-
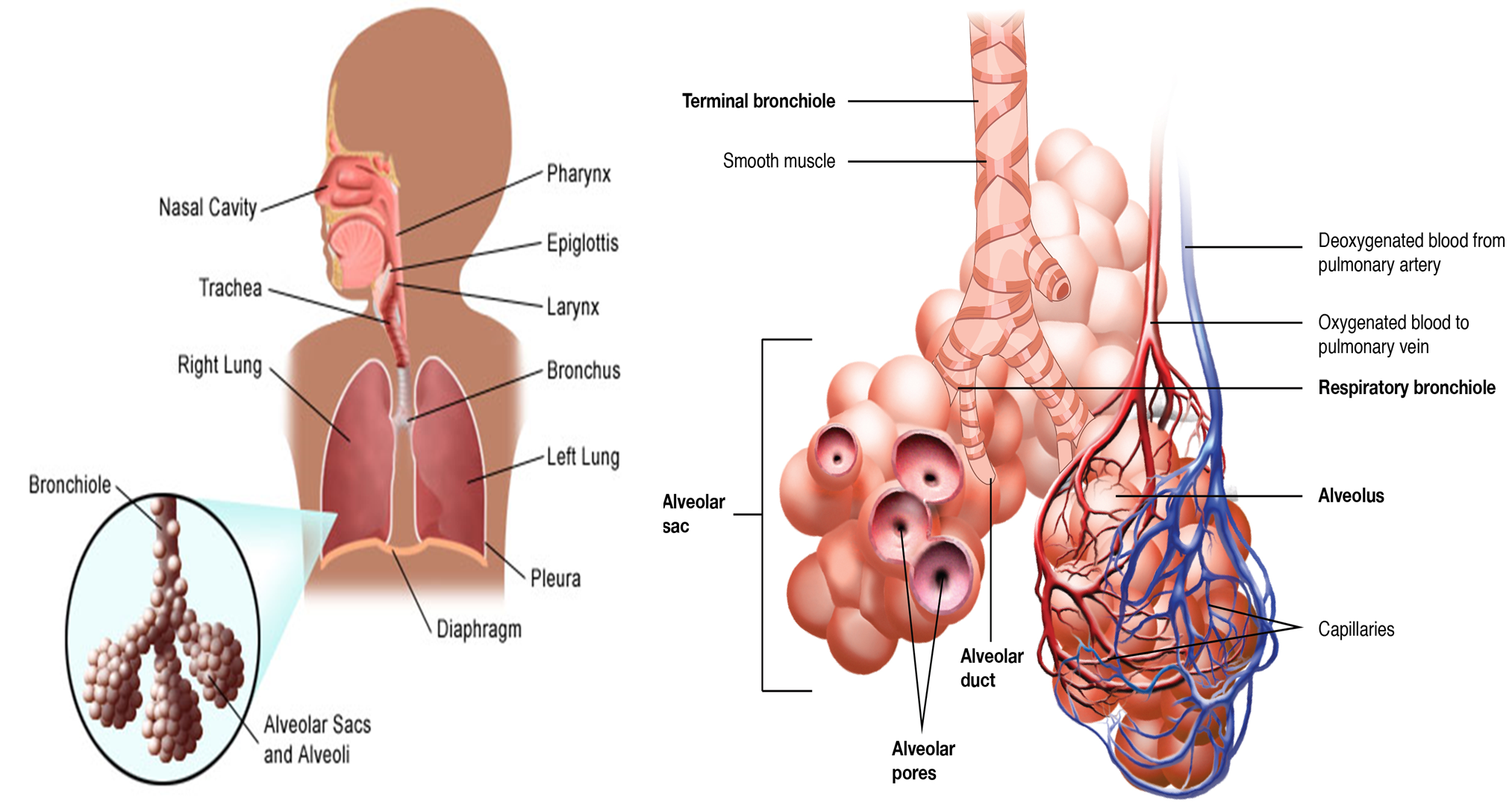
The respiratory tract extends from the nose to the alveoli and includes not only the air-conducting passages also but the blood supply
-
The primary purpose of the respiratory system is gas exchange.
-
The respiratory system is divided into two parts: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
(cc) TAB
The Upper Respiratory Tract
- The nose
- Pharynx
- Adenoids
- Tonsils
- Epiglottis
- Larynx
- Trachea.
The lower respiratory tract
- Bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Alveolar ducts
- Alveoli
- With the exception of the right and left main-stem bronchi, all lower airway structures are contained within the lungs.
Physiology of Respiration
Ventilation: ventilation involves inspiration (movement of air into the lungs) and expiration (movement of air out of the lungs).
Contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscle - Increases chest dimensions, thereby decreasing intrathoracic pressure - Gas flows from an area of higher pressure (atmospheric) to one of lower pressure (intrathoracic)