Coagulation Cascade
-
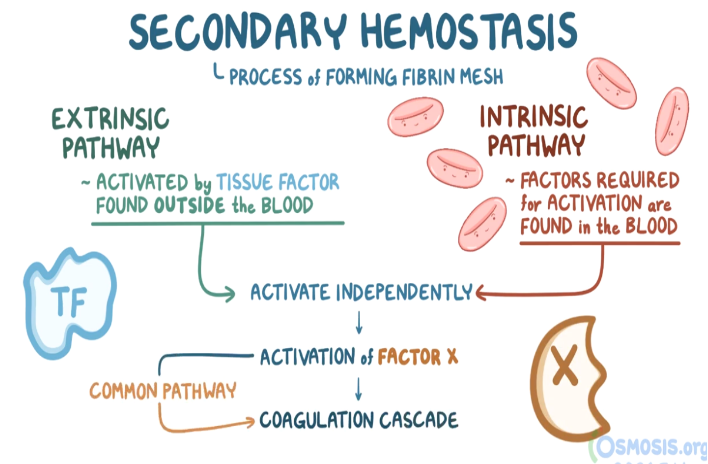
Intrinsic Pathway: Starts with activation of factor XII by subendothelial collagen or activated platelets.
- XIIa activates factor XI, which then activates factor IX.
- Activated factor IX with activated factor VIII activates factor X (leading to the common pathway).
-
Extrinsic Pathway: Tissue factor (factor III) activates factor VII, then activates factor X and the common pathway.
-
Common Pathway: Both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge at factor X.
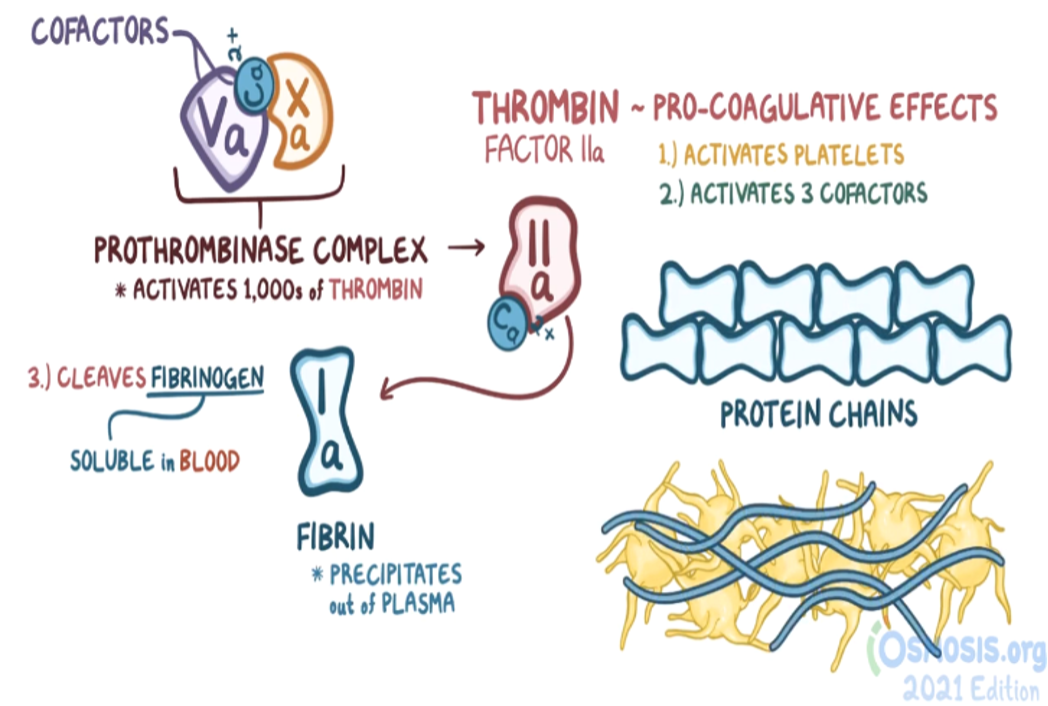
- Factor Xa cleaves factor V into the active form (Va).
- Factor Xa and Va, along with calcium, form the prothrombinase complex.
- The prothrombinase complex cleaves factor II (prothrombin) into the active form IIa (thrombin).
- Factor Xa cleaves factor V into the active form (Va).
Secondary Hemostasis
-
Secondary hemostasis (coagulation) involves the stabilization of the platelet plug formed in primary hemostasis using a fibrin meshwork.
-
Thrombin has 4 main functions:
- Activation of additional factors V, VIII, and IX; activation of platelets.
- Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin is insoluble forming a fibrin meshwork that stabilizes the platelet plug.
- Activation of factor XIII, stabilizing the platelet plug by forming cross-links between the fibrin molecules in the plug.
Question on Coagulation Pathways
Secondary hemostasis involves the activation of clotting factors that lead to the formation of a stable fibrin mesh. Which of the following is true regarding the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways?
A. Tissue factor activates factor VII, leading to the activation of the extrinsic pathway.
B. Tissue factor activates factor XII, leading to the activation of the intrinsic pathway.
C. Both pathways are activated by the same signals.
D. Subendothelial collagen activates factor VII and leads to the activation of the intrinsic pathway.
E. The activation of the intrinsic pathway and the extrinsic pathway is dependent on each other.
Answer: A is the correct answer.
Question on Secondary Hemostasis
A lab study is simulating secondary hemostasis. Both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of coagulation lead to the formation of the active form of factor X (Xa). Which of the following is the correct order of events to occur afterward?
A. Factor Xa cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin.
B. Factor Xa alone activates factor II, which then cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin.
C. Factor Xa activates factor V; then, factor Va alone activates factor II, which cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin.
D. Factor Xa activates factor V; then, factors Xa and Va activate factor II, which cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin.
E. Factor Xa uses factor VIIIa as a cofactor to activate factor II, which then cleaves fibrinogen into fibrin.
Answer: D is the correct answer.