Epistaxis (KITTEN)
Nasal Causes
- Nasal trauma (nose picking, foreign bodies, forceful nose blowing).
- Allergic, chronic, or infectious rhinitis.
- Chemical irritants.
- Medications (topical).
- Drying of nasal mucosa from low humidity.
- Deviation of nasal septum or septal perforation.
- Bleeding polyp of the septum or lateral nasal wall (inverted papilloma).
- Neoplasms of the nose or sinuses.
- Tumors of the nasopharynx (e.g., Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma).
- Vascular malformation.
Systemic Causes
- Systemic arterial hypertension.
- Endocrine causes (e.g., pregnancy, pheochromocytoma).
- Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.
- Anticoagulants (ASA, NSAIDs).
- Hepatic disease.
- Blood diseases and coagulopathies (e.g., thrombocytopenia, ITP, leukemia, hemophilia).
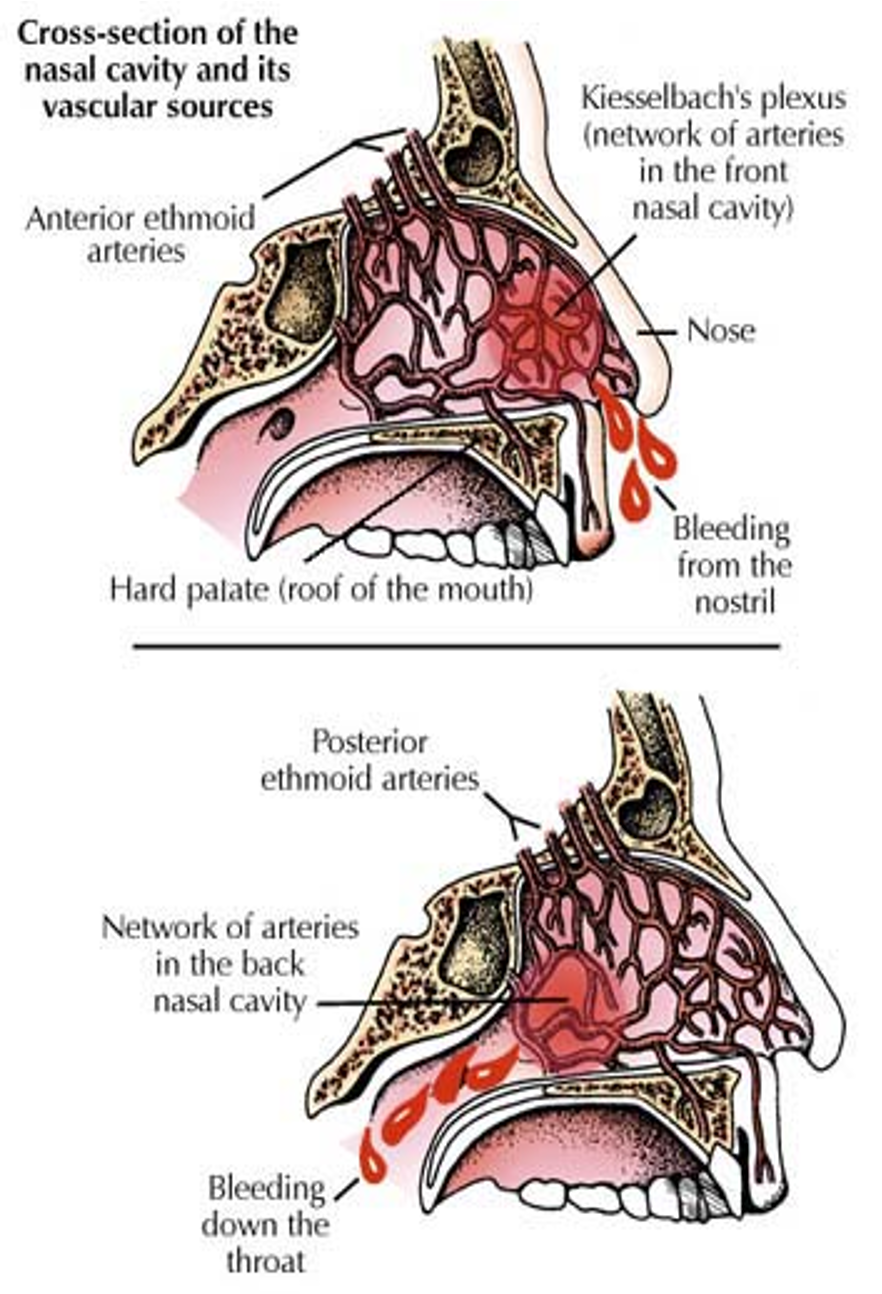
Cross-section of the Nasal Cavity and Its Vascular Sources
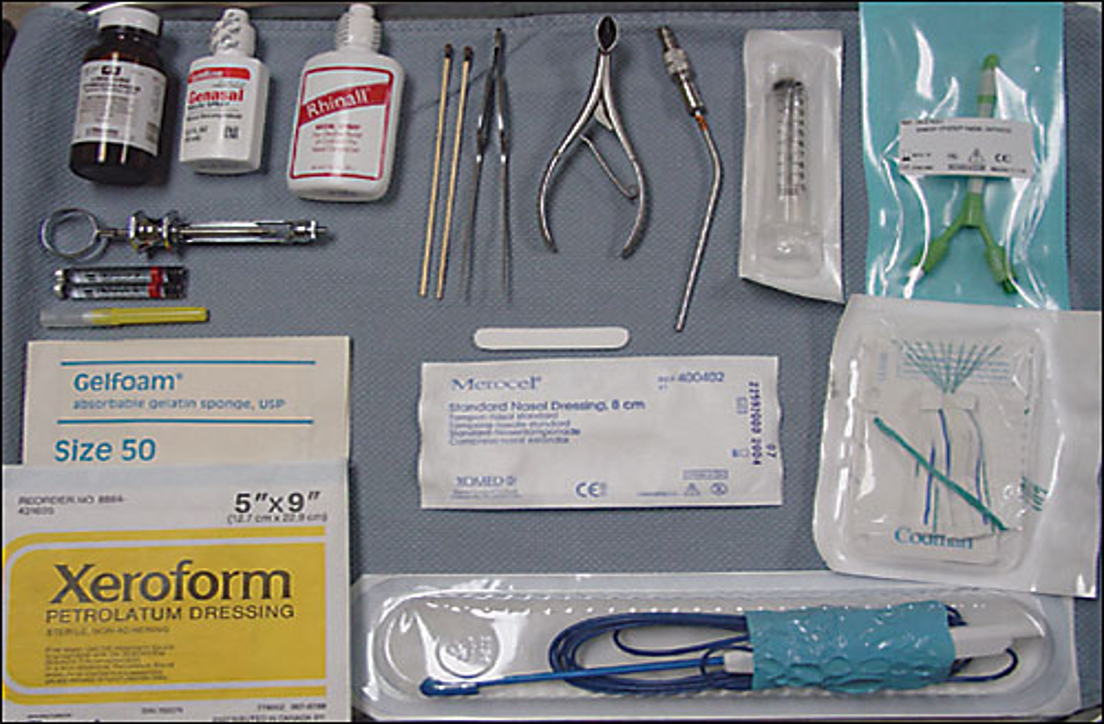
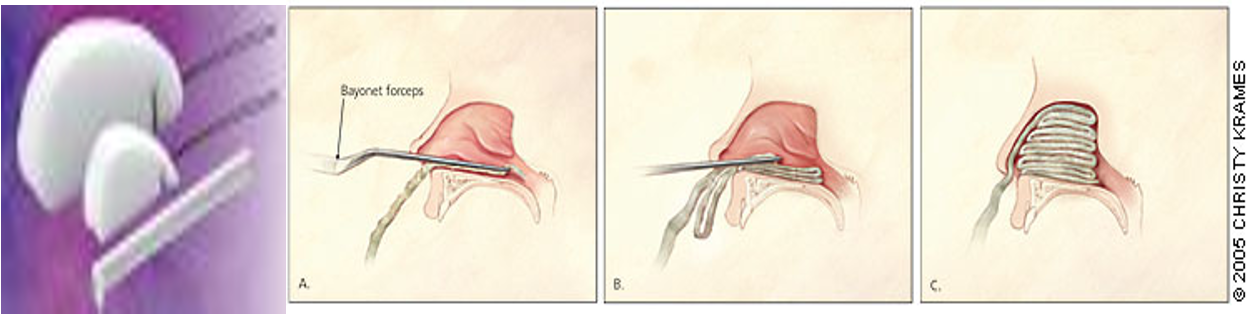
Anterior Packing
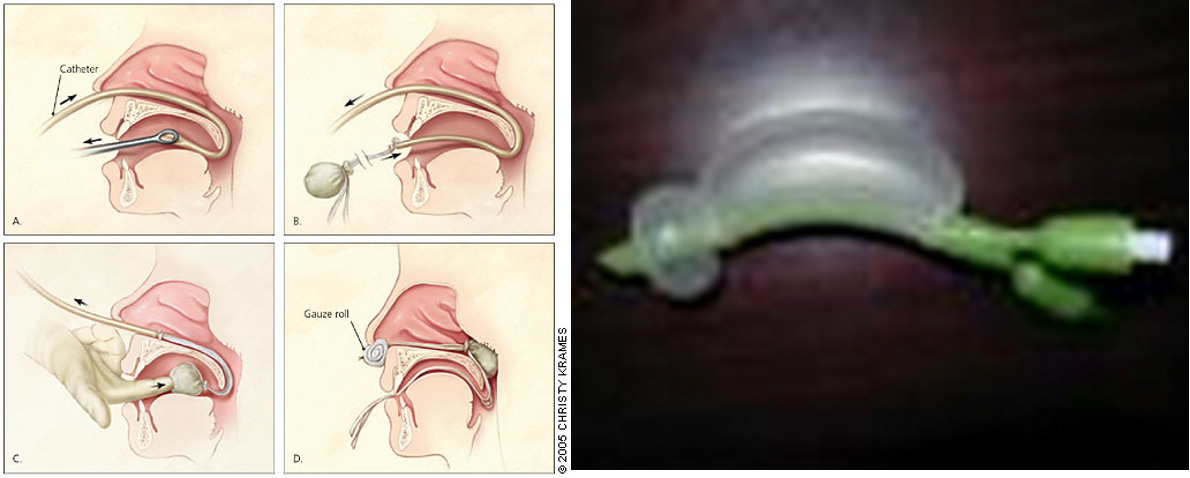
Posterior Packing
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
- Septoplasty.
- Endoscopic cauterization.
- Selective embolization by interventional radiologist.
- Transantral internal maxillary artery ligation.
- Anterior and posterior ethmoid artery ligation.
- External carotid artery ligation.
- Endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation.