Red Eye
Waleed alrashed
Introduction
- Frequent presentation to GP
- Must be able to differentiate between serious vision-threatening conditions and simple benign conditions
Red Eye
- Refers to hyperemia of the superficially visible vessels of the conjunctiva, episclera, or the sclera
- Caused by disorders of these structures themselves, or of adjacent structures like the eyelids, cornea, iris, and ciliary body
Differential diagnosis of red eye
-
Conjunctival
- Blepharoconjunctivitis
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- Viral conjunctivitis
- Chlamydial conjunctivitis
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Toxic/chemical reaction
- Dry eye
-
Lid diseases
- Stye
- Abnormal lid function
-
Corneal disease
- Abrasion
- Ulcer
-
Foreign body
-
Carotid and Dural cavernous sinus fistula
-
Acute angle glaucoma
-
Anterior uveitis
-
Episcleritis/scleritis
-
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Blepharitis
- Adults > children
- Inflammation of the lid margin
- Frequently associated with styes
- Meibomian gland dysfunction
- Lid hygiene, topical antibiotics, and lubricants are the mainstays of treatment
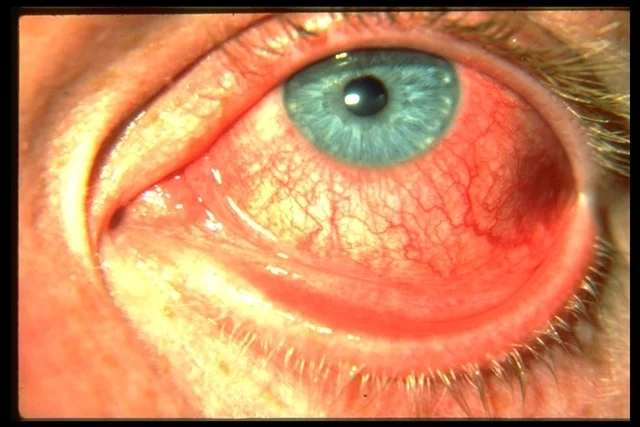
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Both adults and children
- Tearing, foreign body sensation, burning, stinging, and photophobia
- Mucopurulent or purulent discharge
- Lid and conjunctiva may be edematous
- Streptococcus pneumoniae, Hemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus and epidermidis
- Conjunctival swab for culture
- Topical broad-spectrum antibiotics
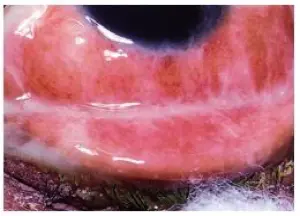
Viral Conjunctivitis
- Acute, watery red eye with soreness, foreign body sensation, and photophobia
- Conjunctiva is often intensely hyperemic, and there may be follicles, hemorrhages, inflammatory membranes, and a pre-auricular node
- The most common cause is an adenoviral infection
- No specific therapy but cold compresses are helpful
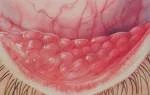
Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Encompasses a spectrum of clinical conditions
- All associated with the hallmark symptom of itching z
- There is often a history of rhinitis, asthma, eczema, and family history of atopy
- Signs may include mildly red eyes, watery discharge, chemosis, papillary hypertrophy, and giant papillae
- Treatment consists of cold compresses, antihistamines, nonsteroidals, mast cell stabilizers, and in severe cases, topical corticosteroids and cyclosporine
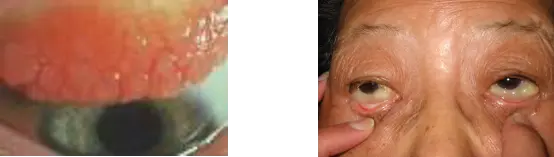
Chlamydial Conjunctivitis
- Usually occurs in sexually active individuals with or without an associated genital infection
- Conjunctivitis usually unilateral with tearing, foreign body sensation, lid crusting, conjunctival discharge, and follicles
- There is often a non-tender preauricular node
- Treatment requires oral tetracycline or azithromycin
Iritis
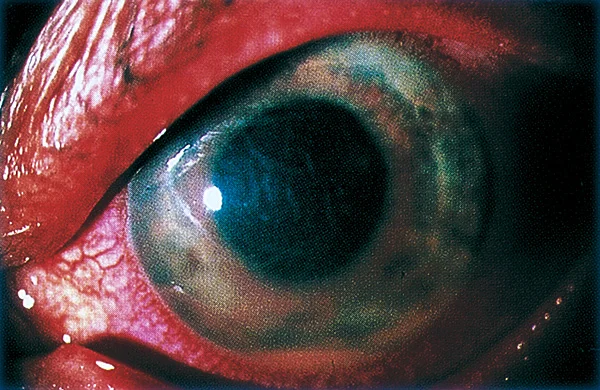

Episcleritis
- Episcleritis
- Can be localized (sectorial) or diffuse redness
- Often asymptomatic
- Usually self-limited
- Treatment: topical or systemic NSAIDs
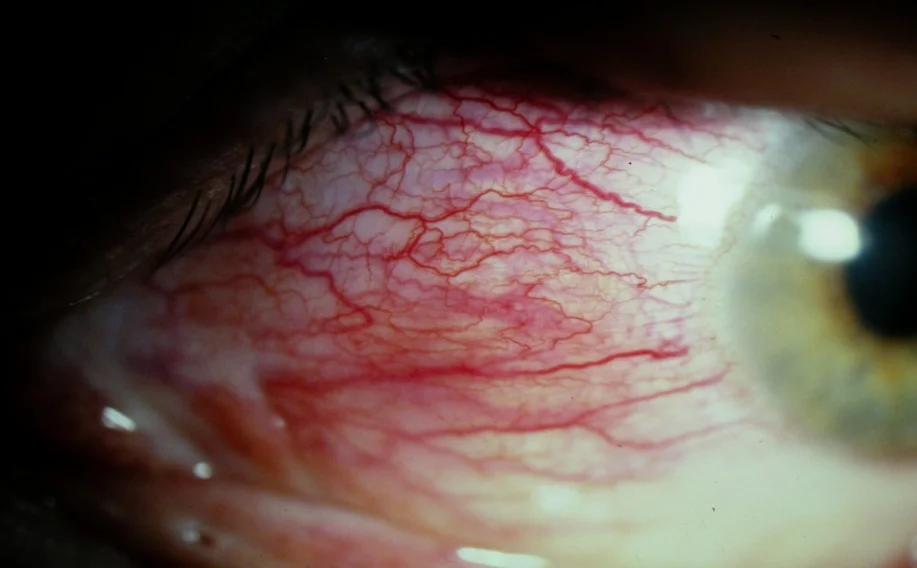
htn, gout - no sequele
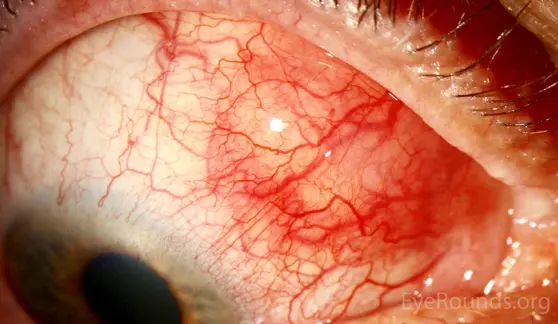
Scleritis Z
- Pain which may be severe with tenderness, tearing, and photophobia
- May be localized, diffuse, or associated with nodules
- Can result in scleral necrosis (scleromalacia perforans)
- 30 to 60% may have an associated systemic disease
- RA …
- May need systemic steroid and immunosuppressive agents
nodular scleritis
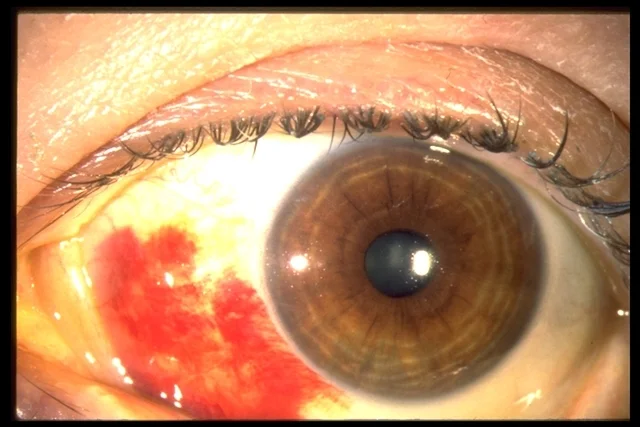
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
- Usually asymptomatic/ self limited
- Blood underneath the conjunctiva, often in a sector of the eye
- Etiology
- Valsalva (coughing or straining)
- Traumatic
- Hypertension
- Bleeding disorder
- Idiopathic
- Postoperative
- Anticoagulants
Red Eye Treatment Algorithm urgency
- History
- Trauma
- Contact lens wearer
- Severe pain/photophobia
- Significant vision changes
- History of prior ocular diseases
- Exam
- Abnormal pupil
- Ocular tenderness
- White corneal opacity
- Increased intraocular pressure
YES
Refer urgently to ophthalmologist
Is it conjunctivitis?
-
History
- Itching
- Exposure to person with red eye
- URTI
- Discharge with morning crusting
- Exposure to drugs
-
Signs
- Discharge what types
- Lid and conjunctival edema
- Conjunctival redness
- Preauricular lymph node
- Facial or eyelid vesicles