Case 1
Patient with severe chest truama, Respiratory rate only 8/minute due to restricted chest movement
- What is expected acid-base abnormality in this case?
- Besides chest truama what else can produce this acid-base abnormality. name any
- What is the role of I.V. bicarbonate in treating this acid-base abnormality
Case 2 Z
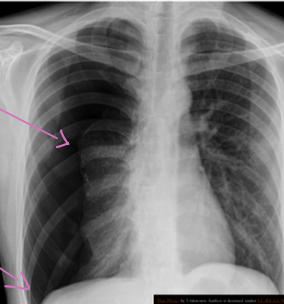
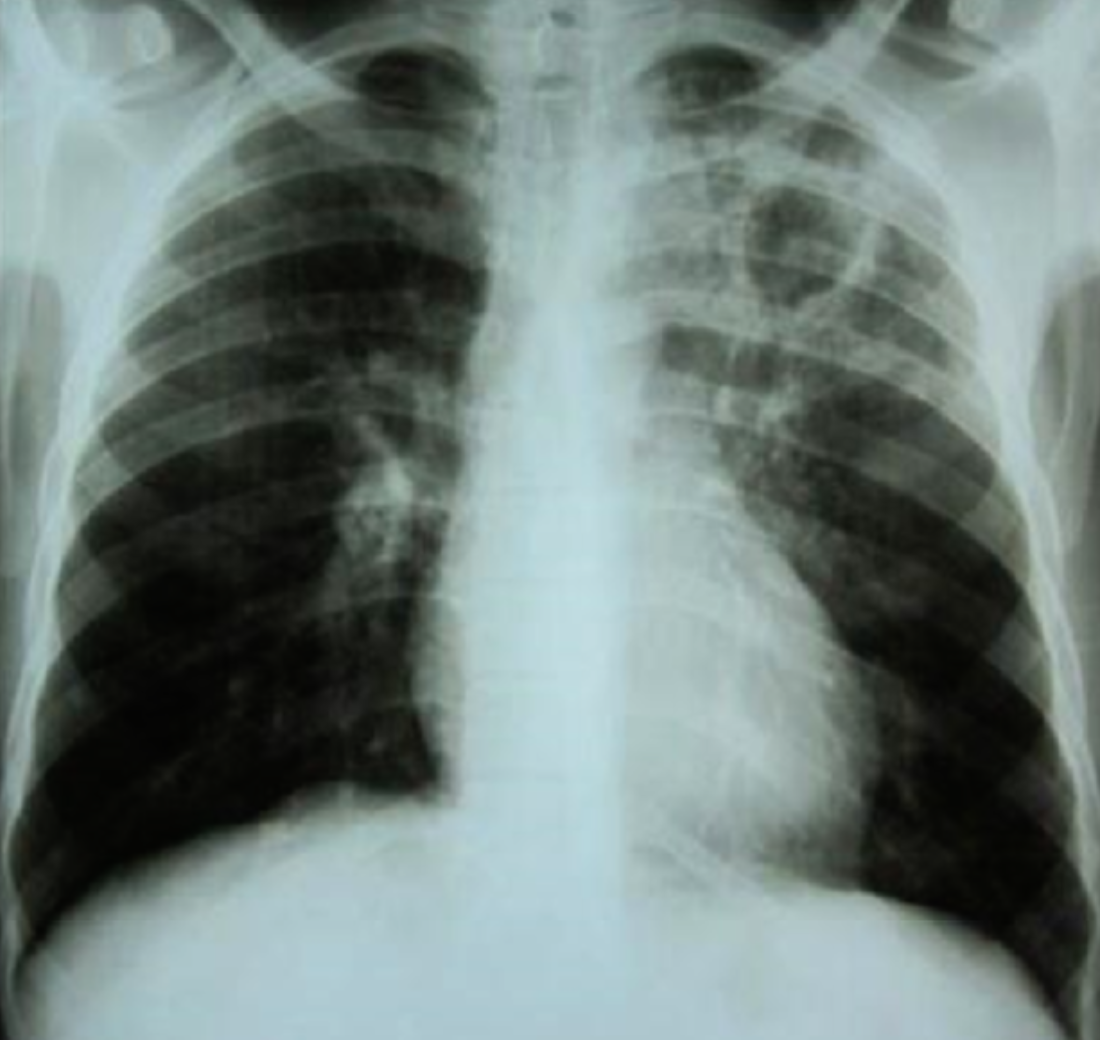 A 32 years old male presented with history of low grade fever, cough with sputum, sometimes blood stained. He has weight loss of 5 kg during this period. His chest X-Ray is shown ABOVE.
A 32 years old male presented with history of low grade fever, cough with sputum, sometimes blood stained. He has weight loss of 5 kg during this period. His chest X-Ray is shown ABOVE.
-
Describe the abnormality seen in the X-Ray?
- Cavitation and consolidation in the left upper lung
- bilateral Hilary lymphadenopathy
-
What is the likely diagnosis? Pulmonary TB
-
Mention 2 other investigations which you will advise?
- o Sputum culture and smear
- o IGRA
-
Mention 2 factors which increase the risk of this disease?
- HIV
- Chemotherapy
-
Mention 2 drugs used to treat this medical condition?
- o Rifampicin
- o INH (Isoniazid)
Case 3
An 18-year-old student. Very stressed due to exams. Having a respiratory rate of 28/min. Also complaining of tingling and numbness around the lips.
-
What is the expected acid-base abnormality in this case?
- Respiratory alkalosis.
-
Besides stress, what else can produce this acid-base abnormality?
- pregnancy, initial aspirin, high attitude.
-
What immediate step will you take to treat this patient?
- Give a paper bag to the patient and ask the breath inside the bag.
-
What is the cause of numbness around the lips? Z
- Hypocalcemia due to respiratory alkalosis.
Case 4
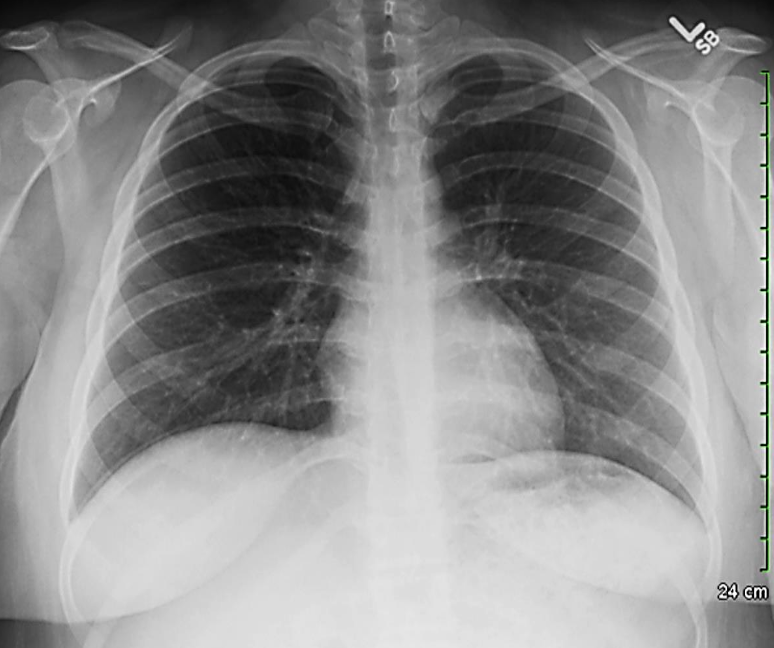
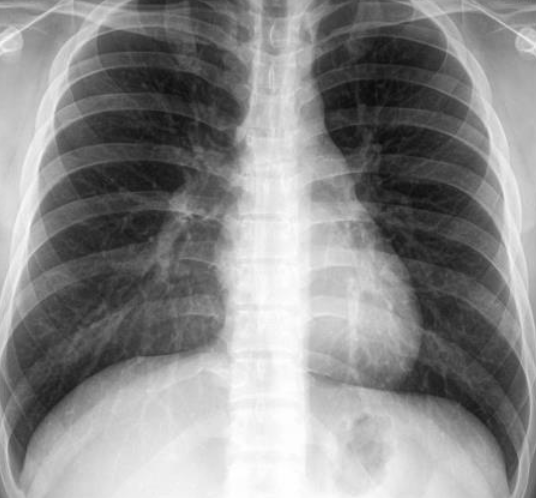 Patient with recurrent attacks of dyspnea and chest tightness after exercise. Clinical diagnosis bronchial asthma. Chest X ray is as follows:
Patient with recurrent attacks of dyspnea and chest tightness after exercise. Clinical diagnosis bronchial asthma. Chest X ray is as follows:
Q1: in this chest x-ray normal or abnormal? Normal.
Q2: on chest auscultation, what added sounds can be heard in asthma? Wheeze.
Q3: Name any drug which can precipitate asthma? NSAIDS, Beta blockers.
Q4: You ordered spirometry for this pt. what will be the expected finding? FEV1 is reduced.
Q5: Name 2 clinical features of severe asthma? Z Can Not complete a sentence in one breath, Tachypnea, cyanosis
Q6: What ttt will you give in moderate to severe asthma? Name any 2. Bronchodilators, corticosteroids.
Case 5
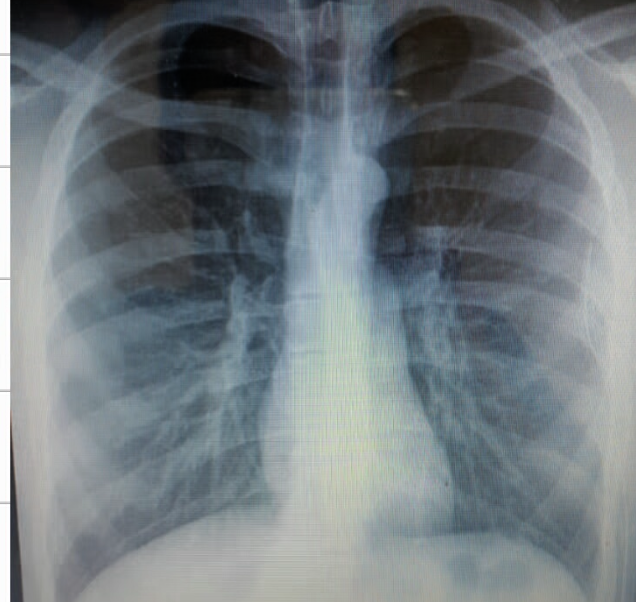
 Patient present with acute chest pain..
Patient present with acute chest pain..
-
Diagnosis?
- Pneumothorax
-
What abnormalities do you see?
- lucency of hemithorax
- absent broncho-vascular markings Z
- shifted trachea to the right
-
Predisposing causes?
- Trauma
- Ruptured alveoli
- Cystic fibrosis
-
important and prompt steps of management
- (Needle decompression) needle in the second intercostal space midclavicular line to decompress.
- Tube in the 5th intercostal space, anterior axillary line, pushed to the back and upward.
Case 6
Patient smoker FEV ↓ Totsi lung capacity ↓ Co2 enzymes ↓
A) what’s the type of Respiratory failure Type II
B) Diagnosis? COPD
Case 7
A 24 year old student was admitted with SOB and tingling in her hands. An ABG was taken on 35% oxygen.
pH 7.52 (NR 7.35-7.45) PaO2 28 kPa (NR 10.0-14.0 kPa) Paco2 2.0 kPa (NR 4.4-5.9 kPa) HCO3- 18.4mmol/l (NR 18-22 mmol/L) Base excess + 6 mmol/l (-3)-(+3)
What is the functional abnormality? Respiratory alkalosis
Circulating auto-antibodies are found in? SLE
Case 8
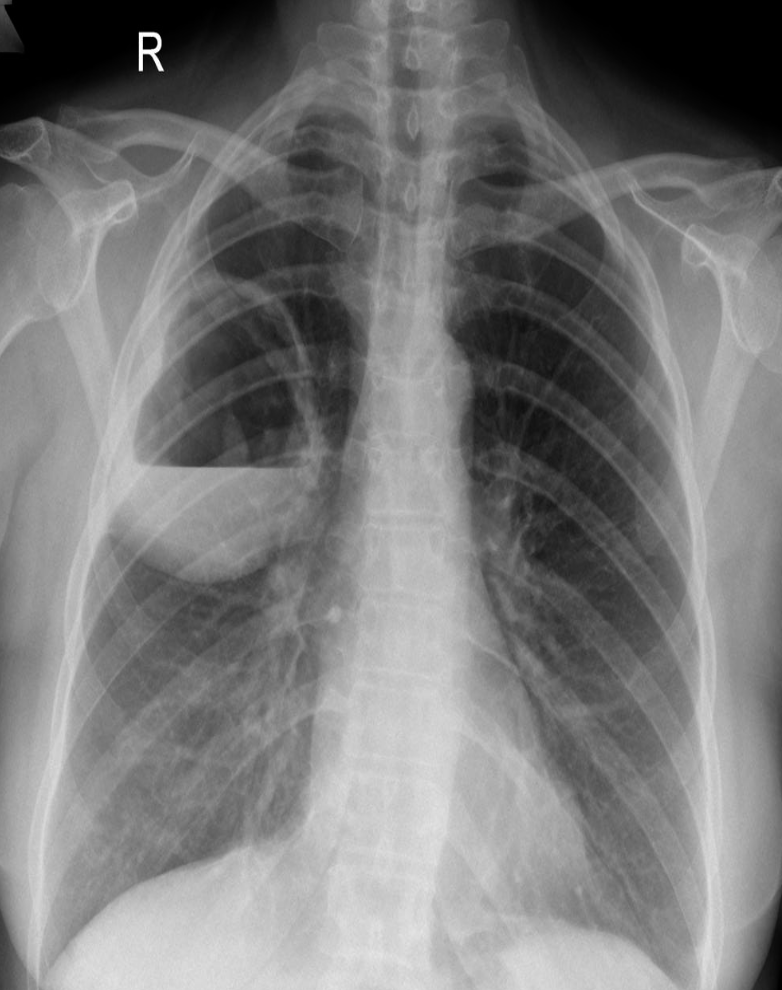 This patient presented with cough, fever, rusty sputum?
This patient presented with cough, fever, rusty sputum?
-
What is radiological abnormality present?
right lung show cavity that contain air fluid level (Post pneumonic abscess) Z -
Name 2 causes for this condition?
a. --------TB--------
b. --------pneumonia-------- C. --------Lung Access /Mass--------
Case 9
Patient in coma. Respiratory rate: 8/min Blood pH: 7.25
Q1: what’s the acid base abnormality seen here? Respiratory acidosis.
Q2: beside coma, name 2 other clinical situations where you can see this acid base disturbance? Chest trauma, which decrease the chest movement, COPD.
Q3: what’s the role of bicarbonate in ttt of this condition? We should not give bicarbonate because it will increase the CO2 which will worsen the situation.
Case 10
 A very anxious student having tachypnea & mild tetany. E.R. doctor advised rebreathing in a paper bag.
A very anxious student having tachypnea & mild tetany. E.R. doctor advised rebreathing in a paper bag.
-
What is the expected acid-base abnormality in this case? Respiratory alkalosis
-
Name 2 etiologies of this acid base disturbance? Panic attack & High attitudes
-
What is the cause of tetany in this acid base disturbance? Low Calcium level
Case 11 Z
A 25 year old female reports to the E/D because of sharp left sided chest pain and shortness of breath of one day duration. The pain worsened with motion and deep breathing.
She is currently on birth control pills.
The physical findings are suggestive of the presence of a small pleural effusion.
Investigations revealed:
- CBC: Hgb 15.0; Hct 43; WBC 11,500; 83 polys, 1 band
- Arterial blood gases: Flo2 .21; pH 7.39; PCO2 30; HCO2 20; PO2 80 and SO2 95%
- ECG reveals sinus tachycardia and non-specific S-T-T.
- CXR reveals a small pleural effusion in the left base. The left diaphragm is elevated.
What is the most likely clinical diagnosis?
pulmonary embolism
What additional studies you would like to do?
spiral CT angiogram and D-dimer
Case 12
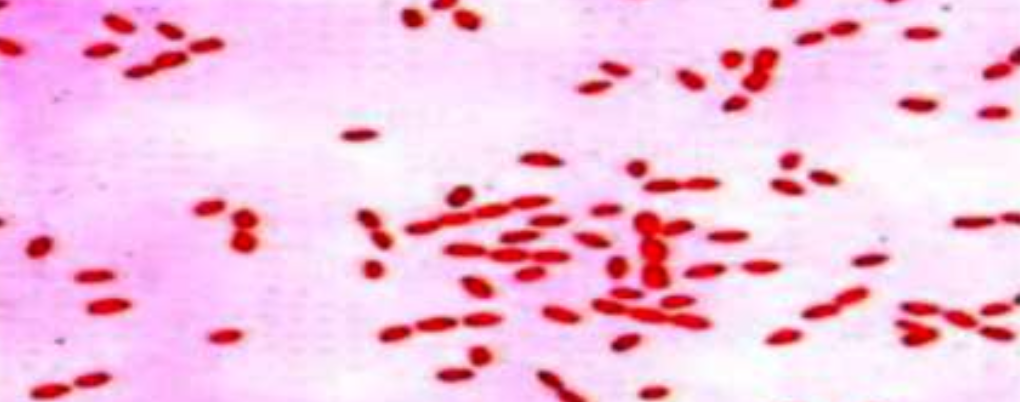 A 30 year old veterinarian complains of general fatigue, malaise, joint pains and lymph node enlargement since many months. Blood culture showed the following bacteria :
A 30 year old veterinarian complains of general fatigue, malaise, joint pains and lymph node enlargement since many months. Blood culture showed the following bacteria :
-
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Brucellosis
-
Name any risk factor for getting this disease?
- Farmers, vets, and drinking unpasteurized milk
-
Name any 3 organs or body systems which are affected by this disease in humans?
- Lymph nodes, liver, and spleen
-
Which is the most commonly used test for diagnosis? Z
- Brucella antibody titers (agglutination test)
-
Name any 2 medicines used in the treatment of this disease?
- Doxycycline and streptomycin Z
Case 13 Z
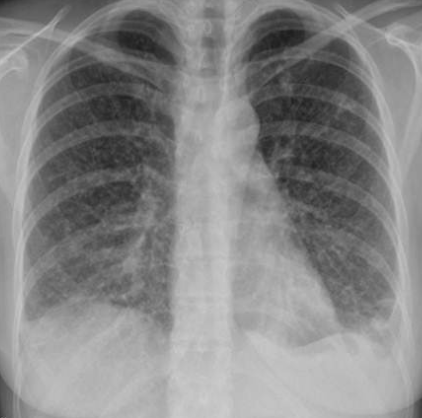 32 year female presented with fever & weight loss
32 year female presented with fever & weight loss
Describe radiological findings
What’s the abnormal here? You should read the whole chest film PA VIEW:
- The trachea looks central.
- Heart looks normal in shape and size.
- What’s abnormal? You have all this reticular shadows and nodules all over the lungs,
Bronchitis does not give a picture like this while miliary TB is a possibility.
differential diagnosis of miliary shadow of the lung?
1- Miliary TB
2- Sarcoid
3- Diffuse metastatic lesions.
4- Lymphomas
5- Silicosis
Case 14
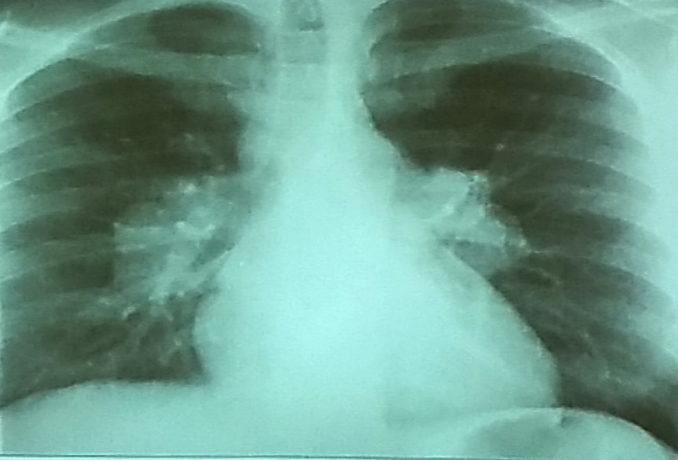 46 year old man presented six month history of with Fatigue, Fever on and off, joint pains and weight loss of 7 Kg.
46 year old man presented six month history of with Fatigue, Fever on and off, joint pains and weight loss of 7 Kg.
O/E
Tender maculopapular rash on his shins, cervical lymphadenopathy.
Investigations:
- CBC: Hb 14.6 g/dl
- WBC 4.7 X 10 /dl
- U/E’s Sodium 136 mmol/l
- Potassium 4.2 mmol/
- Calcium 2.9 mmol/l
-
What is the likely cause of rash on shins? Z a. Erythema nodosum
-
Name 2 most likely diagnoses? Z a. TB
b. Sarcoidosis
Case 15
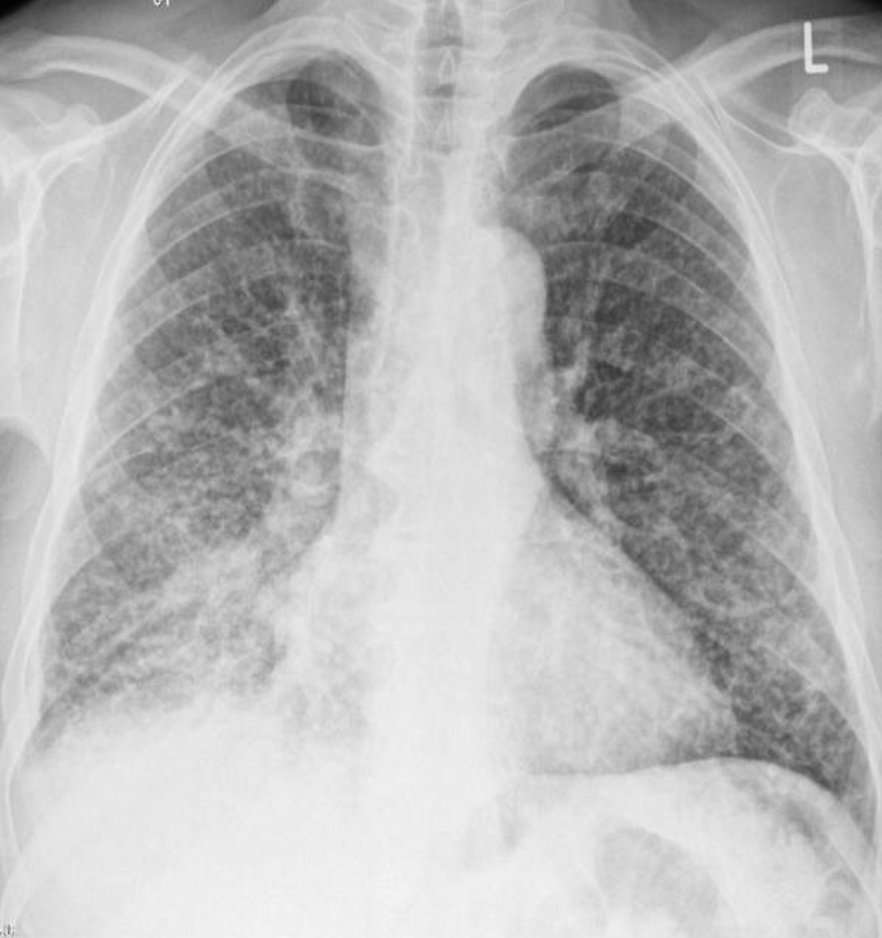 32 year male presented with fever & weight loss
32 year male presented with fever & weight loss
-
Describe radiological findings?
a. Miliary shadow
b. Bilateral reticular shadow—with sligh tracheal deviation to the right -
List two causes?
a. Miliary TB
b. Fungal infection
Case 16
A 50 year old man was diagnosed with Tuberculosis. He was started on a regimen containing INH, Rifampicin and Pyrazinamide. His TB symptoms improved but after about 2 months, he c/o general weakness and lethargy, and pain in many joints. You are his doctor and you suspect drug induced lupus.
Q1) Of all the TB drugs which he is taking, which one can cause drug induced lupus?
- INH
Q2) Which blood test will you do for diagnosis?
- ANA
- Anti histone antibody
Q3)What is the management for this case?
- Stop the drug, if possible
- Symptomatic treatment, eg. NSAIDs
Case 17 Z
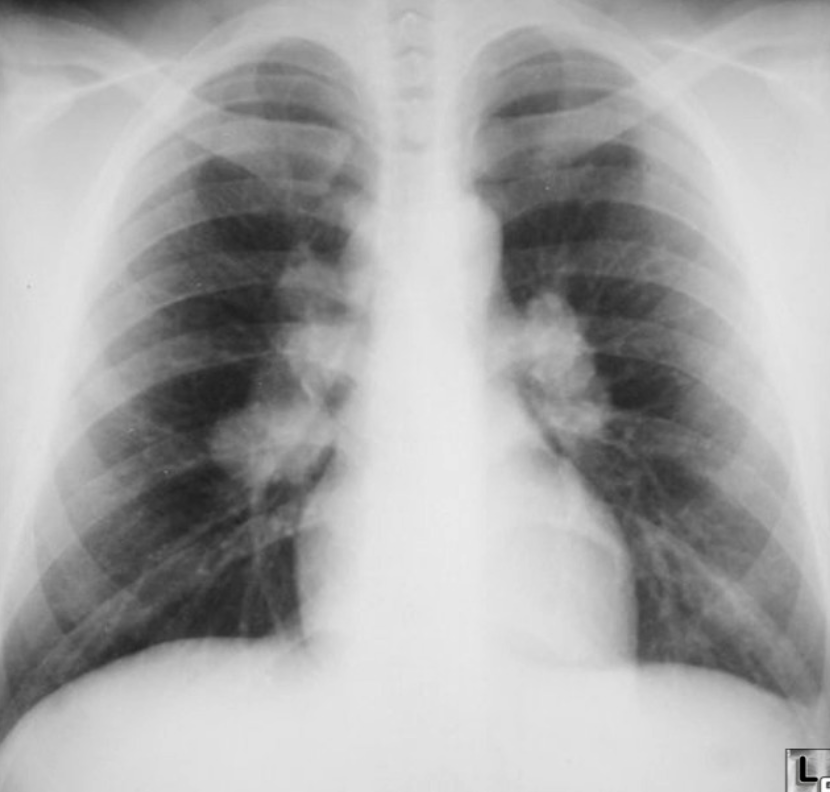 40 year old man presented with cough and shortness of breath for six months. Six weeks ago he noticed painful lumps on the skin of his legs which had resolved in two weeks
40 year old man presented with cough and shortness of breath for six months. Six weeks ago he noticed painful lumps on the skin of his legs which had resolved in two weeks
Investigation:
- FBC: normal
- Sodium 145 mmol/l
- Potassium 2.8 mmol/l
- Chloride 100 mmol/l
- Urea 2.4 mmol/l
- Serum creatinine 83 umol/l
- Calcium 3.4 mmol/l
-
What is the abnormality in CXR? Hilar lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes in the hila of both lungs)
-
What is the most likely diagnosis? Sarcoidosis; lump
Bilateral Hilar Lymphadenopathy: Causes
| Category | Causes |
|---|---|
| Sarcoidosis | Sarcoidosis |
| Infection | * Tuberculosis * Fungal infection * Mycoplasma * Intestinal Lipodystrophy (Whipple’s disease) |
| Malignancy | * Lymphoma * Carcinoma * Mediastinal tumors |
| Inorganic dust disease | * Silicosis * Berylliosis |
| Extrinsic allergic alveolitis | * Such as bird fancier’s lung |
| Less Common Causes | * Churg-Strauss syndrome * Human immunodeficiency virus * Extrinsic allergic alveolitis * Adult-onset Still’s disease |
A 68 year old man presented with long standing progressively worsening breathlessness on exertion. He smoked 20 cigarettes daily and on examination was wheezy. Investigations showed:
- FEV1 1.51 (predicted 2.1 3.1)
- FVC 2.91 (predicted 3.0 4.4)
- FEV1/FVC 52%
- Total lung capacity (TLC) 7.01 (predicted 4.9 7.4)
- Transfer factor for carbon Monoxide (TLCO) 5.5 mmol/min/kPa (predicted 6.4 9.6)
- Transfer coefficient for carbon Monoxide (KCO) 0.85 mmol/min/kPa (predicted 1.1 1.6)
- Hb 17. G/dl
-
What is the type of respiratory failure?
**Type II respiratory failure. This is indicated by the low FEV1/FVC ratio (indicative of obstructive lung disease) and elevated pCO2 -
What is the diagnosis?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), likely due to a long history of smoking. This is supported by the low FEV1/FVC, clinical presentation, and smoking history. Further investigations may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possibilities.