اللهم يا معلّم موسى علّمني، ويا مفهم سليمان فهّمني، ويا مؤتي لقمان الحكمة وفصل الخطاب آتني الحكمة وفصل الخطاب اللهم اجعل ألستنا عامرة بذكرك، وقلوبنا بخشيتك، وأسرارنا بطاعتك، إنك على كل شيء قدير، حسبنا الله ونعم الوكيل
Question 1
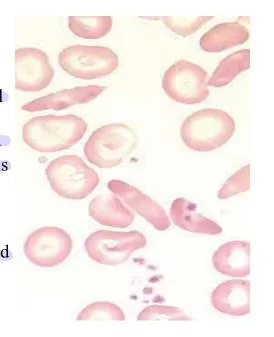
- A 20-year-old male presented with Hb 10 mg/dl, MCV 66 fl, recently on isoniazid for TB. Attached blood smear.
 Characterized by the presence of increased serum iron, ferritin, and transferrin saturation as well as ringed sideroblasts
Characterized by the presence of increased serum iron, ferritin, and transferrin saturation as well as ringed sideroblasts
microcytic, hypochromic cells alongside normocytic cells), possibly Pappenheimer bodies (iron granules in RBCs
Features
- The acquired form: drugs such as chloramphenicol, isoniazid, or alcohol
- Elevated serum ferritin
- Very high transferrin saturation, and very low TIBC
- High serum iron (the only microcytic anemia with elevated iron)
- Prussian blue stain (most specific test) of RBCs in the marrow will reveal the ringed sideroblasts.
- Treatment: Remove the offending drug. Consider transfusion for serious cases.
Question 2
-
A 23-year-old primigravida presented for her antenatal care follow-up. She is in her 28 weeks of pregnancy. She didn’t have any symptoms except for mild dyspepsia.
-
Lab test
-
FBC
-
Antibody testing
-
G challenge test
-
Syphilis
-
Procedure indicated if needed
-
Administer anti D immunoglobulin if indicated.
Question 3
- A 3-year-old child presented with a sore throat for 2 days with fever and tender cervical lymphadenopathy. His weight is 25 kg. Attached picture for his throat examination.
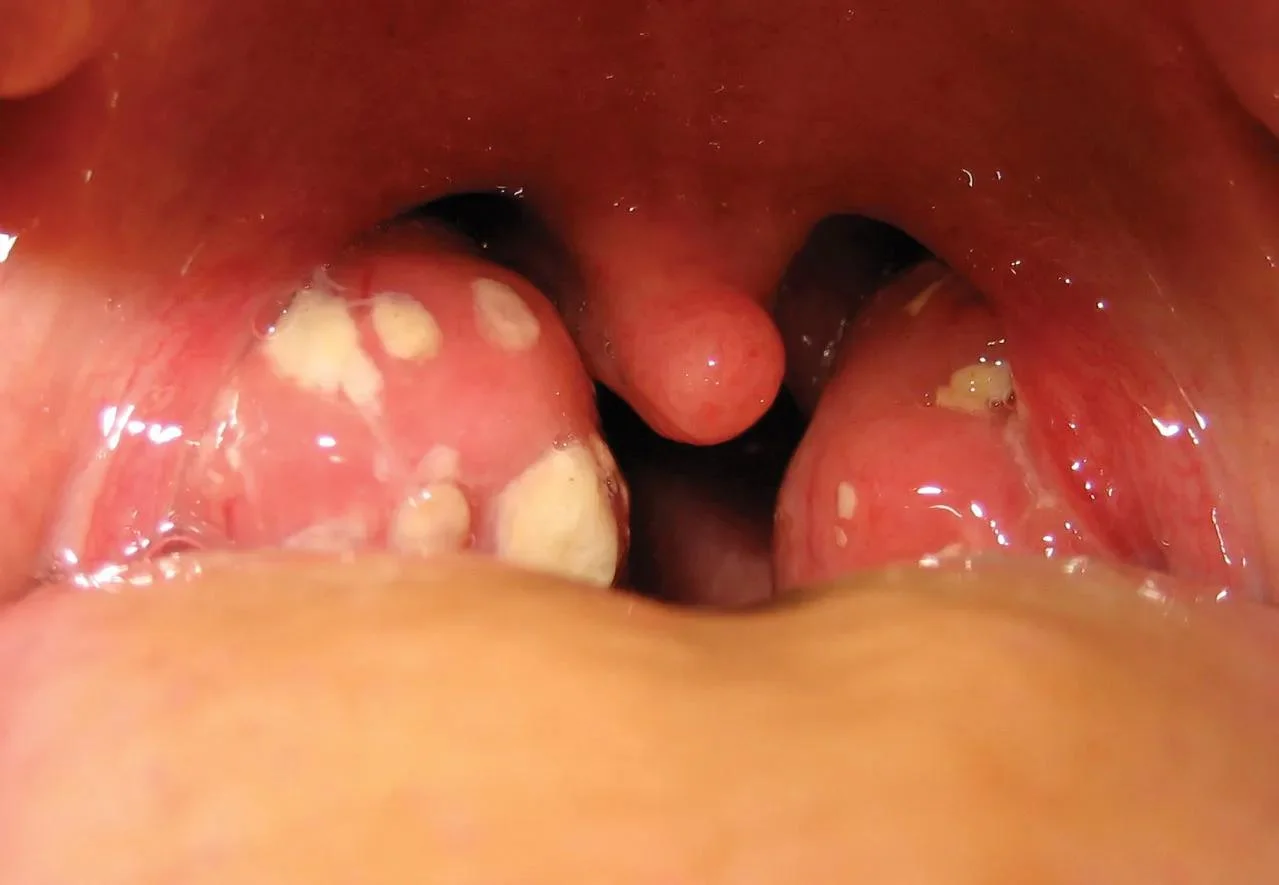
- Acute bacterial tonsillitis - GAS
- Amoxicillin – 15-30 mg/kg or – 125 mg/5 ml twice or 3 times/day for 10 days.
- Ibuprofen – 2.5 ml 3 to 4 times/day
- Paracetamol
Question 4
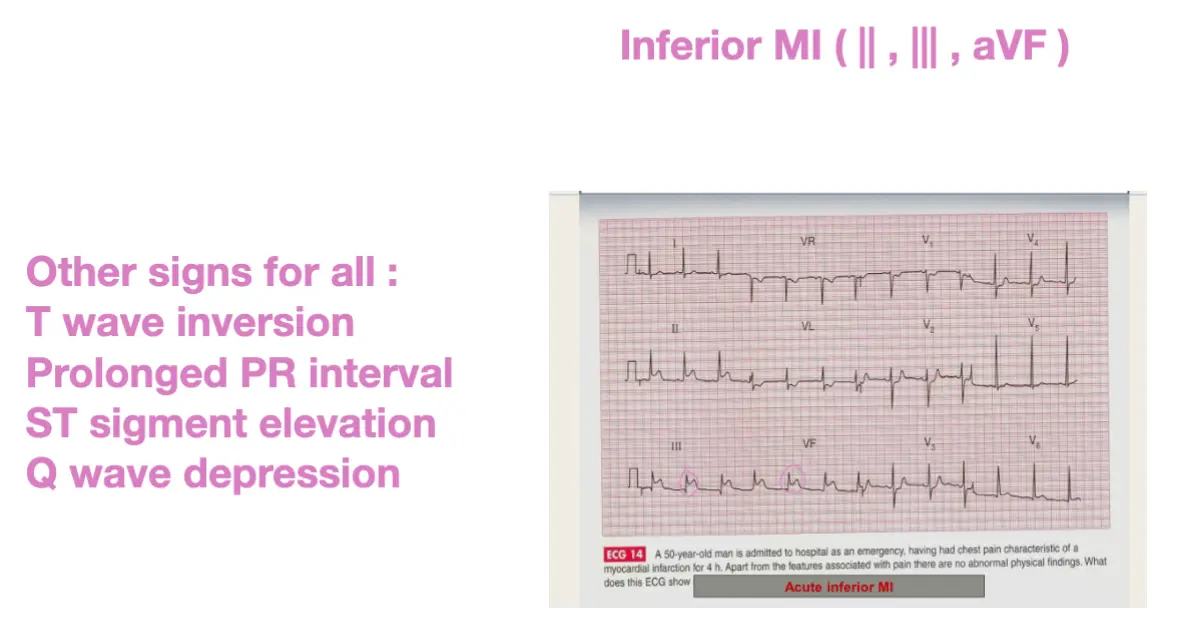
- A 50-year-old man is admitted to the hospital as an emergency, having had chest pain characteristic of myocardial infarction for 4 hours. Apart from the features associated with pain, there are no abnormal physical signs.
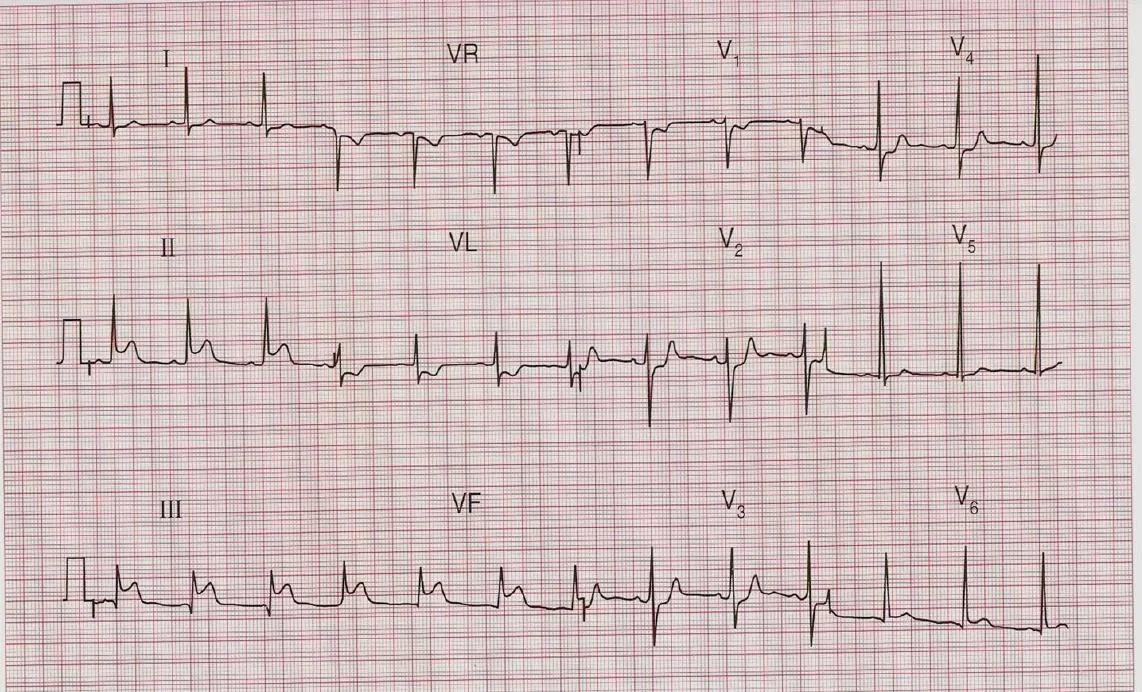 Abnormal findings: ST elevation in 11/111 & aVf.
Abnormal findings: ST elevation in 11/111 & aVf.
- Diagnosis: Inferior MI.
ABC, MONA, ECG, toponin CK, PCI, CBC
Question 5
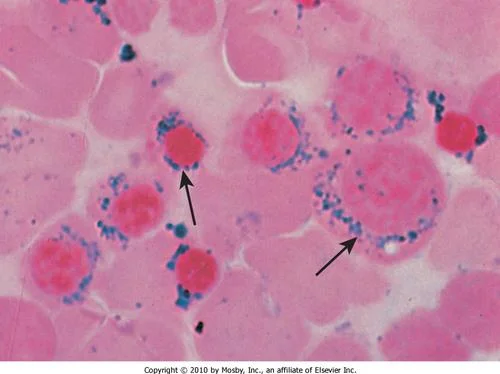
- A 9-year-old child presented with Hb 10 mg/dl, MCV 85 fl, decreased haptoglobin and hemoglobinuria after sulpha drug. Attached blood smear.
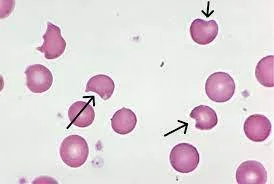 G6PD - Bite cells,
G6PD - Bite cells,
inheritance x-linked
-
Treatment: There is no specific therapy beyond hydration and transfusion if the hemolysis is severe.
-
The main therapy is to avoid oxidant stress in the future.
- (Antipyretic, Sulfonamide, Anti-malarial, or fava beans) producing an acute and severe hemolytic syndrome called FAVISM, Z
- Hb level becomes very low,
- presence of hemoglobinemia /-uria,
- mild jaundice,
- splenomegaly and increased reticulocyte count.
Question 6
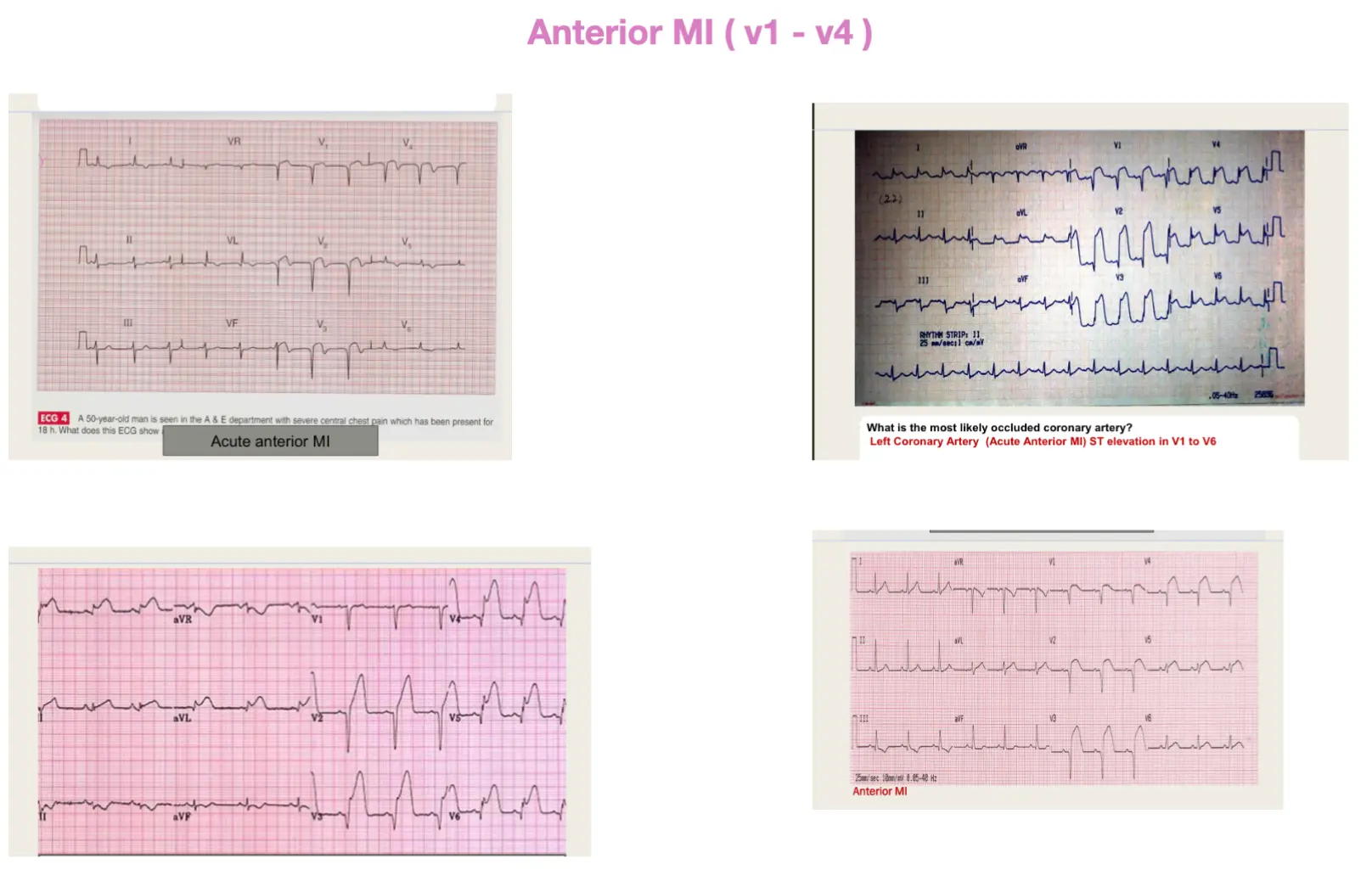
- A 59-year-old male presented with severe chest pain for 30 minutes. His ECG is attached.

Abnormality: ST elevation in V1/V2/V3 & V4 Diagnosis: STEMI or anterior MI.
Question 7
- A 23-year-old primigravida presented for her antenatal care follow-up. She said her last menstrual period (LMP) had finished 07/12/2024, she has regular periods and usually the cycle lasts for 4 days. She didn’t have any symptoms except for mild dyspepsia.
EDD = 10/09/25
Calculations: * Estimated Date of Delivery (EDD) using Naegele’s Rule: (LMP Start Date + 7 days) - 3 months OR + 9 months + 7 days. EDD = (04/12/2024 + 7 days) + 9 months = 11/12/2024 + 9 months = ± 10±11/09/2025.
Question 8 Y
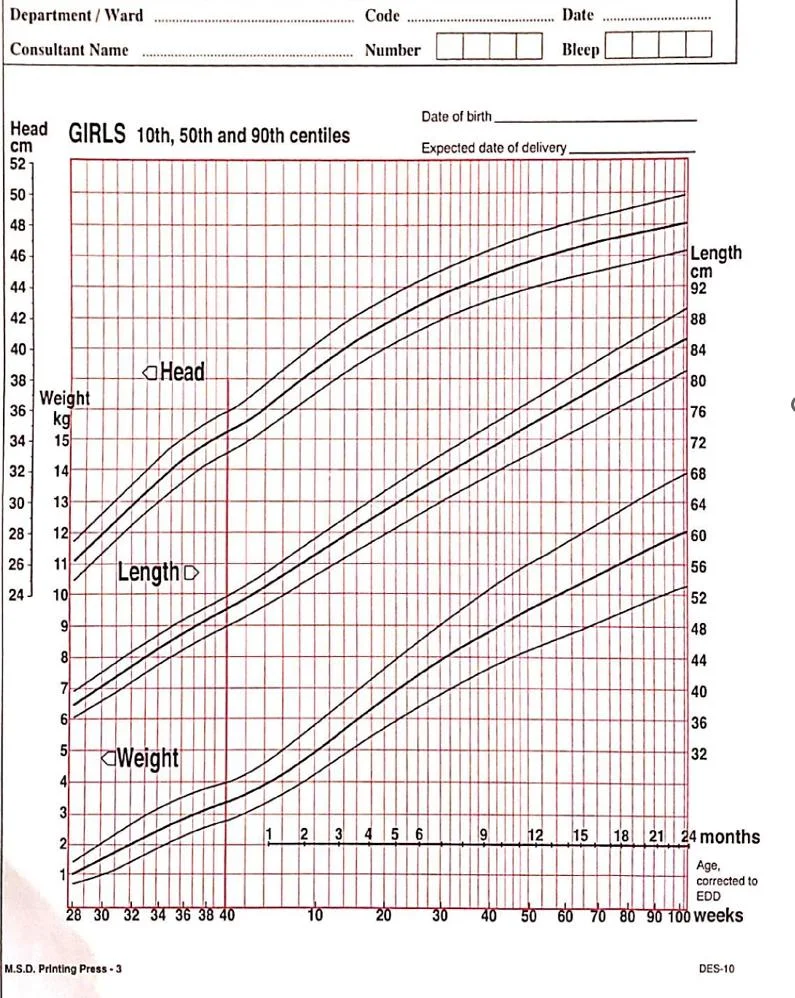
A woman known of gestational DM brought her 12-month-old child for routine immunization: your nurse brought the girl’s immunization card, with this information:
Clinical Findings:
| Head circumference | 46 cm |
|---|---|
| Body weight | 12 kg |
| Length | 74 cm |
- Fill the form provided
-
What you are going to tell her mum about your findings:
-
The head circumference is: ---------------------
-
Her length is: ---------------------
-
Her body weight is: ---------------------
-
Question 9
- A 43-year-old female presented with this skin discoloration in her neck for many years. Her BMI is 34.
 a). Acanthosis nigricans.
b). DM or other metabolic syndromes |
a). Acanthosis nigricans.
b). DM or other metabolic syndromes |
Question 10
- A 10-year-old child with this blood film. He has anemia and unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. MCV is normal.
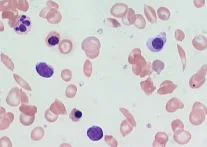 SCA
SCA
- A- Sickle cells - blood smear
- B- HgS – Hg A2 & no HgA - sickle cell anemia
Question 11
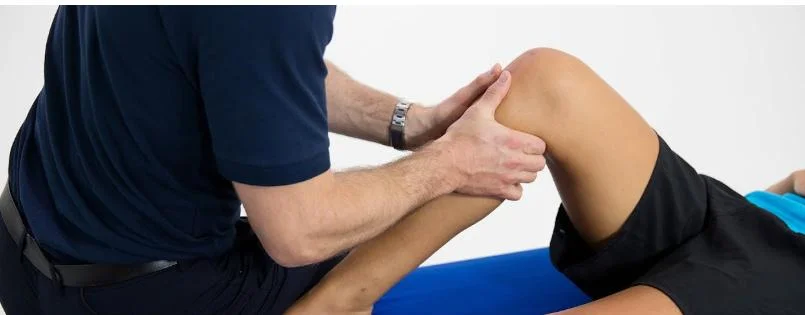
Plain X-ray of the knee for a 60-year-old lady with OA.
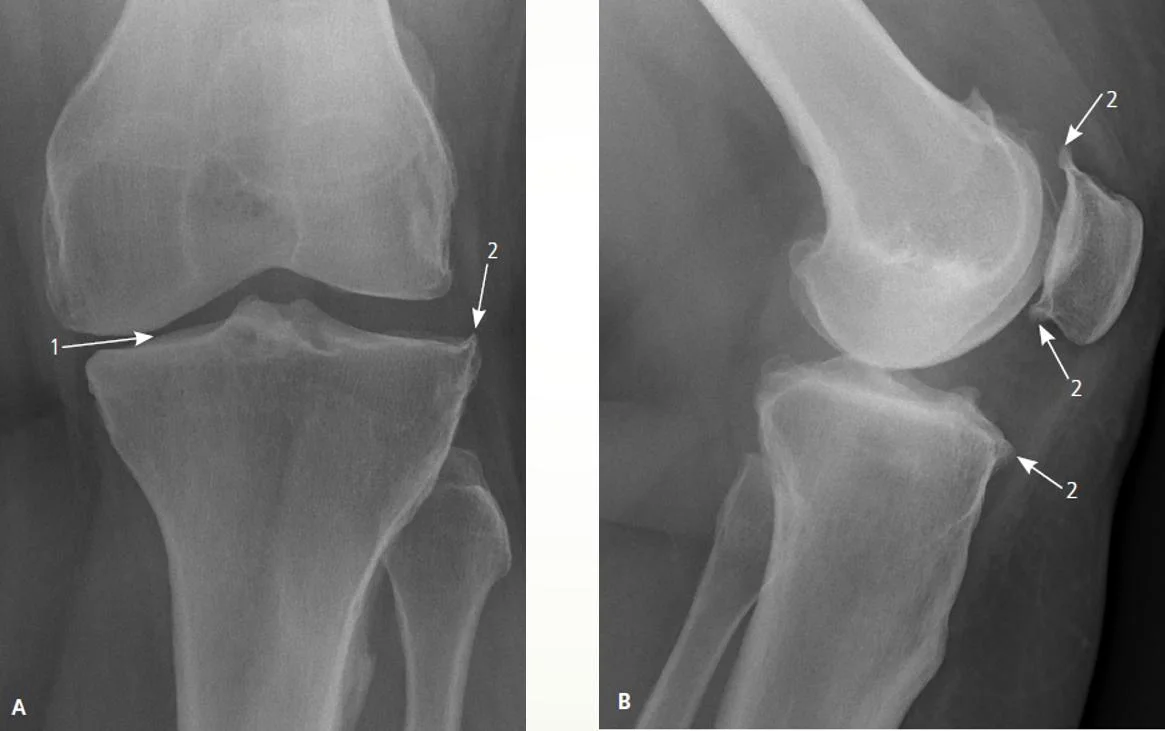
- Joint Space Narrowing: Usually asymmetric, often affecting the medial tibiofemoral compartment more than the lateral. 2. Osteophytes: Bony spurs forming at the joint margins (e.g., tibial spines, femoral condyles, patellar edges).
Other findings that may appear - Subchondral Sclerosis: Increased bone density in the bone immediately beneath the cartilage layer. - Subchondral Cysts: Fluid-filled cavities in the bone near the joint surface. - +/- Malalignment: Varus (bow-legged) or valgus (knock-kneed) deformity may develop.
Question 12.
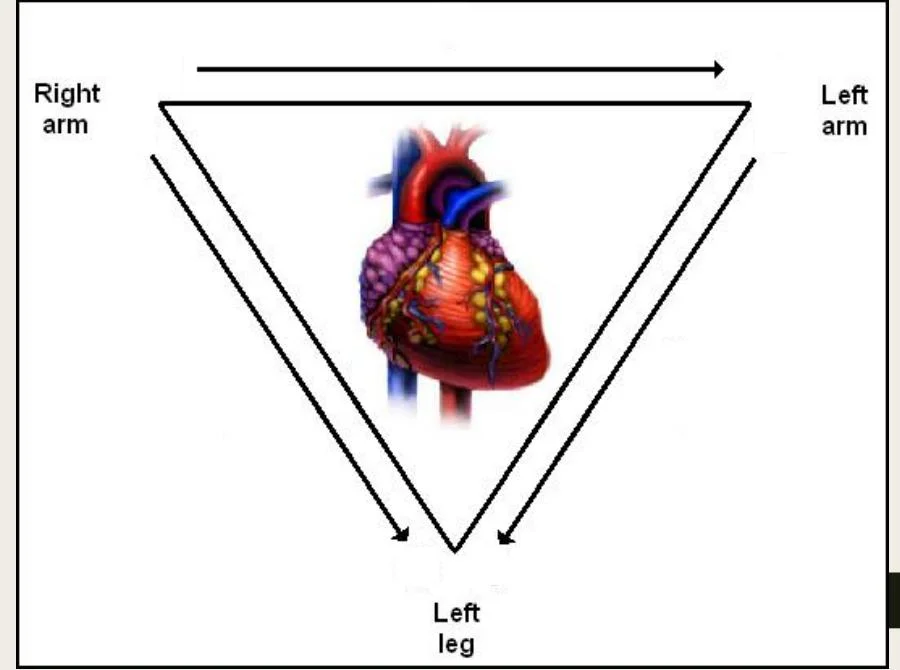
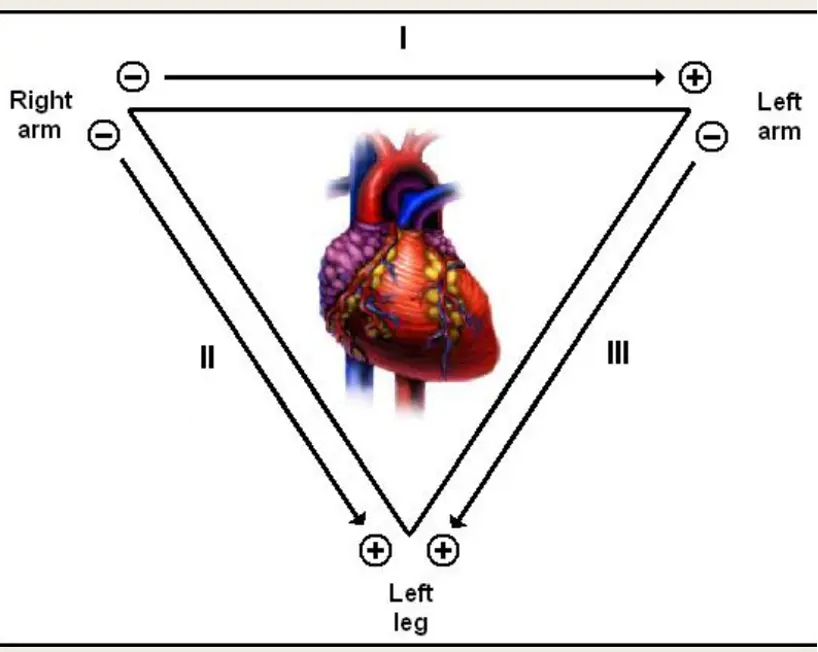
Standard Limb Leads
-
Label The Leads as 1/11/111 – Put + & - electrodes
- Lead I: Potential difference between Left Arm (+) and Right Arm (-). [ LA(+) — RA(-) ]
- Lead II: Potential difference between Left Leg (+) and Right Arm (-). [ LL(+) — RA(-) ]
- Lead III: Potential difference between Left Leg (+) and Left Arm (-). [ LL(+) — LA(-) ] (RA=Right Arm electrode, LA=Left Arm electrode, LL=Left Leg electrode)
Answer:
Question 13.
What is the most occluded coronary artery?
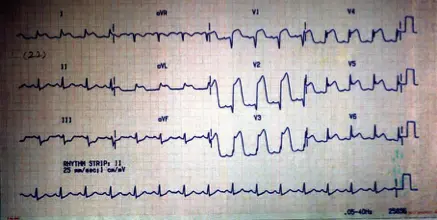
Left ant CA
Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery (also known as the anterior interventricular artery), a branch of the Left Coronary Artery. c
Infarction (STEMI/STE-ACS)
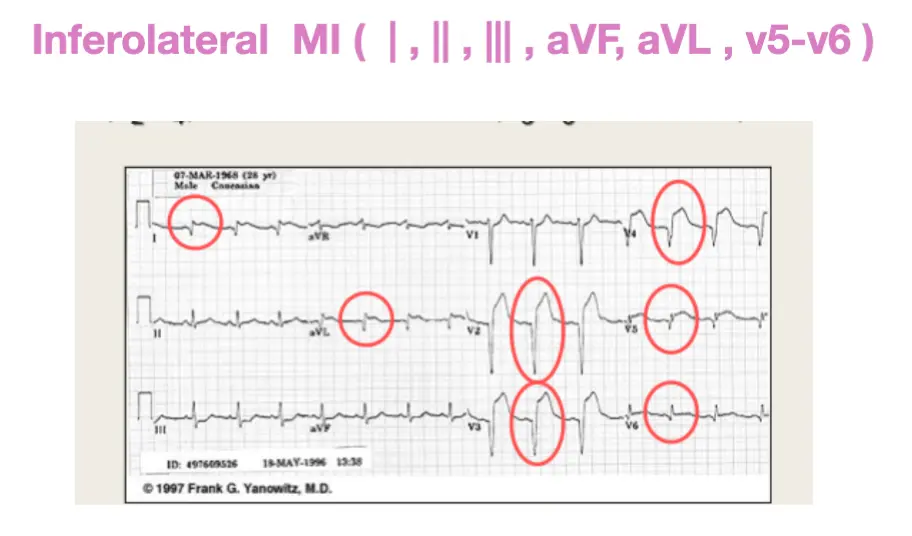
| Leads with ST segment elevations | Affected myocardial area | Occluded coronary artery (culprit) |
|---|---|---|
| V1–V2 | Septal | Proximal LAD. |
| V3–V4 | Anterior | LAD. |
| V5–V6 | Apical | Distal LAD, LCx or RCA. |
| I, aVL | Lateral | LCx. |
| II, aVF, III | Inferior | 90% RCA. 10% LCx. |
Question 14
- A mother brought her 6-month-old infant for asymmetrical hip movement. A special test was performed resulting in a positive sign.
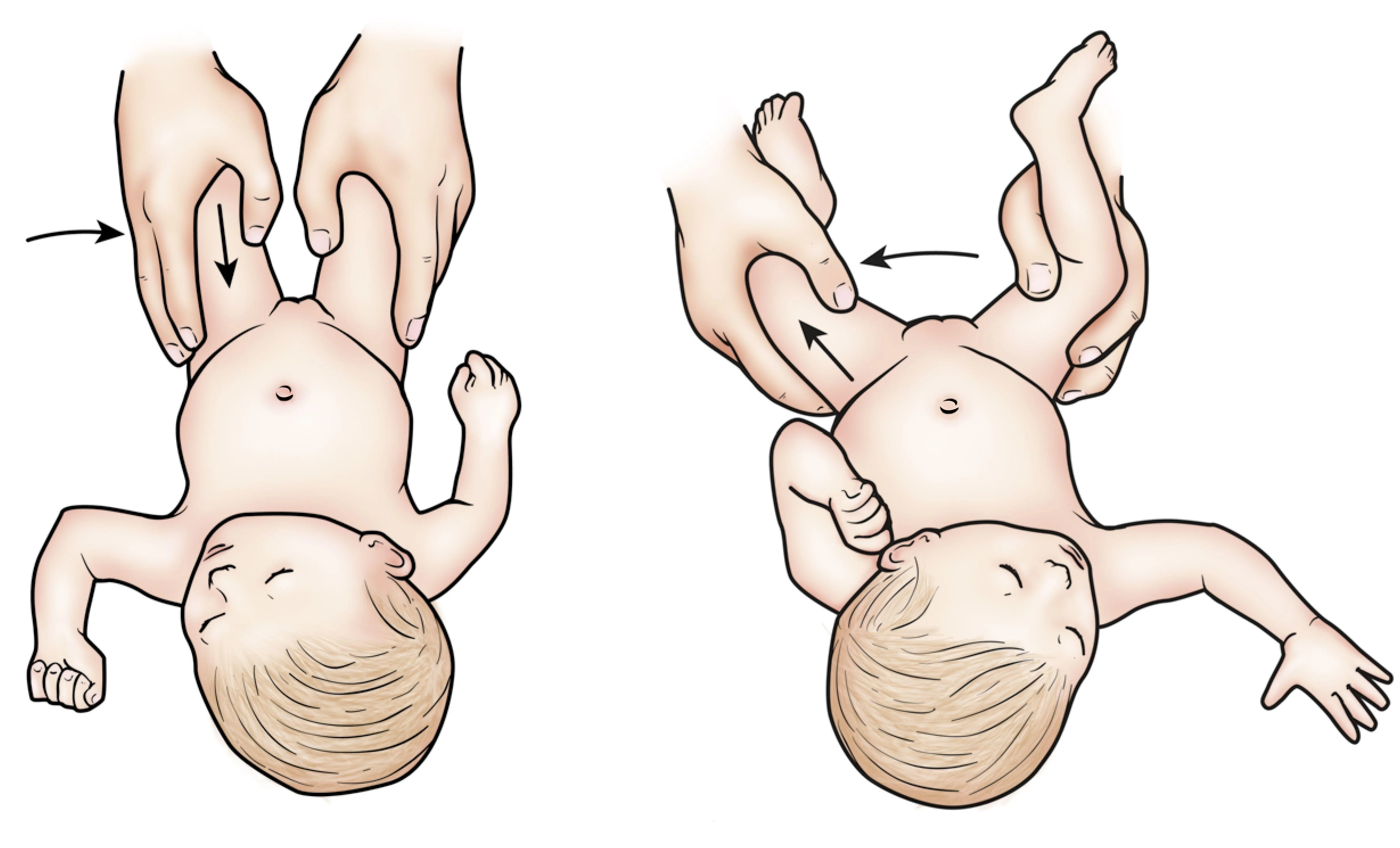 A is Barlow test - *B is Ortolani test *
A is Barlow test - *B is Ortolani test *
* **Barlow Test:** Detects an unstable hip that can be dislocated. Positive = palpable 'clunk' as femoral head slides out of acetabulum upon gentle adduction and posterior pressure.
* **Ortolani Test:** Detects a dislocated hip that can be reduced. Positive = palpable 'clunk' as femoral head slides back into acetabulum upon gentle abduction and forward pressure.
Question 15. Dix-Hallpike

-
To check for right side involvement, rotate the patient’s head to the right 45 degrees while in the long sitting position (this aligns the right posterior semicircular canal with the sagittal plane of the body).
-
The examiner grasps the patient’s head and quickly moves the patient to the supine position with the neck slightly extended (ear down position).
-
The examiner checks for nystagmus. If present, note the latency, duration, and direction (should not last more than 1 minute).
- Purpose: To diagnose Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), specifically of the posterior semicircular canal (most common).
- Procedure Briefly: Patient sits upright, head turned 45° to one side. Examiner rapidly moves patient to supine position with head extended ~20-30° below horizontal, maintaining the 45° turn. Observe eyes for ~30 secs. Repeat for other side.
- Positive Test: Reproduction of vertigo AND observation of characteristic nystagmus (typically torsional/rotatory and upbeating towards the undermost ear, with latency, short duration <1 min, fatigability).
Question 16. How to measure BP?
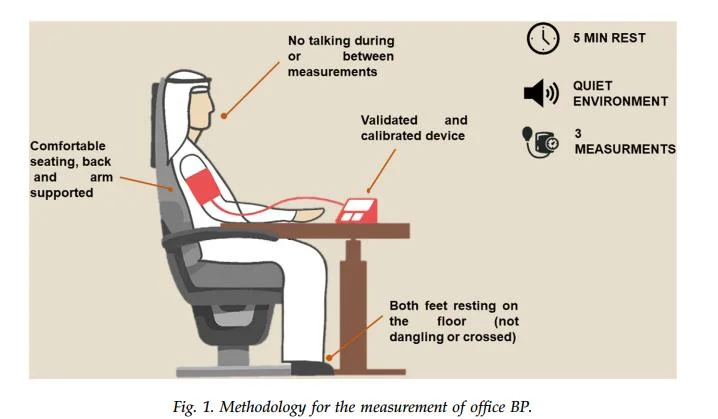
I. Patient-Related Standards
- Comfortable seating, back and arm supported
- Validated and calibrated device
- Both feet resting on the floor (not dangling or crossed)
- No talking during or between measurements
- 5 MIN REST
- QUIET ENVIRONMENT
- 3 MEASUREMENTS
Validated and calibrated device
II. Equipment-Related Standards
-
Appropriate cuff size: The cuff bladder should encircle 80% of the arm, and the cuff width should be 40% of the arm circumference.
-
Correct cuff position:
- a. distance of 2.5 cm (2 fingers) should be maintained between the lower end of the cuff and the antecubital fossa.
- b. Cuff bladder should be centered over the brachial artery.
- c. Cuff should be wrapped around the upper arm, firmly in contact with the arm, but not too tight and not too loose, allowing 2 fingers to be put under the cuff comfortably.
-
Correct stethoscope position:- The bell orifice of the stethoscope should be placed just above and medial to the antecubital fossa but below the edge of the cuff. The stethoscope bell orifice should not touch the cuff bladder or tubing.
-
Correct manometer position: (for mercury BPM) The position of the mercury manometer should be upright at examiner’s eye level, and at zero level.
Question 17.
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
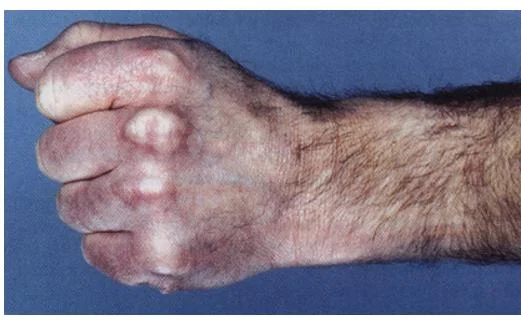



-
1. Arcus cornealis ~ eyes
-
2. Xanthelasma ~ around eyes
-
3. Xanthomas ~ hand
-
Familial hypercholesterolemia (hereditary) is a common genetic disease caused by mutation of one or more of the genes critical for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) catabolism.
-
- Autosomal dominant genetic disease.
-
The diagnosis can be made with genetic testing or clinical criteria like the Dutch Lipid Clinic Network criteria.
-
Once we identify familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) in a patient, we recommend screening of all first-degree relatives.
Question 18. Straight Leg Raising (SLR)
In SLR after you perform the test, to further assess the neurological tissue, move out of the painful range & then either do:
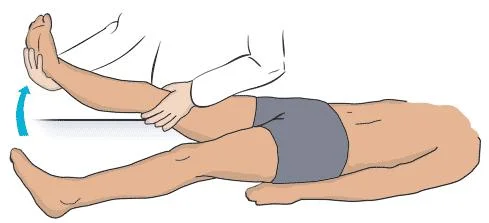
-
Dorsiflex the neck - Bragard’s sign
-
Flex the neck - Neri sign
-
Raise the patient’s extended leg with the ankle dorsiflexed.
-
Normally 80 – 90 degrees no pain
-
It will be limited by sciatica pain in lumbar disc prolapse. (<70 ) → (exactly from 30 to 70)
Question 19.
During knee examination, to assess knee ligaments:
 Ant. Drawer test * Post. Drawer test
Ant. Drawer test * Post. Drawer test
* **ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament):** Lachman test, Anterior Drawer test, Pivot Shift test.
* **PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament):** Posterior Drawer test, Posterior Sag sign (Godfrey's test).
* **MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament):** Valgus stress test (apply outward force to knee at 0° and 20-30° flexion).
* **LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament):** Varus stress test (apply inward force to knee at 0° and 20-30° flexion).
Question 20.
Classification of Obesity Risks based on BMI & WC Classification of disease risks by WHO.
| BMI (Kg/sq. m) | Classification | Men WC 94-102 cm / Women WC 80-88 cm | Men WC > 102 cm / Women WC > 88 cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18.5–24.9 | Normal weight | - | 1 |
| 25-29.9 | Overweight | Increased | High |
| 30-34.9 | Obese class 1 | High | Very high |
| 35-39.9 | Obese class 11 | 2 | Very high |
| ≥ 40 | Obese class 111 | 3 | Extremely high |
| 1- No risk | |||
| 2- Very high | |||
| 3- Extremely high |
* Overweight + High WC = Increased Risk
* Obesity I + Normal WC = High Risk
* Obesity I + High WC = Very High Risk
* Obesity II = Very High Risk
* Obesity III = Extremely High Risk
*
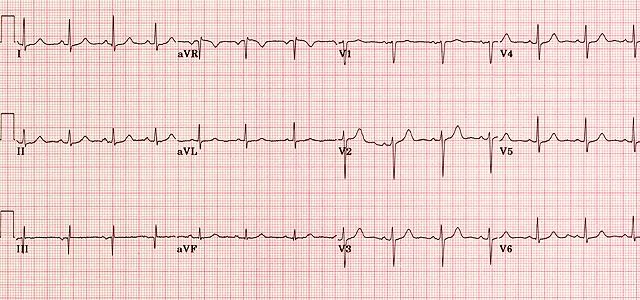
Question 21. Normal ECG
-
*Heart Rate: 60 - 100 bpm
-
*The P waves in leads I and II must be upright (positive) if the rhythm is coming from the sinus node
-
*Each QRS complex is preceded by a normal P wave
-
Normal P wave axis: P waves upright in leads I and II, inverted in aVR.
-
*The PR interval remains constant
-
In the normal ECG the T wave is always upright in leads I, II, V3-6, and always inverted in lead aVR.
- Rate: 60-100 bpm
- Rhythm: Regular
- P waves: Upright in lead II, one preceding each QRS, consistent morphology
- PR interval: 0.12-0.20 sec (3-5 small squares), constant
- QRS duration: < 0.12 sec (< 3 small squares)
- QT interval: Corrected (QTc) typically < 0.44 sec (varies slightly by sex/rate)
- Axis: Normal (e.g., 0° to +90°)
- ST segment: Isoelectric (no significant elevation/depression)
- T waves: Appropriate direction (usually upright except aVR, V1)
- No significant abnormalities (e.g., pathological Q waves, bundle branch blocks, hypertrophy patterns, arrhythmias).
-
Question 22.
Haemoglobin Electrophoresis in Sickle Cell Anemia

Haemoglobin electrophoresis in sickle cell anaemia - Typical Result for Sickle Cell Anemia (HbSS): * Hb S: Predominant fraction (usually 85-95% or more) * Hb A: Absent * Hb F: Variable, often elevated (e.g., 5-15%) * Hb A2: Normal levels (approx. 2-3.5%)
Question 23.
The 5 As Model for Treatment of Tobacco Use and Dependence. Smoking Cessation Treatment for Those Willing to Quit.
- 5As
-
Ask about a patients’ smoking status.
-
Advise those who smoke to stop.
-
Assess their readiness to stop.
-
Assist smokers in their stopping attempts.
-
Arrange for follow-up on these attempts.
- Behavioral treatment examples: Recommend a quit plan, such as STAR.
- S = Set a quit date: Choose a specific date, usually within 2 weeks.
- T = Tell family, friends, co-workers: Inform support network and ask for help.
- A = Anticipate challenges: Identify triggers and plan coping strategies for withdrawal/cravings.
- R = Remove tobacco products: Discard cigarettes, lighters, etc., from environment.
-
Question 24
A 27-year-old lady has burning micturition, increased frequency of urination, and lower abdominal pain since 3 days.
- She had similar attacks 3 times during the last 6 months.
Prophylaxis treatment
- Trimethoprim 100 mg -
- Co-Trimoxazole 480 mg -
- Cefalexin 125 mg at night)
Question 25.
Urine Dipstick Result
 UTI
Low ph, Positive Leukocytes and nitrite, high Glucose
UTI
Low ph, Positive Leukocytes and nitrite, high Glucose
* **Leukocyte Esterase:** If positive, suggests pyuria (WBCs), indicative of inflammation/infection. *(an enzyme released by leukocytes, reflecting pyuria)*
* **Nitrites:** If positive, suggests presence of nitrate-reducing bacteria (common UTI pathogens like E. coli). *(reflecting the presence of Enterobacteriaceae which convert urinary nitrate to nitrite)*
* **Blood:** If positive, indicates hematuria (microscopic or macroscopic). Causes: infection, stones, malignancy, renal disease.
* **Protein:** If positive (>trace), suggests renal pathology (glomerular/tubular disease) or can be transient.
* **Glucose:** If positive, suggests hyperglycemia exceeding renal threshold (Diabetes).
* **Ketones:** If positive, suggests fat metabolism (DKA, starvation, low-carb diet).
* **pH:** Assesses acidity/alkalinity. Can be altered by diet, systemic state, infection (urea-splitting organisms cause alkaline pH).
* **Specific Gravity:** Measures concentration/hydration status.
* **Bilirubin/Urobilinogen:** Screen for hepatobiliary disease/hemolysis.
- Example UTI: Dipstick might show positive Leukocyte Esterase and positive Nitrites, possibly positive Blood. Other parameters usually normal in uncomplicated cystitis.
OSBE
Lina Serhan
1. Dermatological Conditions
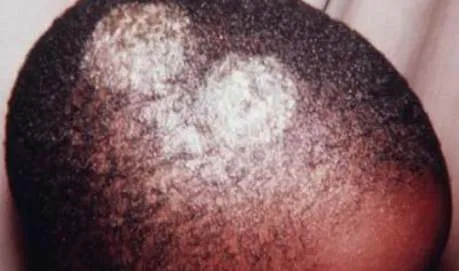
1.1 Tinea Capitis
- Diagnosis: Tinea Capitis
- Treatment: Oral terbinafine 250mg/day for 1.2-3 months
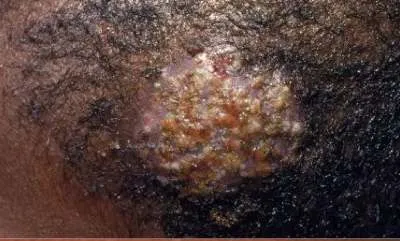
1.2 Tinea Pedis
- Diagnosis: Tinea Pedis
- Treatment: Local antifungal for 3 weeks
- Common to see in which patient?: Diabetic
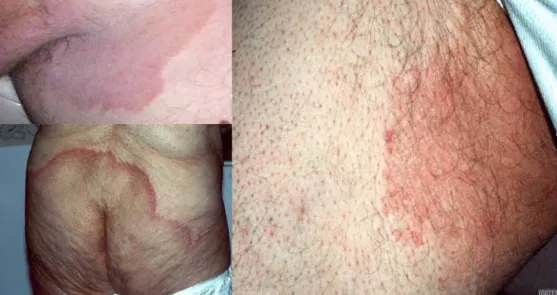
1.3 Tinea Cruris
- Diagnosis: Tinea Cruris
- Treatment: Topical antifungal twice daily for 3 weeks; apply 2 cm beyond the lesion
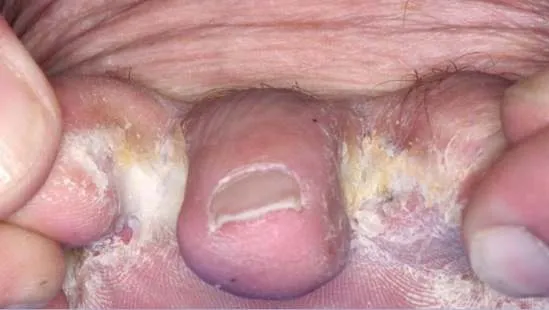
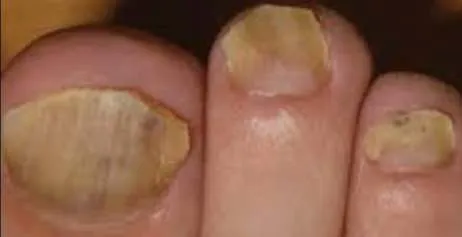
1.4 Tinea Unguium
- Diagnosis: Tinea Unguium
- Treatment: Oral terbinafine 250mg/day for 1.2-3 months
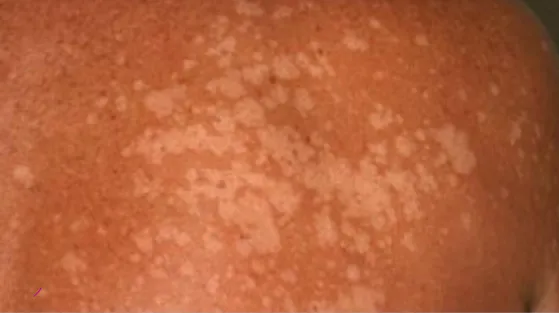
1.5 Tinea Versicolor (Hypopigmented Type)
- Diagnosis: Tinea Versicolor (Hypopigmented Type)
- Treatment: Topical antifungal twice daily for 3 weeks; apply 2 cm beyond the lesion
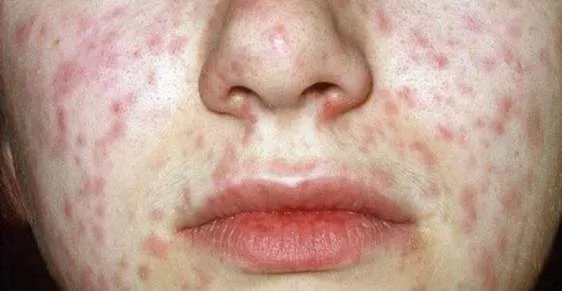
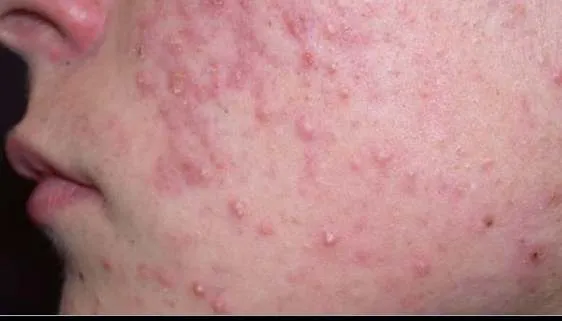
1.6 Acne Vulgaris
- Diagnosis: Acne Vulgaris
- Treatment:
- Topical Retinoid
- Topical Antibiotic
- Oral Erythromycin 250 mg/day 4 times for 3 months
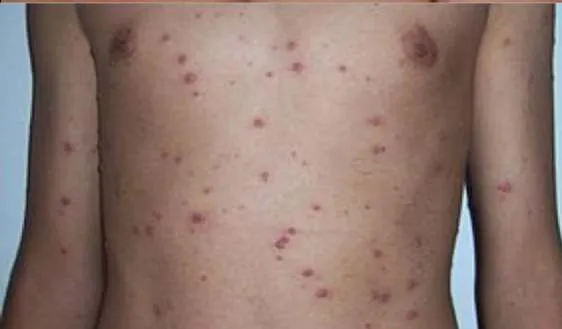
1.8 Herpes Zoster
- Diagnosis: Herpes Zoster
- Treatment: Acyclovir 800 mg/day 5 times for 7-10 days
- Most common complication?: Post herpetic neuralgia
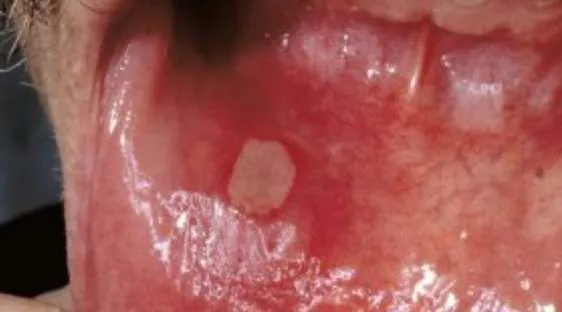
1.9 Herpes Simplex
- Diagnosis: Herpes Simplex
- Treatment:
- Topical analgesic (in children)
- Acyclovir 200 mg/day 5 times for 5 days
1.10 Varicella (Chicken Pox)
- Diagnosis: Varicella (Chicken Pox)
- Treatment:
- Symptomatic treatment; can use permanganate 1/8000 to dry the vesicles
- Paracetamol 15 mg/kg/dose every 6 hours for the first 2 days, then as needed
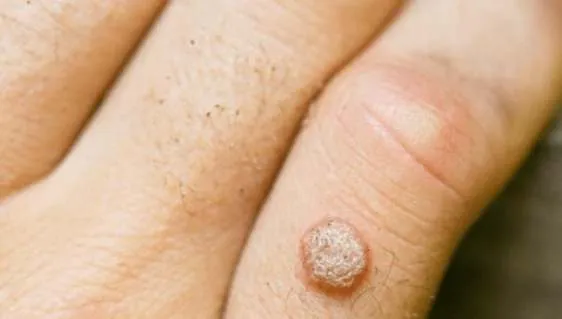
1.11 Verruca Valgaris (Wart)
- Diagnosis: Verruca Valgaris (Wart)
- Treatment: Salicylic acid
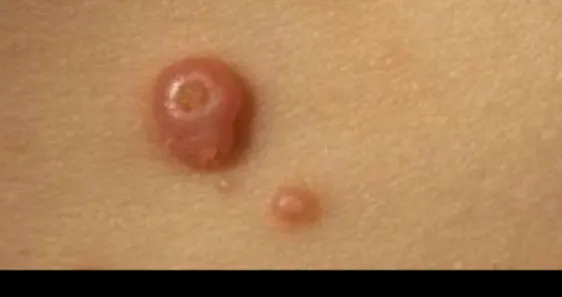
1.12 Molluscum Contagiosum
- Diagnosis: Molluscum Contagiosum (characterized by central umbilication)
- Treatment: Cryotherapy
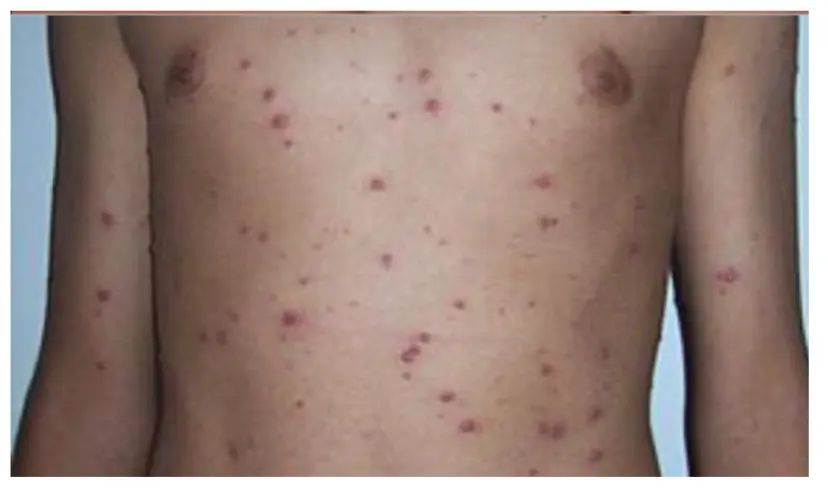
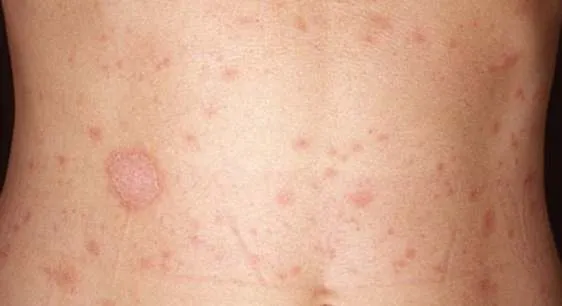
1.13 Pityriasis Rosea
- Diagnosis: Pityriasis Rosea
- Treatment: Symptomatic Antihistamine and topical steroid
- How did you know?: Herald patch
 ]]
]]
1.14 Impetigo
- Diagnosis: Impetigo
- Treatment: Topical antibiotic 2 times a day for 7-10 days
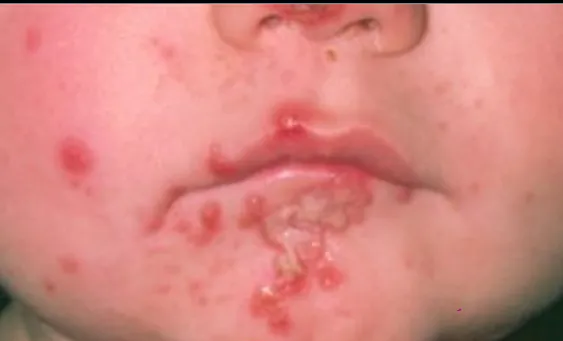
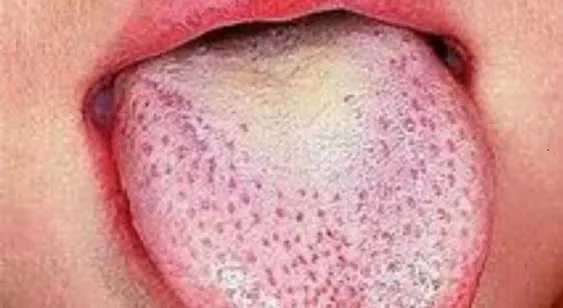
1.15 Scarlet Fever
- Diagnosis: Scarlet Fever
- Treatment: Amoxicillin 50-100 mg/kg/day 3 times for 7-10 days
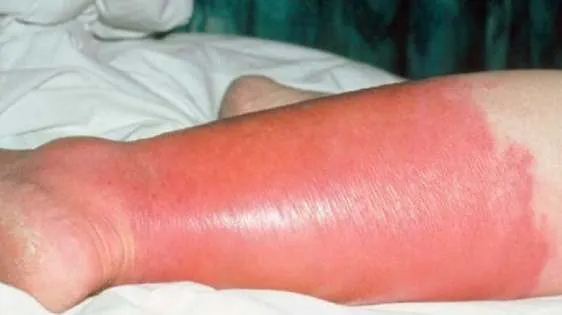
1.16 Erysipelas
- Diagnosis: Erysipelas
- Treatment:
- Diabetic: 2nd - 3rd generation cephalosporin; may need hospitalization for IV antibiotics
- Non-diabetic: 1st generation
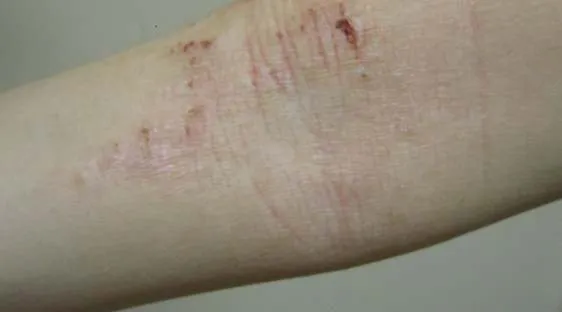
1.17 Atopic Dermatitis
- Diagnosis: Atopic Dermatitis
- Treatment:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Emollient
1.18 Napkin Contact Dermatitis
- Diagnosis: Napkin Contact Dermatitis
- Treatment:
- Drying
- Topical corticosteroids
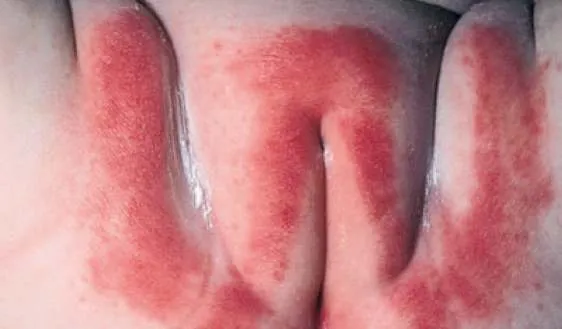
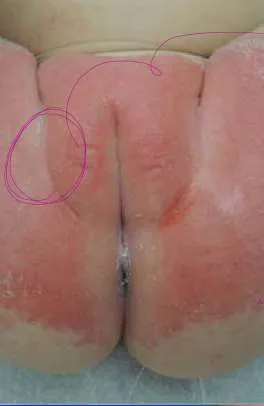
1.19 Napkin Candidiasis
- Diagnosis: Napkin Candidiasis
- Treatment:
- Drying
- Topical antifungal
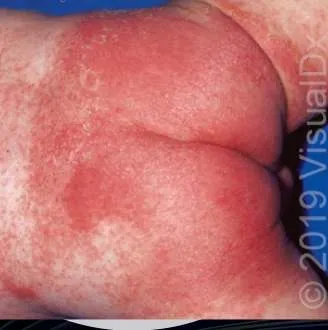
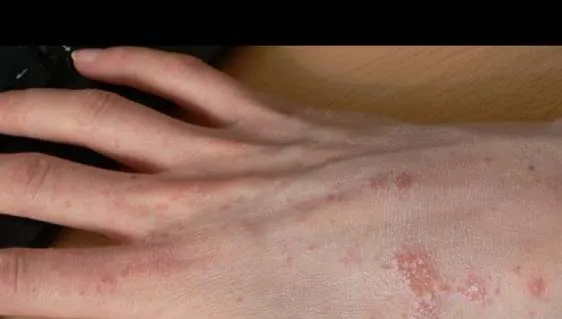
1.20 Scabies
- Diagnosis: Scabies
- Treatment:
- Permethrin 1%; repeat after 7 days
- How did you know?:
- Burrows
- Interdigits
- Pleomorphic lesions
1.21 Pediculosis
- Diagnosis: Pediculosis
- Treatment:
- Permethrin 1%; repeat after 7 days
1.22 Acanthosis Nigricans
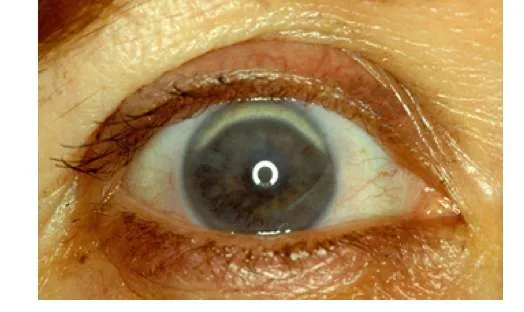
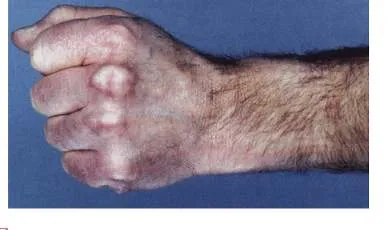
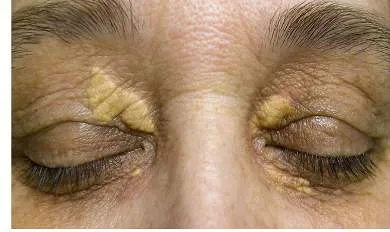
- In Dyslipidemic Patients using Statins for a Long Time:
- Arcus Senilis
- Xanthelasma
- Tendon Xanthoma
- In Diabetic Patients:
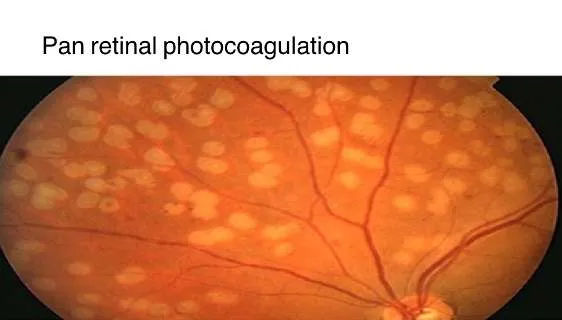
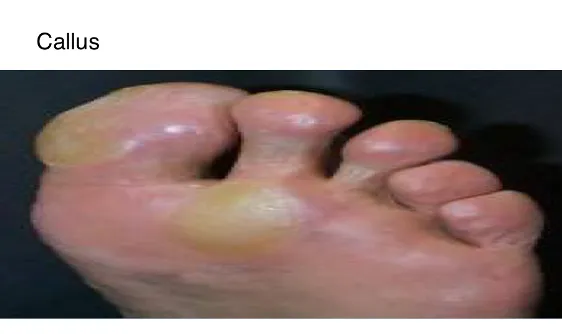
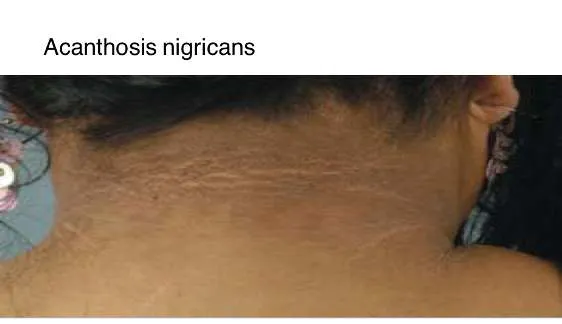
2. Musculoskeletal Conditions
2.1 Spondylolisthesis
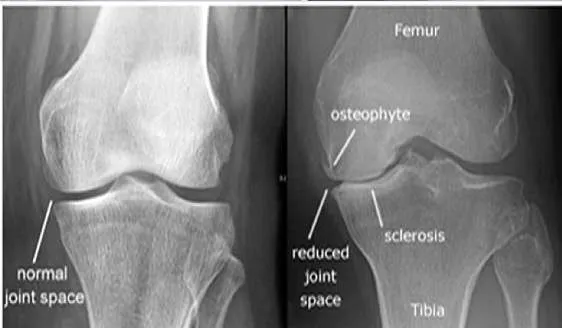
- Diagnosis: Osteoarthritis
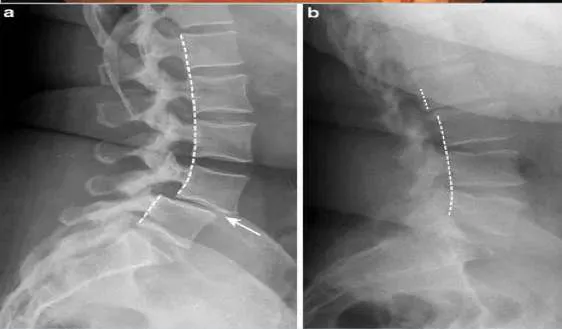
Osteoarthritis
- Signs:
- Narrowing the space of joint
- Bone erosion
- Subchondral sclerosis
- Osteophyte formation
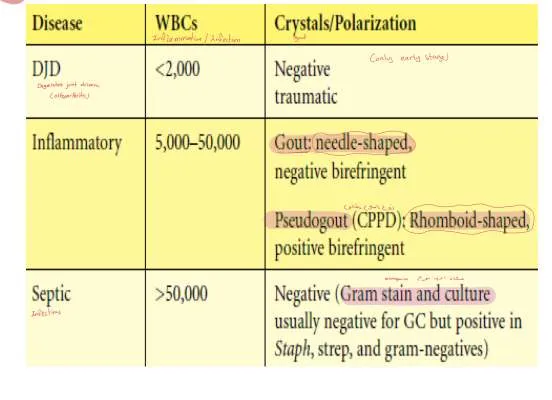
| Disease | WBCs | Crystals/Polarization |
|---|---|---|
| DJD | <2,000 | Negative traumatic |
| Inflammatory | 5,000-50,000 | Gout: needle-shaped, negative birefringent |
| Pseudogout (CPPD): Rhomboid-shaped, positive birefringent | ||
| Septic | >50,000 | Negative (Gram stain and culture usually negative for GC but positive in Staph, strep, and gram-negative) |
3. Contraceptive Methods
3.1 IUD
- Contraindications:
- Active PID
- Uterine anatomical abnormality
- STD

3.2 Progesterone Only Contraceptive Pills
- Non-contraceptive Benefits:
- Safe in lactation
- Reduce PID
- Reduction of heavy menstrual bleeding
- No drug interactions

3.3 Combined Oral Contraceptive Pills
- Non-contraceptive Benefits:
- Menorrhagia and dysmenorrhea
- PMS
- Hyperandrogenism
- Contraindications:
- Headache with Aura
- Hypertension
- Ischemic heart disease
3.4 Progesterone Only DMPA Injection
- Non-contraceptive Benefits:
- Reduce heavy menstrual bleeding
- Reduce PID
- Reduction of Sickle cell crisis
- Lack of drug interactions
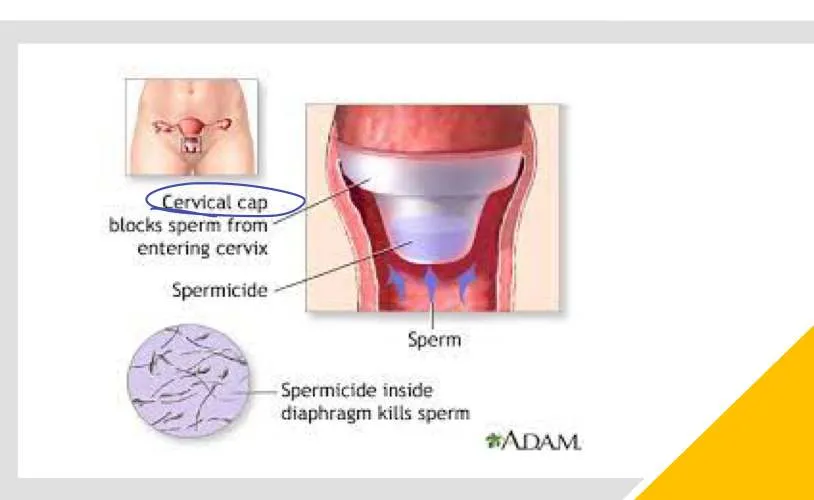
3.5 Cervical Cap
- Advantages:
- Without prescription
- Protection from STD
- Safe during lactation
- Disadvantages:
- High risk of urethral infection
- Loss of sensation
- Breakage
3.6 Male Condom
- Advantages:
- Without prescription
- Protection from STD
- Safe during lactation
- Disadvantages:
- High risk of urethral infection
- Loss of sensation
- Breakage

4. ENT Conditions
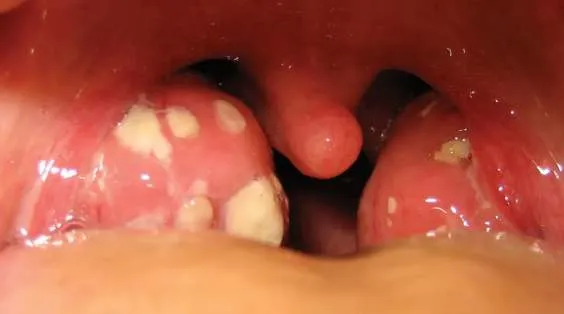
4.1 Bacterial Tonsillitis
- Diagnosis: Bacterial Tonsillitis
- Treatment: Amoxicillin 50-100 mg/kg/day 3 times for 7-10 days
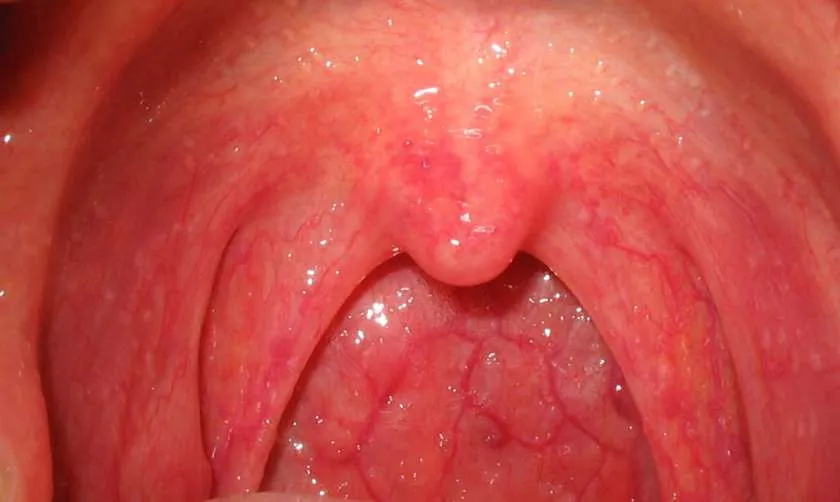
4.2 Viral Tonsillitis
- Diagnosis: Viral Tonsillitis
- Treatment:
- Good hydration
- Paracetamol 15mg/kg/dose every 6 hours for 2 days as needed
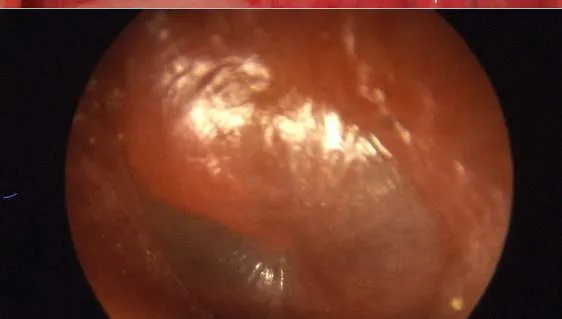
4.3 Acute Otitis Media with Effusion
- Diagnosis: Acute Otitis Media with Effusion
- Treatment: Augmentin 90 mg/kg/day 2 times for 10-14 days
5. Pediatric Conditions
5.1 Absence of Red Reflex in Left Eye
- Cause:
- Retinoblastoma
- Phenylketonuria
- Congenital Rubella Syndrome
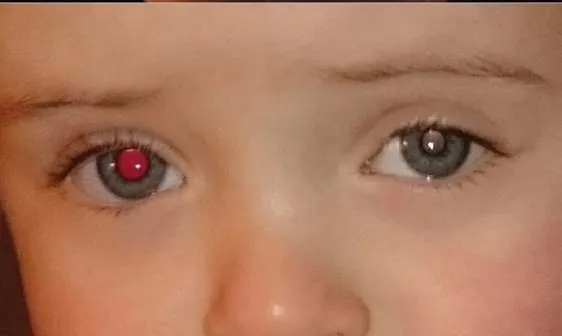
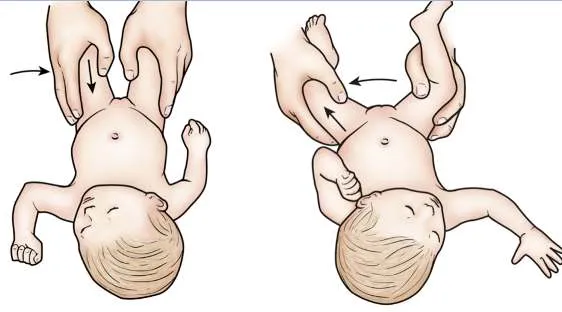
5.2 Hip Dysplasia
- لازم اححد الاتجاه دائماً (اختبار الرجل الي عليها السهم)
5.3 Tests
- Barlow Test: Adduction and pushing backward
- Ortolani Test: Abduction and pushing forward
6. Growth Assessment
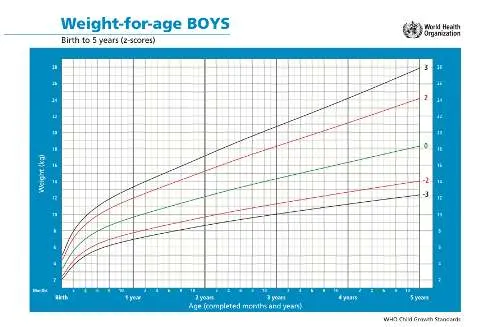
6.1 Z Score (Percentile)
-
3 (99)
- Length/height for age: May be abnormal
- Weight for age: Obese
- BMI for age:
-
2 (97)
- Length/height for age: Normal
- Weight for age: Use BMI
- BMI for age: Overweight
-
≥1 (85)
- Length/height for age: Normal
- Weight for age: Use BMI
- BMI for age: Risk of overweight
-
0 (50)
- Length/height for age: Normal
- Weight for age: Use BMI
- BMI for age: Normal
-
<1 (15)
- Length/height for age: Normal
- Weight for age: Normal
- BMI for age: Normal
-
<2 (3)
- Length/height for age: Stunted
- Weight for age: Underweight
- BMI for age: Wasted
-
<3 (1)
- Length/height for age: Severely Stunted
- Weight for age: Severely underweight
- BMI for age: Severe wasted
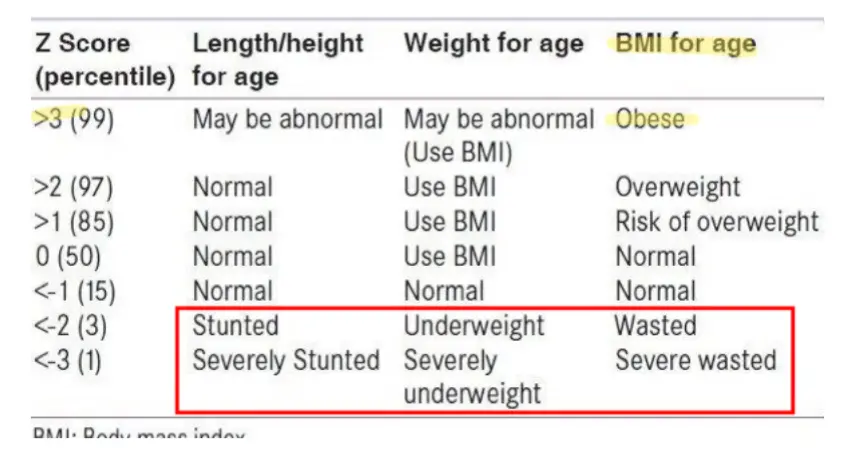
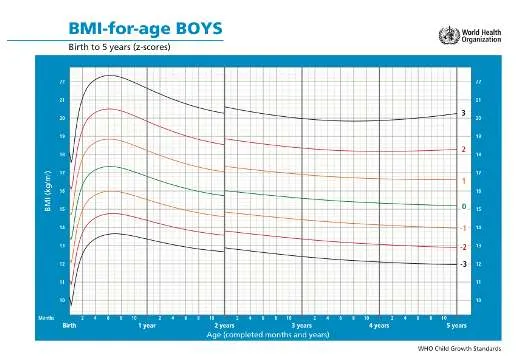
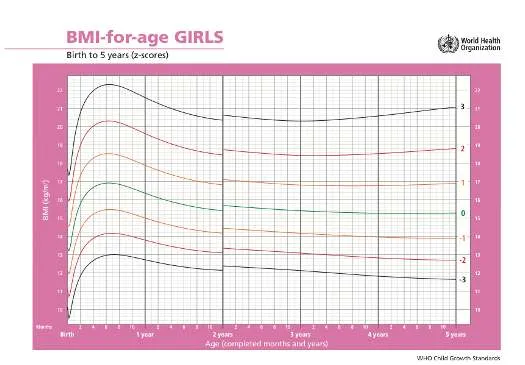
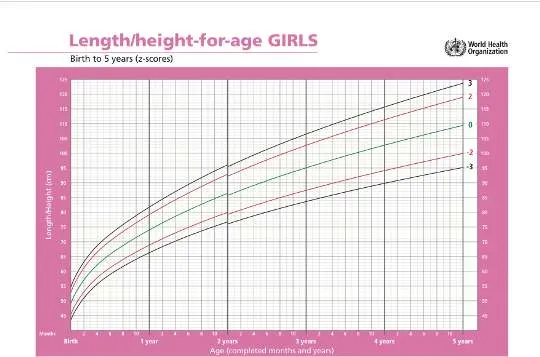
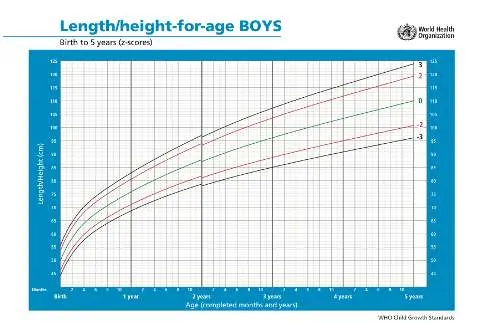
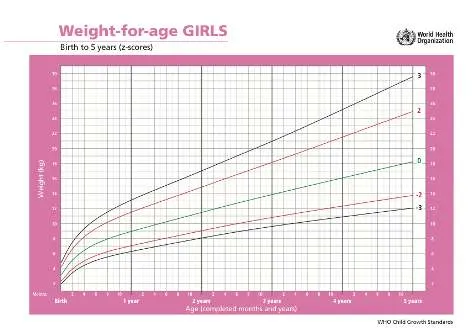
7. Cardiac Conditions
8. Obstetric Care
First visit
- cbc (repeat 24-28 & 32-35 wks)
- ABO -Rh (atypical antibody screen in 24-28 wks)
- Urine culture (repeat 12-16 wks)
- Syphilis, hiv, gonorrhea, chlamydia (repeat in 32-36 wks)
- PAP smear
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg)
- Rubella Antibody Titre
8.1 Prenatal Care
8.1.1 12-16 Weeks
- Urine culture (USPSTF, AAFP)
- Nuchal translucency in US (Down syndrome)
16-18 weeks or 15-20 weeks (triple screen for Down syndrome)
- Alpha-fetoprotein for neural tube defect
- BhCG increased in trisomy 21
- Unconjugated estriol decreased in trisomy 18 & 21
8.1.2 24-28 Weeks
- Gestational diabetes (by 75 gm OGTT - 92, 180, 153)
- CBC
- Antibody screen for Rh negative and administration of immunoglobulin
8.1.3 32-35 Weeks
- STD
- Repeat CBC
8.1.4 35-37 Weeks
- Group b streptococcal rectovaginal culture
- genetic counseling, thyroid disease, infectious disease - bv & rubella -, domestic violence, smoking, alcohol, depression
8.2 How to Manage Gestational Age
- LMP: تاريخ آخر دورة شهرية
- Fertilization Day: Add 2 days
- EDD: Subtract 3 from Fertilization month.
- Fertilization = تاريخ الحمل المتوقع = GA


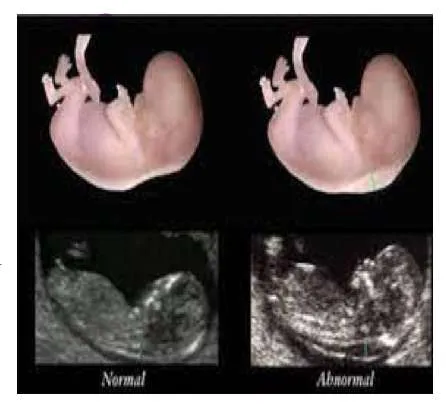
9. Hematological Conditions
9.1 Anemia Types
- Diagnosis: Sidroblastic Anemia
- Sign: Ring sideroblast
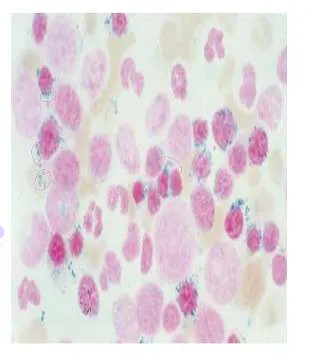
- Sign: Ring sideroblast
- Diagnosis: Megaloblastic Anemia (Vitamin B12 deficiency)
- Sign: Hypersegmented neutrophils
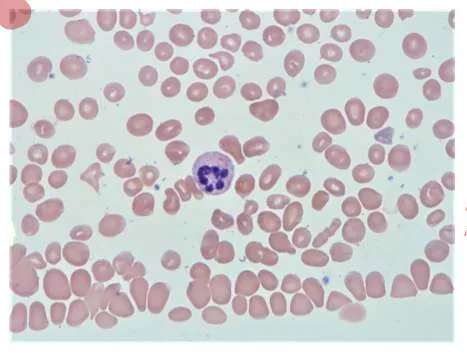
- Sign: Hypersegmented neutrophils
- Diagnosis: G6PD Deficiency Anemia
- Sign: Bite cells - Heinz bodies
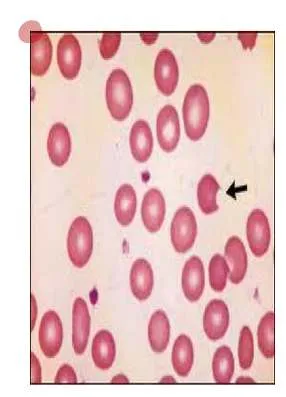
- Sign: Bite cells - Heinz bodies
- Diagnosis: Sickle Cell Anemia
- Sign: Sickled cell