Pediculosis
Definition
- Humans are parasitized by three species of Anoplura:
- Pediculus humanus capitis or head louse.
- Pediculus humanus corporis or body louse.
- Phthirus pubis or pubic louse.
Clinical types
- Pediculosis Capitis
- Pediculosis Corporis
- Pediculosis Pubis
1) Pediculosis Capitis
Synonym: Head lice. Cause: Pediculus humanus capitis. Epidemiology:
- Common in children & homeless people
- Spread from person to person by head- to-head contact, and by shared combs or hats.
- Often seen in epidemics amng kindergarten and school children
Morphology and biology
- Female lifespan is approximately 40 days
- Lays about 300 eggs, at the rate of 7-10 daily
- Eggs are cemented to hair shafts with a material secreted by female’s accessory glands
- Eggs hatch in about 8 days.
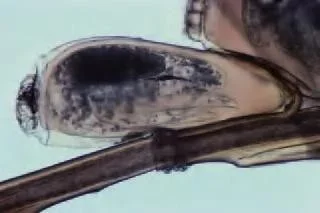
Pathogenesis
- Lice live on the scalp and suck blood
- They firmly attach their eggs (nits) to the hair shaft just at the skin surface
- The head louse measures some 3-4 mm in length and is greyish, and often rather hard to find
Clinical features
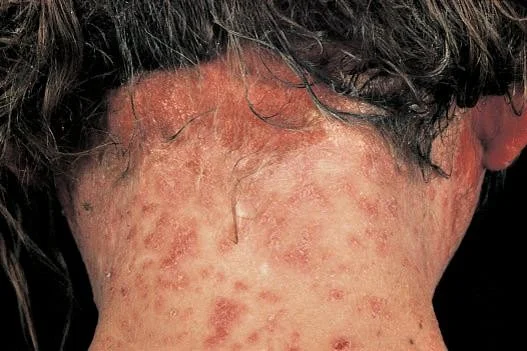
- Pruritic eruption on back of scalp and nape
- Excoriations & secondary infections (lice drmt)
- Hairs may become matted due repeated scratch
- Lice identified especially when combing hair
- Nits may be present throughout the scalp, but most common in the retroauricular region (ova close to scalp are viable)
Diagnostic approach:
Look for: – Nits on the hair shafts (retro-auricular), – Lice on the scalp.
Therapy
Effective therapeutic agents must kill/remove both lice and ova.
- Pyrethrins and the synthetic permethrin:
- 1% and 5% cream
- Must be applied (10 min) after shampooing and drying hair completely
- No hair washing for 24 hours
- Malathion 0.5% lotion.
- Has the extra value of sticking to the hair, so protecting against re-infection for 6 weeks.
- Lindane (gama benzene hexachloride)
- Has potential neurotoxicity if abused
- Crotamiton (Eurax)10% cream or lotion
Nits treatment: Nits are always a problem
- No treatment is available
- Re-treatment in a week is advsable for all pnts
- Combing with a metal or plastic nit comb (fine-toothed) is an important adjunctive measure
Other therapy methods: Oral treatment Ivermectin
- Has no ovicidal activity
- Two doses separated by an interval of 10 days would be more effective.
2) Pediculosis Corporis
Synonym: Body lice. Cause: Pediculus humanus corporis. Epidemiology:
- Is primarily a disease of the unwashed “Vagabond’s disease”
Morphology and biology
- Identical in developmnt & appearance to head louse
- Its natural habitat is the clothing of its host, it only visits the skin to feed.
- Eggs are cemented to clothing fibres
- With a preference for clothing close to the skin.
- Seams are a favoured site

Pathogenesis
- The lice feed on the body, but live in the clothing
- The parasite obtains its nourishment by descending to the skin and taking a blood meal.
- Lay their eggs in the seams of clothing
Clinical features
- Pruritus,
- Itching is accompanied by erythematous and copper-colored macules, wheals
- Excoriations and secondary infections (lice dermatitis) on trunk (vagabond skin) are common.
Diagnostic Approach
- Look for the lice and nits on the clothing, not on the skin.
- Is differentiated from scabies by the lack of involvement of the hands and feet 19
Therapy
• Same pediculicides as for Pediculus humanus capitis can be used • Lice may live in clothing for 1 month without a blood meal. • Disinfection of clothing and bedding (boiling, hot ironing). • Attempt to change living conditions.
- Pyrethrins and the synthetic permethrin:
- 1% and 5% cream
- Malathion 0.5% lotion. – Has the extra value of sticking to the hair, so protecting against re-infection for 6 weeks.
- Lindane (gama benzene hexachloride)
- Has potential neurotoxicity if abused
- Crotamiton (Eurax)10% cream or lotion
3- Pediculosis Pubis
Synonym: Pubic lice. Cause:Phthirus pubis Epidemiology:
- Is found in the pubic region, as well as hairy areas of legs, abdomen, chest, axillae, arms
- Spread through close physical contact
- Usually transmitted by sexual contacts
Clinical features
• Lice and nits present in the hair of pubic area • The signs and symptoms are similar to those of body louse infestation.
Therapy
-
Pyrethrins and the synthetic permethrin:
- 1% and 5% cream
-
Malathion 0.5% lotion.
- Has the extra value of sticking to the hair, so protecting against re-infection for 6 weeks.
-
Lindane (gama benzene hexachloride)
- Has potential neurotoxicity if abused
-
Crotamiton (Eurax)10% cream or lotion Numerous eggs (nits) seen
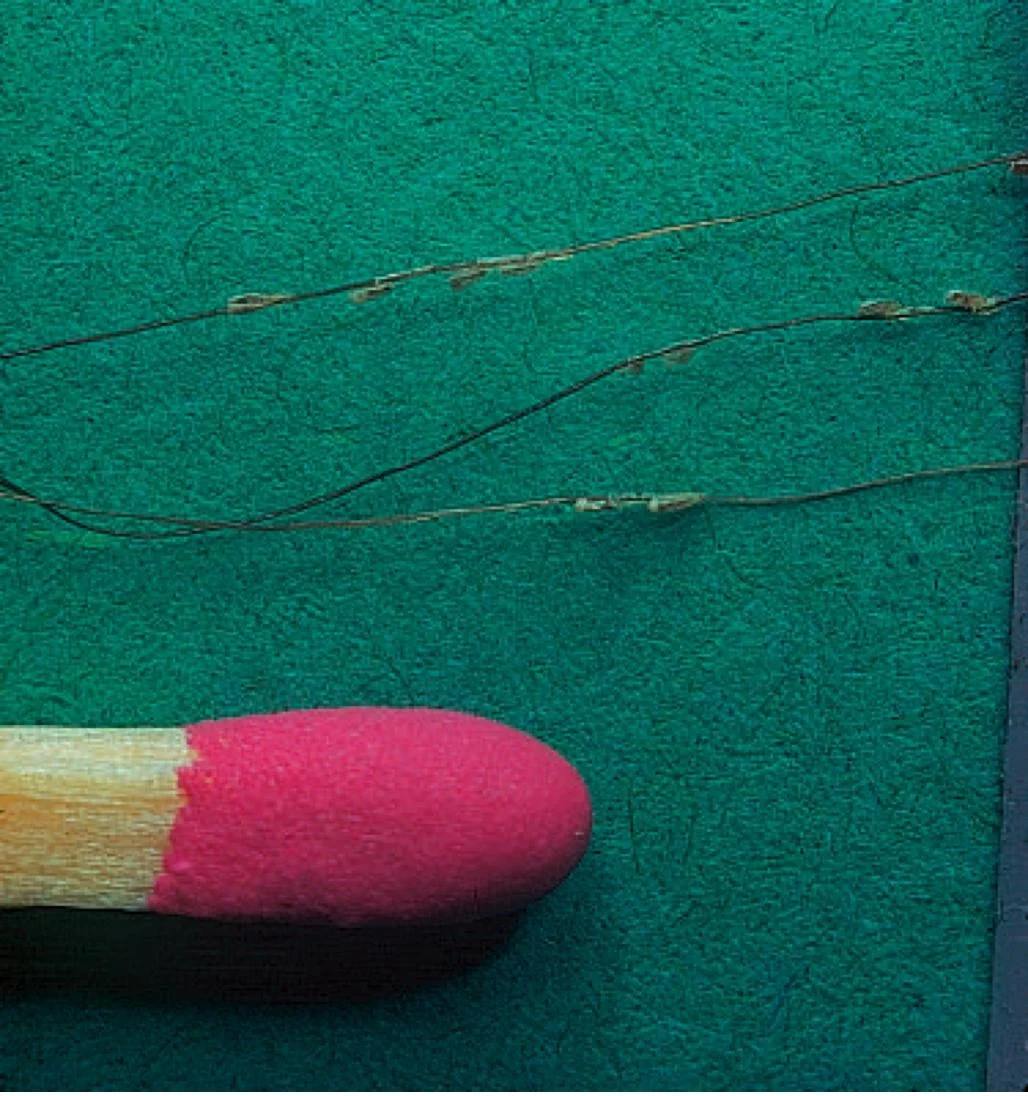

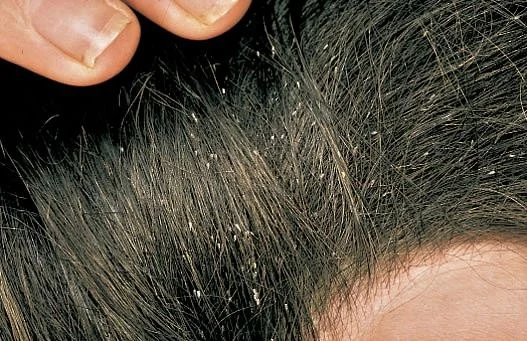

Case One: History
- HPI: Marium a 6-year-old girl with a two-week history of an itchy scalp. It has not improved with over-the-counter dandruff shampoo. She recently stayed over at her cousin’s house who now has the same problem.
- PMH: no chronic illnesses or prior hospitalizations
- Allergies: no known allergies
- Medications: none
- Family history: noncontributory
- Social history: lives with her parents and attends first grade
- ROS: negative
Exam of the Occipital Scalp
Structures on the hair are not freely movable
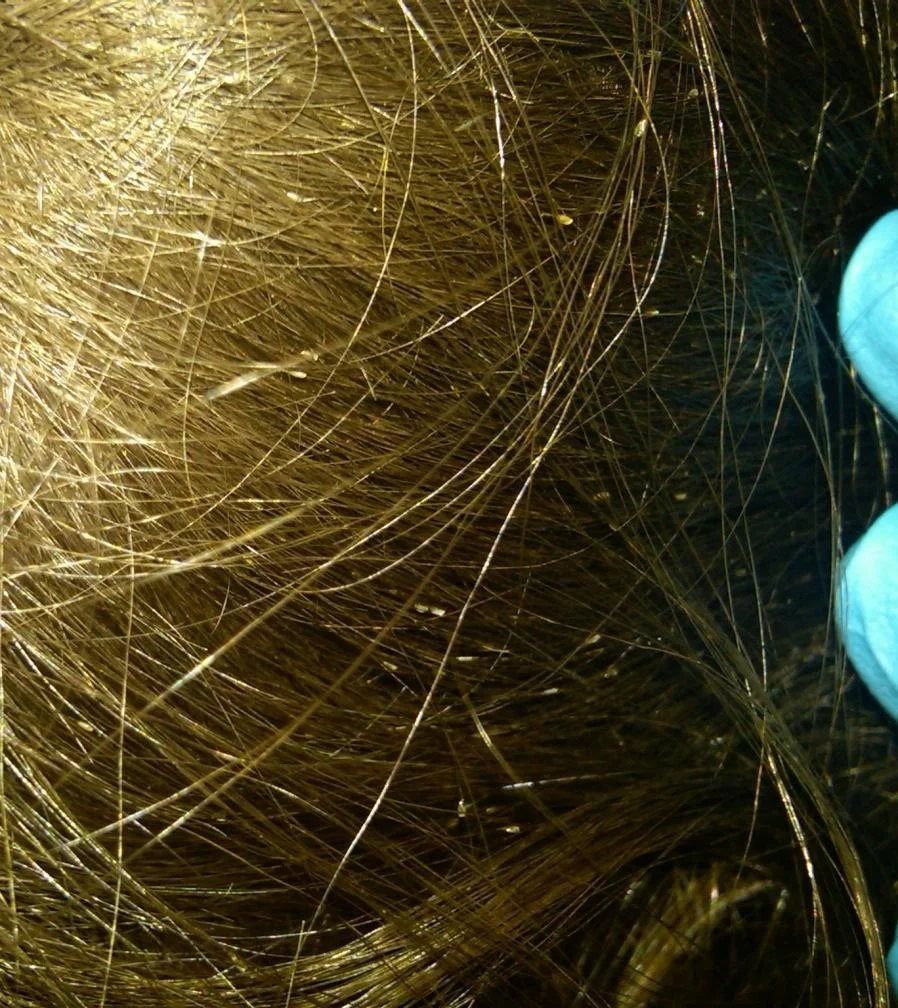
Exam Findings
Numerous nits (oval egg capsules) firmly fixed to the hair shaft
Case One: Question 1
How would you describe Mary’s exam? a. Multiple hair casts present. No nits or lice noted. b. Multiple lice present. No nits noted. c. Multiple nits present. No lice noted. d. Negative exam, no nits or lice noted.
Pediculosis (Lice)
- Three different varieties of lice may infest humans
- Head louse – Pediculus humanus var. capitis
- Body louse – Pediculus humanus var. corporis
- Pubic or crab louse – Phthirus pubis
- Head lice are spread by close physical contact and fomites (e.g., brushes, helmets, bedding)
- Commonly affects school-age children
- Affects all ethnic and socioeconomic groups, but is less common in African-Americans
Clinical Features
-
Frequently has associated scalp pruritus
-
May also have posterior cervical lymphadenopathy
-
Dermatitis may be present on the posterior neck
-
Nits are noted more commonly than lice on exam (live lice scurry away from light)
-
The most common sites to find nits are on the retroauricular and occipital scalp.
-
Nits within 1 cm of the scalp are typically viable. The distance may be greater in warm environments.
-
Nits must be distinguished from hair casts.
- Hair casts encircle the hair shaft and move freely in contrast to the nit which is cemented to the hair.
Pediculosis: Pathogenesis
- Female adult lice live 30 days and lay 5-10 eggs (nits) per day at the base of the hair where it meets the scalp.
- Eggs hatch in 8-12 days.
Pediculosis: Treatment
- Individual patient factors should be assessed prior to choosing a topical therapy (age, allergy history, prior treatment, etc.).
- First-line over-the-counter and prescription topical therapies are listed on the following slide.
- Use OTC permethrin 1% or pyrethrins when resistance is not suspected.
- Use malathion 0.5% when resistance to permethrin or pyrethrins is documented or when treatment with these products fails.
Case One: Question 2
- If Mary had live lice in the scalp on follow-up, which of the following answer choices would be possible causes of treatment failure? a. Did not clean daily hair care products b. Did not re-treat in 7-10 days c. Did not treat contacts d. Incorrect application of the medication e. Resistance of the organism to medication f. All of the above
Pediculosis: Patient Education
- All persons living in the home should be examined to avoid re-infestation.
- Those with live lice or nits within 1 cm of the scalp should be treated.
- It is prudent to treat family members who share a bed with the person with infestation, even if no lice are found.
- If it is not possible to examine household members, treat without an exam if the treatment is not contraindicated.
Pediculosis: Patient Education
- Clothing and bedding should be washed and dried on the hot cycle of the dryer.
- Brushes, combs and other hair care items can be placed in hot (> 60°C) water for 10 minutes.
- Non-washable items may be placed in the dryer or stored in a sealed plastic bag for 3 days.
- Children should not be restricted from attending school because of lice.