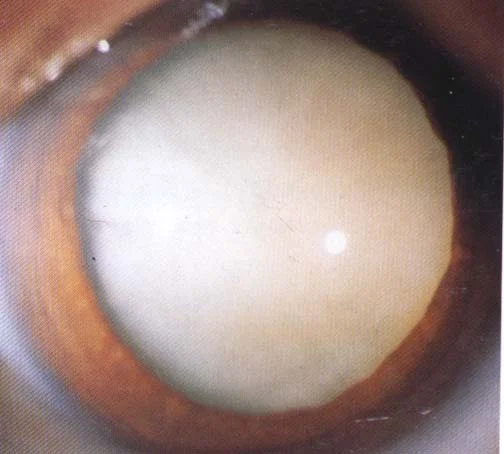
Senile Cataract
-
Now called Age-related Cataract
-
Most commonly seen
-
50 years old
-
80 years old → 100%
-
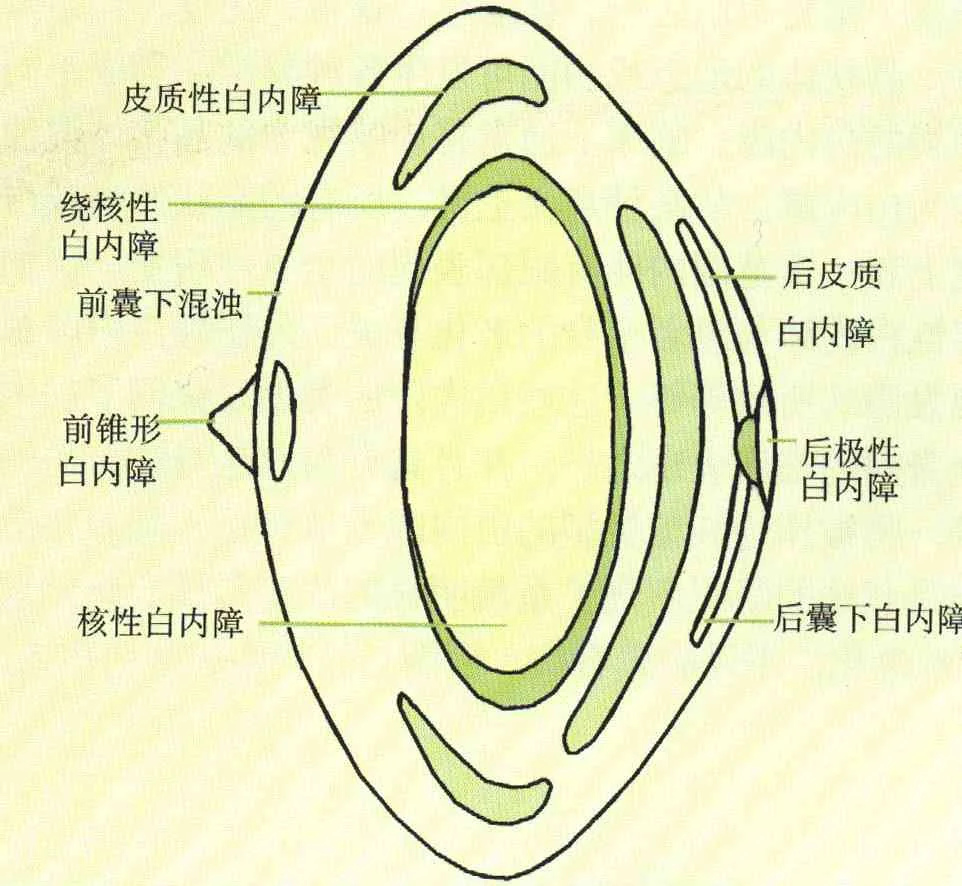
Classification
-
On location:
- Cortical
- Nuclear
- Subcapsular
-
On degree:
- Immature
- Intumescent
- Mature
- Hypermature
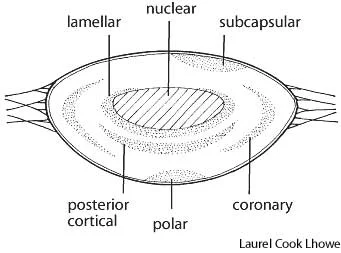
Additional Classification
- Lamellar
- Nuclear
- Subcapsular
- Posterior cortical
- Polar
- Coronary
Laurel Cook Lhowe
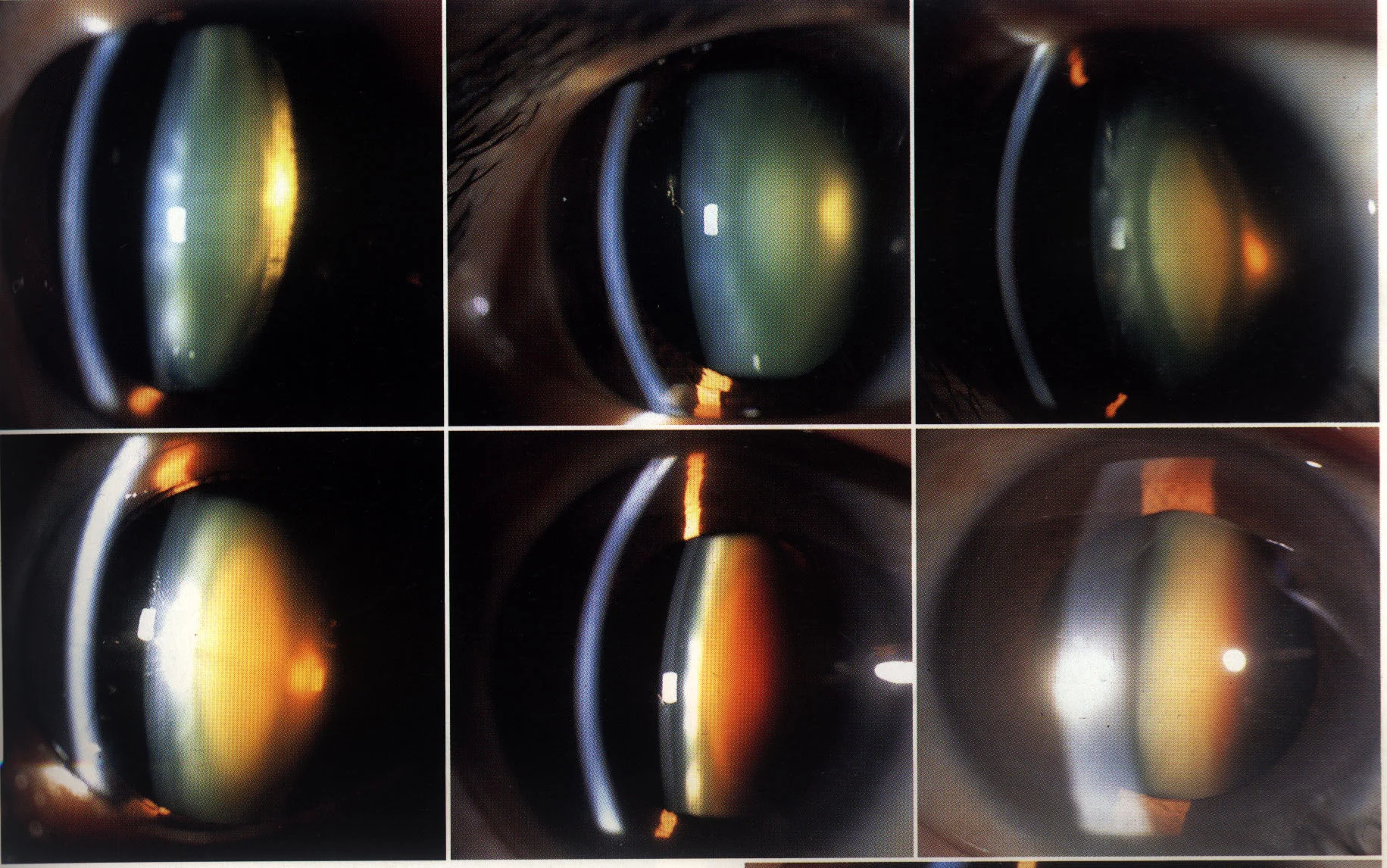
Cortical Cataract
-
4 stages
-
Incipient stage: Wedge turbidity
-
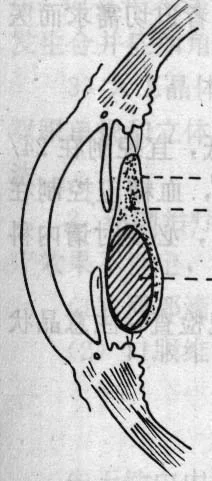
Intumescent stage (immature):
- Iris projection & shallow anterior chamber
- *Induce acute angle-closure glaucoma
-
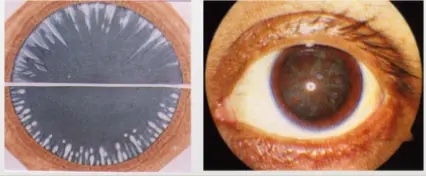
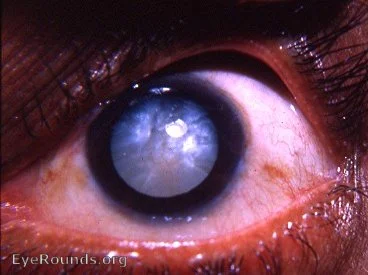
- Mature stage:
- a. Complete opacity, milky white, iris shadow disappear
- b. Volume and anterior chamber regain normal
- c. Vision: LP or HM before the eye
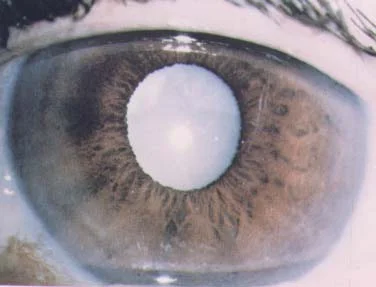
- Hypermature stage:
- Phacoanaphylactic uveitis
- Phacolytic glaucoma
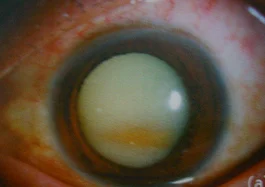
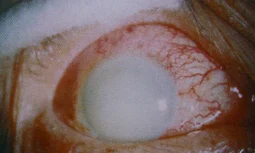
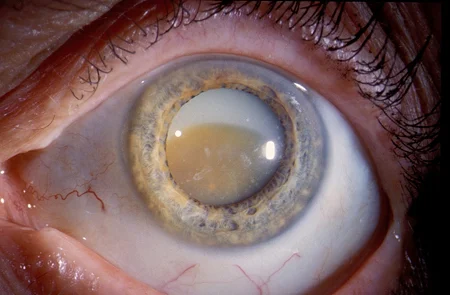
Nuclear Cataract
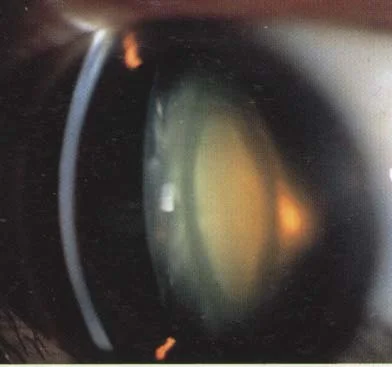
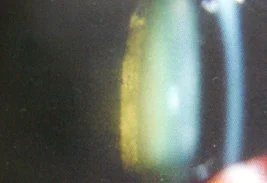
Subcapsular Cataract
-
Features:
- a. Start earlier
- b. Cause obvious early vision defect
- c. Opacity of posterior pole
-
Affecting vision early
Clinical Manifestations
- Symptoms:
- Progressive vision decrease
- Contrast sensitivity decrease
- Refraction changes: Myopia, astigmatism
- Diplopia
- Glare
- Change of color sensation
- Visual field defect
Contrast
Contrast is the difference in visual properties that makes an object distinguishable from other objects and the background. In visual perception of the real world, contrast is determined by the difference in the color and brightness of the object and other objects within the same field of view.


Vision Abnormality

Clinical Manifestations
- The lens is best examined with the pupil dilated with a slit-lamp or by using the direct ophthalmoscope
- Signs:
- Turbidity of lens