Neuroconduction of Retina
-
3 neurons:
- Photoreceptor
- Bipolar
- Ganglion cell
-
Supporting tissue:
- Müller cell
-
Rod (scotopic vision)
-
Cone (photopic vision)
-
Connecting cell between photoreceptor and ganglion
-
Conduct to brain
Vasculature of Retina
- Inner layer → central retinal vascular system
- Outer layer → choroid (ciliary vascular system)
- Macula lutea → choriocapillaries
Retina Barrier
-
Inner barrier ( blood-retina barrier )
- Dense connection of retinal capillary endothelium
-
Outer barrier ( choroid-retina barrier )
- Zonula occludens between the RPE
RPE- Bruch’s membrane- choriocapillaries complex
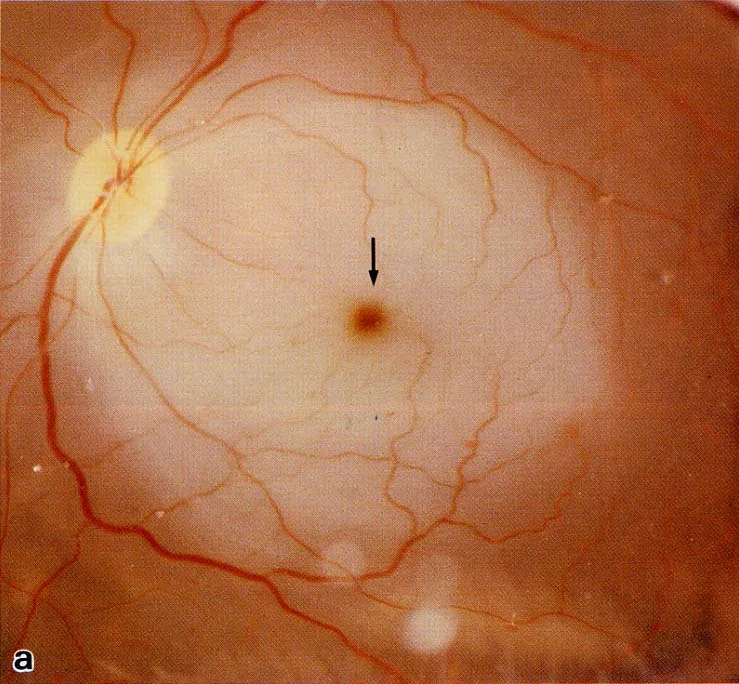
Symptoms
-
Visual impairment
- Related to lesion site
-
Metamorphopsia
-
Flickering
- Vitreous traction to the retina
-
Macropsia
-
Micropsia
- Retina edema → fewer cones stimulated → micropsia
Signs
-
Intracellular edema
- Retinal artery occlusion: ischemia leads to edema of bipolar cell, ganglion and RNFL
-
Extracellular edema
- Capillary endothelium injury, and then exudation
-
Cystoid macular edema
- Henle’s fibers are radially located; This pooling forms a flower-petal pattern.
Intracellular Edema
Extracellular Edema
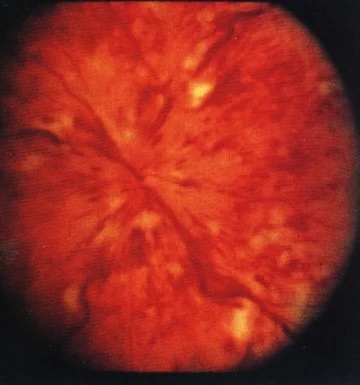
Exudates
-
Leakage of capillary → absorb → deposition of lipid in outer plexiform layer
-
Since be called “soft exudation”
- Precapillary arteriole occlusion → axoplasmic transport blocked → organelles stack