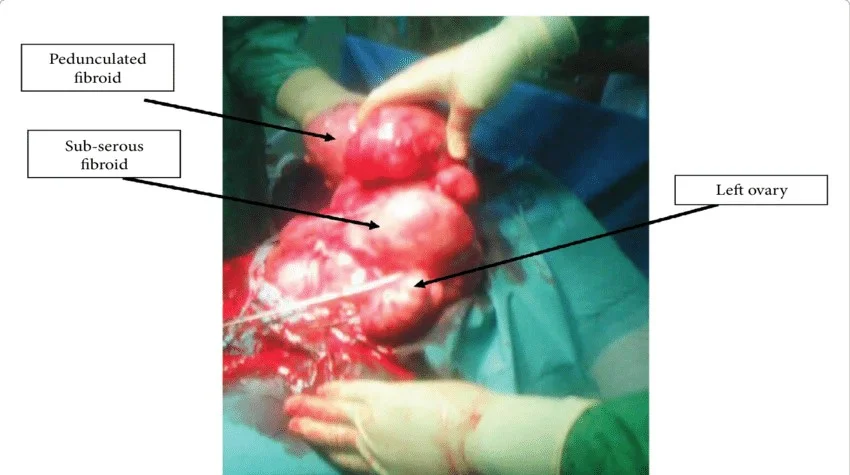
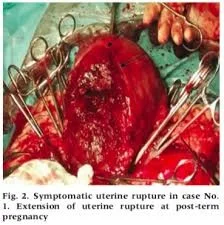
Obstetric Indications for Hysterectomy
- Uncontrolled postpartum haemorrhage.
- Rupture uterus.
- Placenta accreta.
- Invasive mole.
- Couvelaire uterus.
Types of Hysterectomy
- Abdominal
- Vaginal
- Laparoscopic
- Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy (vaginal + laparoscope).
- Caesarean hysterectomy.
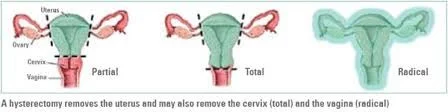 Types of Abdominal Hysterectomy
Types of Abdominal Hysterectomy
- Subtotal: removal of the uterus with preservation of the cervix
- Total: removal of the uterus & cervix
- Radical: removal of the uterus, cervix, parametrial tissue, endopelvic fascia, uterosacral ligaments & pelvic lymph nodes
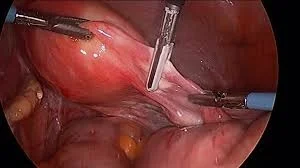
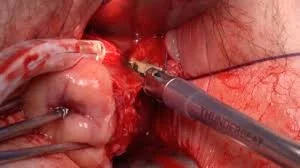 Caesarean Hysterectomy
Removal of the uterus after C.S due to
Caesarean Hysterectomy
Removal of the uterus after C.S due to
- Atonic uterus.
- Postpartum haemorrhage.
- Placenta accreta.
Cervical Cerclage
 Indications
Indications
- (1) Prophylactic (elective). Suspected cervical incompetence. Cerclage at 14 weeks {early miscarriage caused by other factors}.
- (2) Urgent (therapeutic) Asymptomatic women with sonographic evidence of cervical shortening and/or funnelling.
Contraindications
- Uterine contractions.
- Uterine bleeding
- Chorioamnionitis
- Premature rupture of membranes
- Fetal anomaly incompatible with life
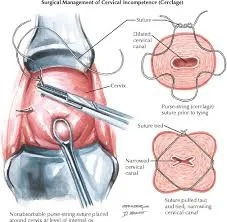
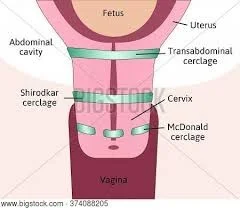
Types of Cervical Cerclage
Mc Donald. Shirodkar. Transabdominal.
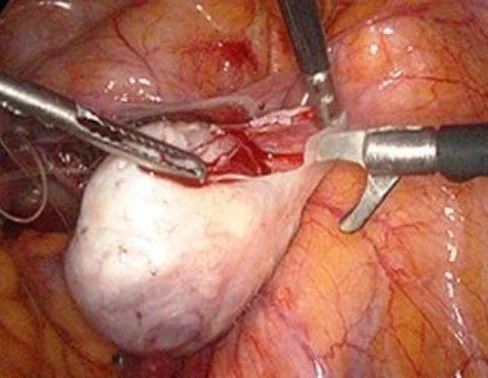
Ovarian Cystectomy
-
Indication:
- Ovarian cyst.
-
Complication:
- Rupture of ovarian cyst.
- Bleeding.
- Adhesion.
- Bladder injury.
- Bowel injury.
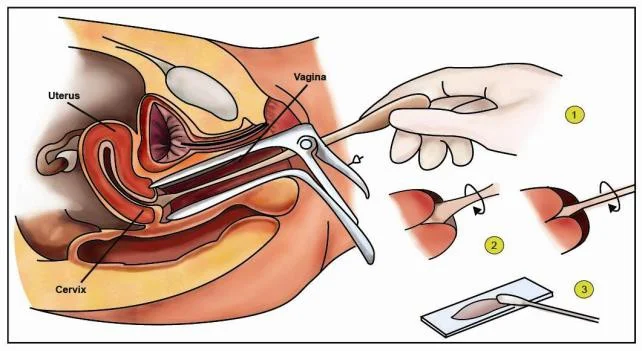
Pap Smear
- Indication: Screening for cervical cancer.
- Complication:
- Infection.
- Failure.
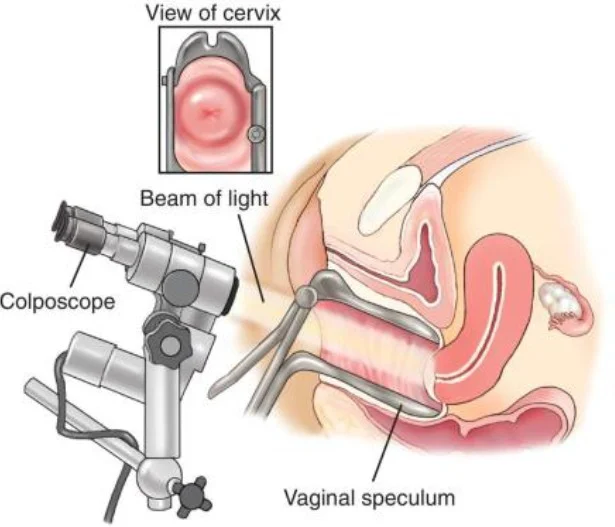
Colposcopy
Indication:
- Abnormal pap smear
- Punch biopsy.
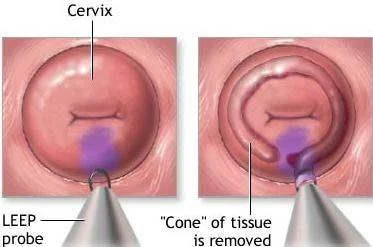
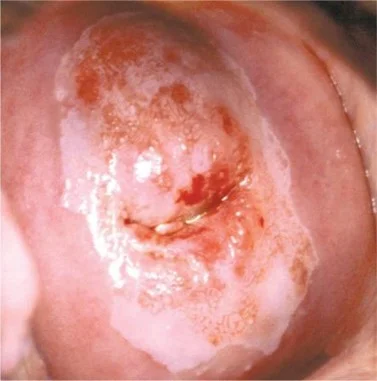
Cone Biopsy
Indication:
- CIN
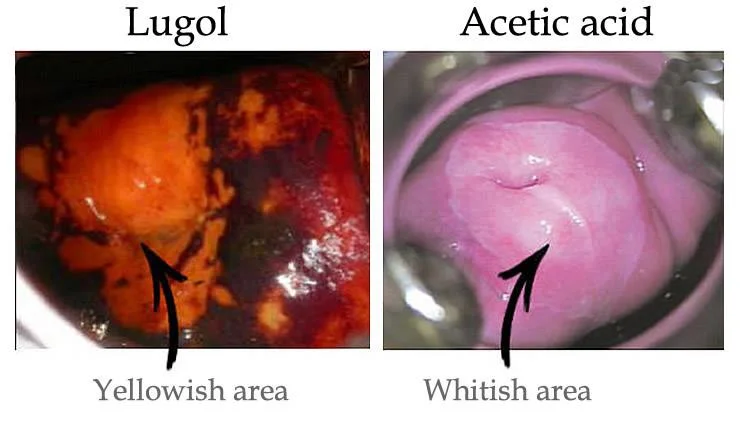
Under anaesthesia The dye we use in biopsy:
- Acetowhite test:
Acetic acid, abnormal cell will absorb so take the biopsy from the white cell. - Iodine test:
Lugol solution normal cell absorb and become brown because it contains glycogen so take biopsy from non-absorbed cells.
Laparoscopy
- Minimal invasive procedure.
- Diagnostic or therapeutic.
Complications of Laparoscopic ProceduresZ
- Bowel perforation.
- Bladder perforation.
- Cardiac arrest by fluid overload.
- Hyperkalaemia.
- Hydrothorax.
- Bleeding
- Infection.
- Risk of anaesthesia.
Laparoscopic Procedures
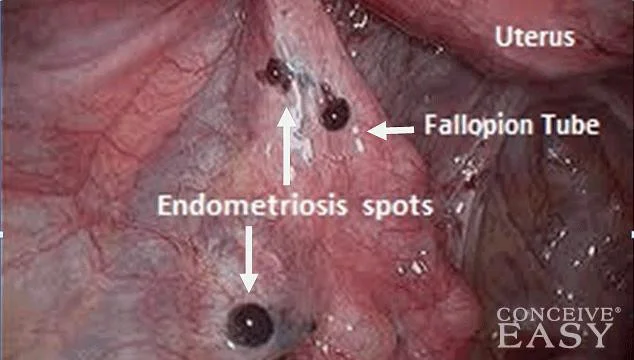 Diagnostic for endometroisis
Diagnostic for endometroisis
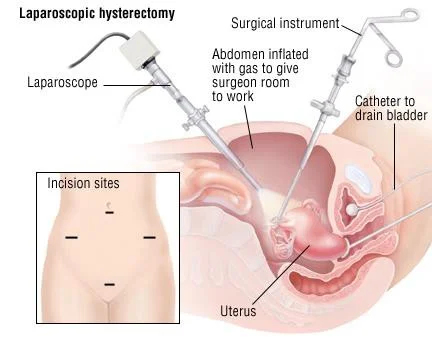 Laparoscopic hysterectomy
Laparoscopic hysterectomy
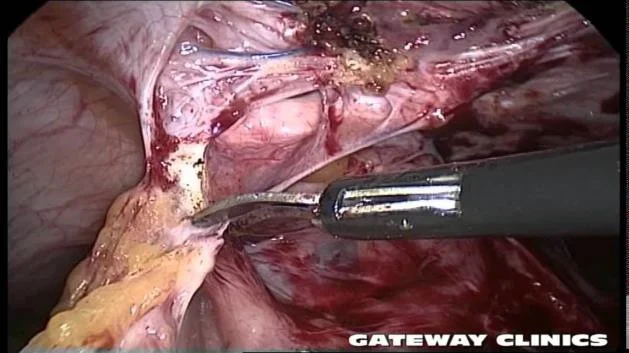 Laprascopic Adhesiolysis
Laprascopic Adhesiolysis
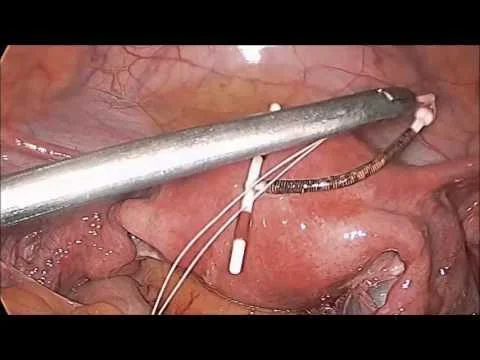 Laparoscopic removal of IUCD
Laparoscopic removal of IUCD
Additional Laparoscopic Procedures
- Laparoscopic ovarian hysterectomy.
- Laparoscopic removal of ectopic pregnancy.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy.
- Laparoscopic drilling for PCOS.
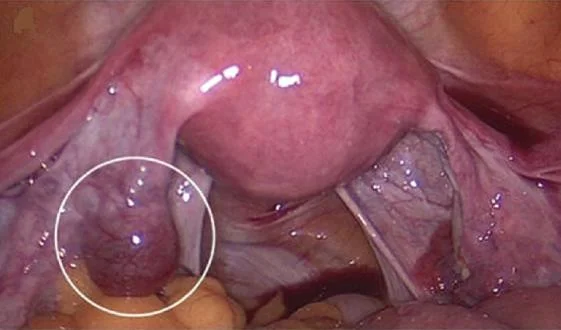 laparoscopic ovarian hysterectomy. laparoscopic removal of ectopic pregnancy
laparoscopic ovarian hysterectomy. laparoscopic removal of ectopic pregnancy
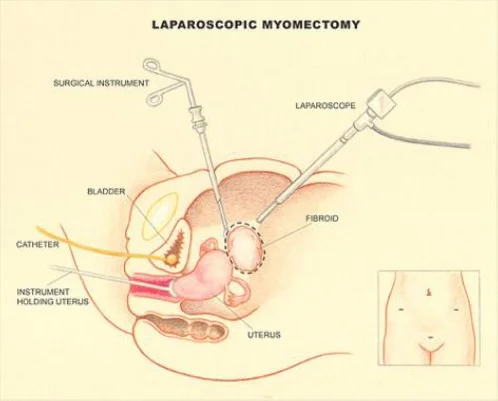 laparoscopic myomectomy
laparoscopic myomectomy
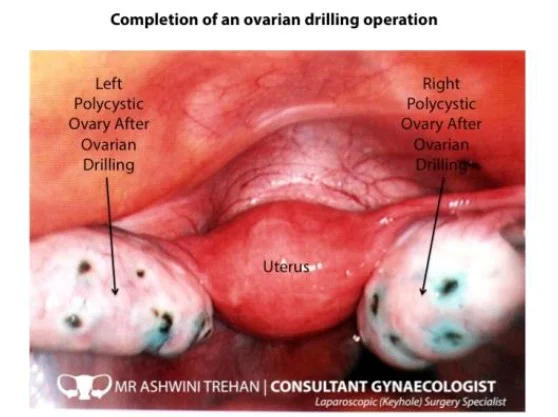 Laparoscopic drilling. PCOS
Laparoscopic drilling. PCOS
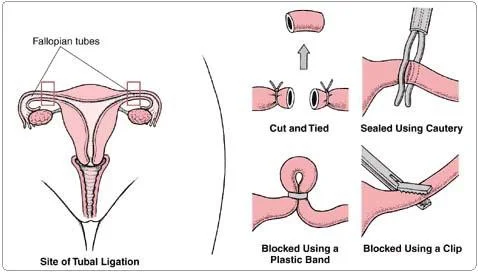
Bilateral Tubal Ligation
Indication: Family planning. Routes:
- Laparotomy
- Laparoscopy
- Hysteroscopic.
Complication:
- Failure.
- Risk of ectopic pregnancy.