Case Study: Mrs. Hanaa Ahmed
Mrs. Hanaa Ahmed is 38 years old, G v P ii + ii, came to the antenatal clinic to follow her pregnancy. LMP 16/8/2023. What are the questions you will focus on in history?
How to Take History?
Steps
- Identification
- Past Medical History
- Family History
- Drug History
- Social History
- Obstetrical History (current & previous)
- Gynaecological History
- Complain of & History of presenting illness
- Summary
Remember
- Obstetrical History (if obstetrical case in detail) & Gynae History will be in brief.
- In gynae history, vice versa; Gynae history will be in detail, and obstetrical history will be in brief.

Identification
- Name (at least three names)
- Age
- Occupation
- Blood grouping
- Husband’s name, age, BG, occupation, consanguinity
- Address
- Date of marriage
- Date of first examination
Notes
Women who have their first pregnancy at the age of 35 or more are called elderly primigravida.
Extremes of age (teenagers & elderly) are obstetric risk factors.

Past Medical History, Family History, Drug History, and Social History
Past Medical History
- DM
- ASTHMA
- HEART DISEASES
- HTN
- RENAL DISEASES
- (OTHERS)
Family History
- DM
- ASTHMA
- HEART DISEASES
- HTN
- RENAL DISEASES
- CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
Drug History
- Chronic medications
- Allergy
Social History
Obstetric History
Gravidity Parity LMP EDD History of current pregnancy:
- 1st trimester
- 2nd trimester
- 3rd trimester
- History of previous pregnancies
Risks Associated with Grand Multiparity
- Anaemia
- Increase risk of miscarriage
- Abnormal Fetal presentation
- Preterm delivery
- Uterine atony
- Placenta praevia
- Uterine rupture
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Postpartum haemorrhage
- Stress incontinence and urinary urgency symptoms
Example: Gravidity and Parity
Ex: A woman who has had six miscarriages with only one live baby born at 32 weeks and is pregnant again will be: gravida 8, para 1. (para 1+6.)(G viii P i+ iv)
OR to say ‘Mrs Wafaa is in her eighth pregnancy. She has had six miscarriages at gestations of 8–12 weeks and one spontaneous delivery of a live baby boy at 32 weeks. Baby Ahmed is now 2 years old and healthy.
LMP and EDD
- Use LMP to date pregnancy if the cycle was a normal cycle.
- The EDD is calculated by taking the date of the LMP, counting forward by 9 months, and adding 7 days.
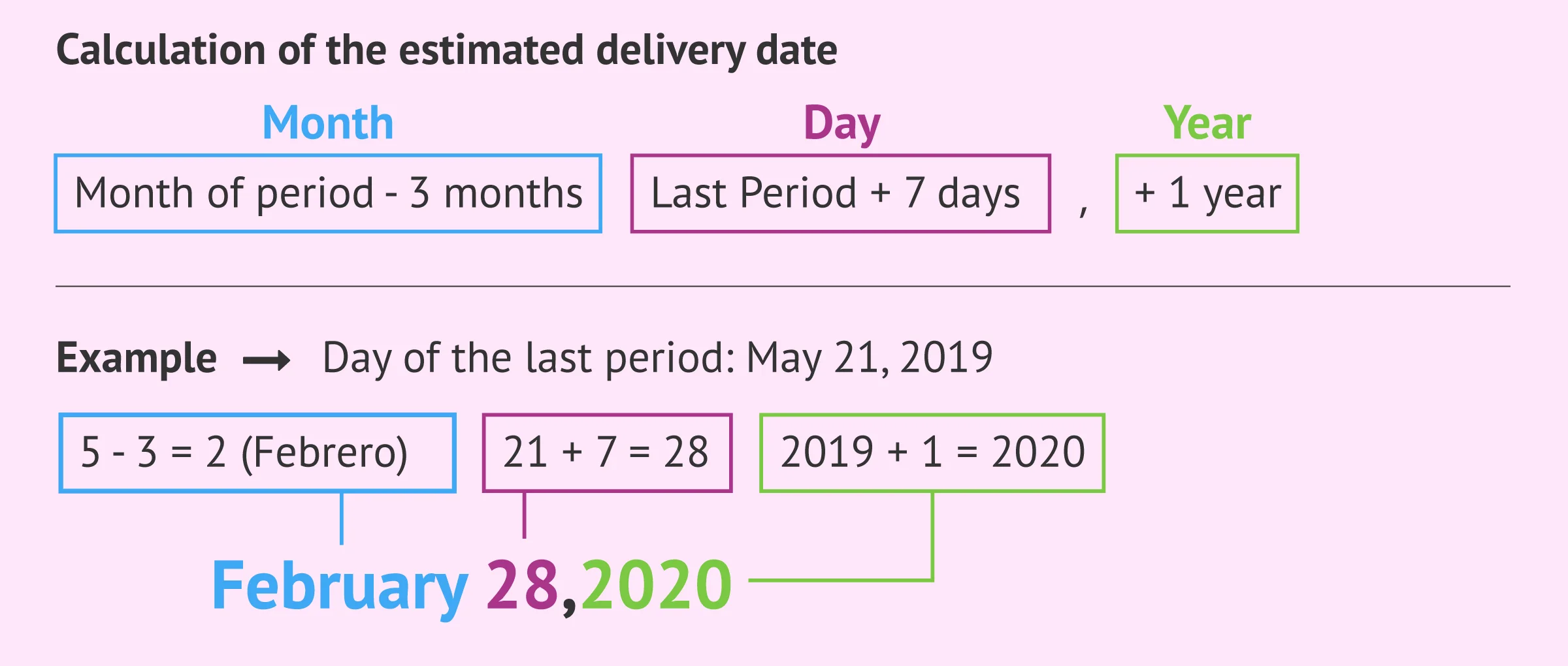
Calculation of the Estimated Delivery Date
| Month | Day | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Month of period - 3 months | Last Period + 7 days | + 1 year |
EDD (by Naegele’s Rule)
- The expected date of pregnancy.
- The median duration of pregnancy is 280 days (40 weeks), and this gives the estimated date of delivery (EDD).
How to Calculate EDD
- Add 7 to days.
- Subtract 3 (or add 9) to months.
- Add 1 to the year if (month is bigger than 3rd month).
EX:
- LMP 7/7/2021AD
- EDD 14/4/202AD
- GA(gestational age) calculate the pregnancy age today
In previous ex GA 34 weeks. GA Calculation
History of Current Pregnancy
1st Trimester (0-13 weeks)
- Folic acid (drug history - teratogens)
- NVP
- Dating scan
- Downs syndrome screening



2nd Trimester (14-26 weeks)
- Quickening
- Vaccination
- Anomaly scan Z (24th wk for heart anomalies specifically and 18-22 generally for anomaly scan)
- Iron supplementation Z

3rd Trimester (27-40 weeks)
-
Baby’s movement
-
Assessment scan
-
Mode of delivery
-
Puerperium & breastfeeding
Don’t Forget
In all trimesters: Z
- Bleeding
- UTI (asymptomatic UTI 80%, every visit Urine test is done to exclude) Z
- Signs of anaemia

Previous Obstetric History
1. Organising the Record
- List all pregnancies chronologically (earliest → most recent).
- For each pregnancy indicate the outcome (live birth, miscarriage, stillbirth, termination, etc.).
2. Details to Capture for Every Pregnancy
| Item | What to Record |
|---|---|
| Antenatal course | Any complications during pregnancy (e.g., gestational diabetes, hypertension, infection). |
| Gestational age at delivery | weeks + days (or “pre‑term,” “term,” “post‑term”). |
| Labor & delivery | • Duration of labor (first and second stages). • Mode of delivery (spontaneous vaginal, induced, instrumental, elective; forceps or term? Preterm? emergency C‑section at what time). • Complications that occurred during labor or delivery. |
| Post‑partum haemorrhage (PPH) | Presence or absence of PPH; amount of blood loss; need for transfusion; interventions used. |
| Neonate information | • Birth weight (grams or kilograms). • Sex of the infant. • Current age of the child. • Vital status (alive and well, ill, or deceased). |
| Puerperium | Any post‑natal complications (e.g., infection, wound dehiscence, thrombo‑embolism). |
3. Parity Summary
Provide a concise overview of the woman’s reproductive history:
- Number of deliveries (e.g., G 5 P 3 A 2 L 0).
- Nature of each birth: term vs. pre‑term, singleton vs. twins.
- Complications: maternal (e.g., pre‑eclampsia, PPH, need for blood transfusion), obstetric (e.g., placenta previa, uterine rupture), and neonatal (e.g., low birth weight, congenital anomaly).
- Outcomes: live birth, stillbirth, miscarriage, or therapeutic abortion; indicate the gestational age at loss and whether any pathology (e.g., product histopathology) was performed.
Possible Complications of Puerperium
- PPH
- Urinary tract infections
- DVT
- Perineal wound
- Psychological complications (e.g., postpartum depression)
Gynaecological History in Current Pregnancy
- Ask about cycle regularity
- Vaginal discharge (colour, odour, itching; if so abnormal)
- Cervical smear
- Contraceptives (prior to conception)
- Gynaecological operations
- Assisted conception
Complain of & History of Presenting Illness
- If no complaint, ask her about:
- Sleep
- Appetite
- Bowel habit
- Urination
Gynaecological History (for Gynae Case)
Steps
- Identification
- Past Medical History
- Family History
- Drug History
- Social History
- Obstetrical History (in brief)
- Gynaecological History
- Complain of & History of presenting illness
- Summary
Gynaecological History Details
- Cycle
- Menarche
- Kata
- Regularity
- Amount
- Dysmenorrhoea
- Bleeding PCB IMB
- Vaginal discharge (amount, colour, odour, itching, time)
- Dyspareunia
- Cervical smear
- Contraceptives
- Gynaecological operations
- Assisted conception
Summary
- Summarise your history