File?
Causes of FTT
- Nonorganic, referred to as psychosocial (70%)
- Psychosocial Dwarfism
- Familial dysfunction
- Maternal depression
- Poverty (Major risk factor)
- Child Abuse?
- Organic (30%) (A) Causes of excessive calorie loss
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Intestinal malabsorption
- Pancreatic disease
- Short gut syndrome
- Celiac disease
- Milk protein intolerance
- Endocrine Disorders
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Renal Disorders
- Nephrogenic DI
- Chronic renal failure
(B) Causes of increased caloric requirements
- Cardiopulmonary disorders
- Congenital heart disease
- CF (Cystic Fibrosis)
- Malignancies
- Hyperthyroidism
- Chronic recurrent infections
- HIV
- Primary immunodeficiency
SIgns of FIT
- Loss of subcutaneous fat stores
- Poor muscle mass
- Loose skin folds
- Prominent ribs
- Thin limbs
- Sparse hair
- Acrodermatitis enteropathica
- Pallor
- Lethargy
- Decreased appetite and mental abilities
Tools used
Electronic weight scale, infantometer, vernier height gauge, measuring tape


To diagnose abnormal growth pattern for children children
- Lying >97 percentile or <3 percentile
Indicators to determine:
- Weight for age
- Length/height for age
- Weight-height/length ratio
Other indicators:
- BMI; used or children above 2 years of age
- Head circumference for age
Read … Interpretation … Differential diagnosis …
Failure to thrive
Initially malnutrition will result in decrease of weight: wasting/acute malnutrition - measured by weight for age
If not corrected eventually linear growth will be affected (after several months): - Measured by weight for height stunning/chronic malnutrition
- Projection dropped more than 2-3 percentile totally (Failure to thrive) - i.e. chronic malnutrition if heigh/length is disturbed
- Patient is dropped to below 3rd percentile
- Weight, height are both affected
Weight for age: measure of underweight or wasting and stunning combined Head circumference is lastly affected with severe chronic malnutrition
cases on growth
Differential below 3rd percentile: Interpetation Short stature, caxcehcix
Differential
- Turner syndrome
- Child Neglect / Abuse
- Neonatal diabetes
- Rickets
Management
- Karyotyping (turners, down)
Differential Above 97 percentile:
- Giantism
Differential platue:
- Malnutrition
Acute malnutrtion weight / age
- Pyloric stenosis
- Down syndrome
- Child Abuse
child with diarrhea
- gastro enteritis
Chronic malnutrtion
- …
distended abdomen, pathetic face, thin limbs, on off diarrhea, proximal myopathy - anemia
- celiac disease
above average weight, height short Cushing syndrome differential
All below average from birth
- TORCH
- Genetic; down syndrome, sunjet saket syndrome
- Fetal Alcohol syndrome
Measurement Guidelines
Weight Measurement
- Age: Over 2 years
- Tool: Electronic weight scale
Height Measurement
- Age: Under 2 years
- Tool: Infantometer for length, otherwise use giraffe
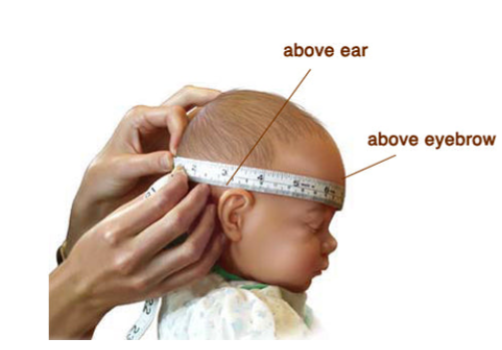
Head Circumference Measurement
- Position: Ensure the height is in front of you.
- Units: Use centimeters, not inches.
- Procedure: 1. Start at the forehead, with no space from the eyebrows. 2. Rotate the measuring tape above the ears. 3. Continue around the occiput (back of the head). 4. Pass the tape over the next to above the ear. 5. Complete the circle back to the starting point.
- Note Accuracy: Measure three times and calculate the average to account for movement.
Note
if weight normal could be short stature only rather than chronic malnutrition
if growth normally then stopped, growth hormone abnormality. constitution if his puberty caught on the normal variability.
Process
- Prenatal
- Nutrition
- Growth parameters
- first 2 years of life rapid growth, any diseases - 1st year 25 cm, second year 12.5cm, after which 6 cm and so on…
- 1.5.-2.5kg
- 50 cm length
- 34cm head circumfrence
History taking
Chief of complaint
Short stature
Prenatal History
Prenatal
- Consanguinity? Neonatal
- small gestational age (Birth weight [term/preterm])
- Cessarian
- Oxygenation, intubation, complications
- Admissions to NICU
Postnatal
HOPI
-
Jaundice, recurrent hypoglycemia; Hypopituatiry resulting in decreased Growth hormone
-
SOLs; reccurent headache, photophobia
-
Nutrition: formula fed?, breast fed?
-
Hypothyroidism:
-
Celiac Disease:
-
Organ Chronic diseases:
Past History
Medical
-
Admissions
-
Immunization,
-
Surgeries,
-
Transfusions
-
Mid parental height
-
Family Hx of diseases
Drugs:
- Steroids stunting growth
- Estrogen, early closure of growth plate
Social:
- Residency
- Level of education
- who takes care of child
Systemic Review
- CNS
- Cardiac
- GI
- Respiratory
- Hematological
- Dermatological
- Musculoskeletal
Examination
Genereal Appearance
-
Dysmorphic; Turner, nonan??
-
Midline defect: Hypopituitarism - cleft lip & palate, central incisors, Umbilical Hernai, micropenis
-
Disability:
-
Growth chart / Growth parameters: Head Circumference, Length/Height, Weight, BMI - related to age | weight to height below 2 years
Growth charts
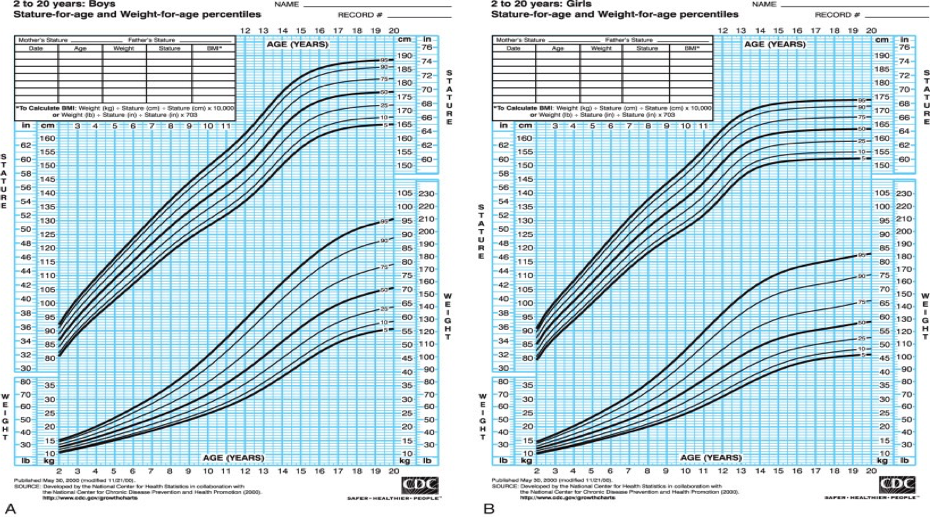
Definition of short stature crossing percentile, below 3rd percentile, shorter than expected mid parental height, two standard deviation below mean; 50th percentile
I- Read patient age is 18 months, girl, 75 cm
II- Interpretation Bellow 3rd percentile or between 3rd and 5 if not exact
III- Measure Mid Parental heihgt -+ 13 cm female/male average
IV- Differential diagnosis for short stature
-
Physiological: Familial, constitutional delay of growth and puberty.
-
Pathological: indication to initiate Growth hormone treatment
- Turner
- Neonan syndrome
- Brother willy; Obese & Short
-
Genetic:
- Down syndrome
- Any genetic diseases
- Celiac
- SSS
-
Chronic diseases
- Cystic Fibrosis - gene mutiation.
-
Rheumatologic diseases
- RA
- SLE
- IBD
-
Endocrinal
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypopituatirism
- Growth hormone deficiency
- Cushings
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia may appear late
-
Idiopathic: when everything is excluded
Investigations
-
CBC: Anemias
-
LFT, TFT (TSH, T4) , RFT
-
Insulin like growth factor - IGF-1 Growth hormone not usually measure GRH not measured IGF-Binding protein can be measured; differential malnutirtion
-
Electrolytes (Rickets)
-
Celiac investigation: Antibodies tissue tra… initially - diagnostic by biopsy
-
Cortisol - not an early investigation
Initial bone age
-
Left hand X-ray: Early closure of growth plates
- Increased bone age
- precinous pubery
- Estrogen supplementation
- Increased bone age
-
Atlas:
Further Examination
- Growth hormone stimulation test (suspected growth hormone deficiencies)
- Karyotyping (any girl with short stature should be done)
Late
-
MRI - pituitary
growth velocity:??? further exam? Height related - speeding of height increase - every 4 - 6 - 1 yr groowth increase - in one year, till puberty is measured.
Management
-
Malnutiriton: refer to distance, high calorie formula
-
Hormonal:
- Growth hormone:
- Daily (daily) / once weekly treatment with Growth hormone
- small ga turner neonan brother willy, specific gene mutations, idoipathic low growth hormones
- Daily (daily) / once weekly treatment with Growth hormone
- Growth hormone:
Differential tall
- Giantism…
Y ?