Moneer Almadani
Diseases Of Spleen
-
Splenic Injury
-
Immune Thrombocytopenia
-
Hereditary Spherocytosis
-
Acquired Haemolytic Anaemia
-
Hypersplenism
-
Left sided portal hypertension
-
Proliferative disorders
-
Splenectomy
Anatomy
Objectives
- Anatomy & functions
- Causes of splenomegaly
- Splenic diseases of surgical interest
- Indications of splenectomy
- Hematological changes post-splenectomy
- Post-splenectomy sepsis
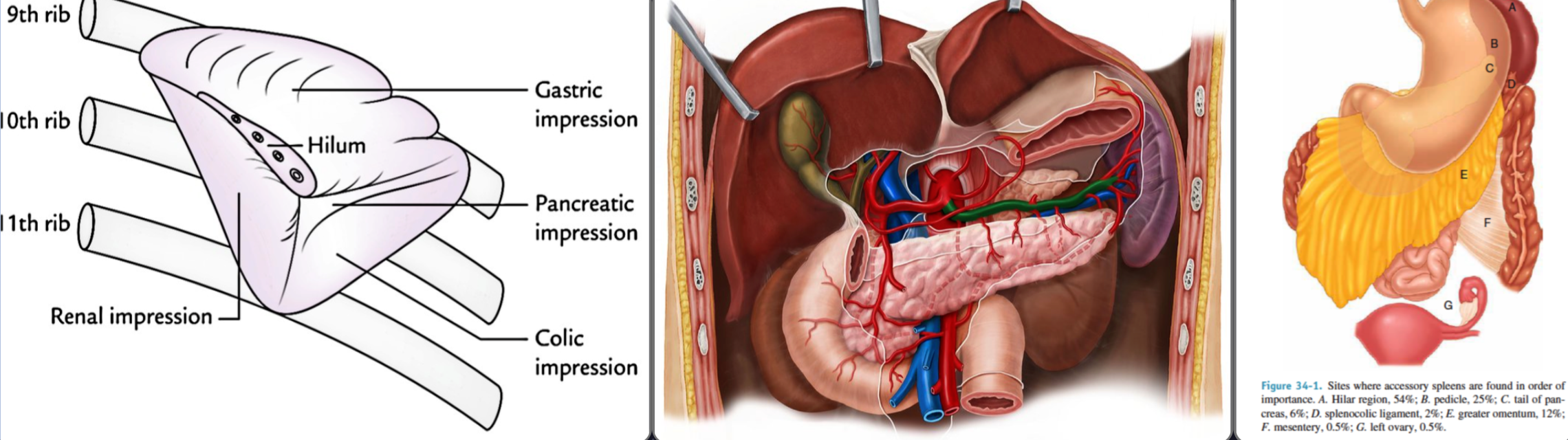
Surgical Anatomy
 A patient after tuma 9,10,11th rib fracture with browses maybe hypotensive
A patient after tuma 9,10,11th rib fracture with browses maybe hypotensive
- Convex surface & upper pole:
- related to diaphragm (9-11 ribs).
- Concave surface:
- Fundus of stomach, tail of pancreas, & upper pole of left kidney
- Lower pole: rests on splenic flexure of colon
Surgical Anatomy
A presence of spleen
- Accessory spleen:
- (10-20%)
- Mostly hilum, may be anywhere
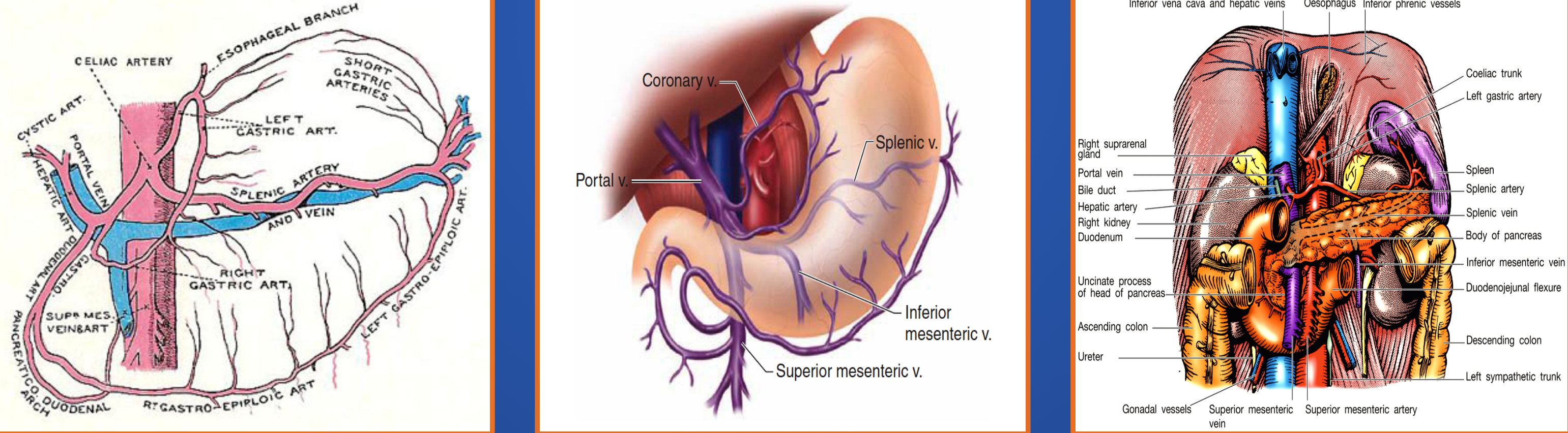
- Splenic artery: branch from celiac axis
- Splenic vein: joins SMV to form portal vein
Surgical Physiology
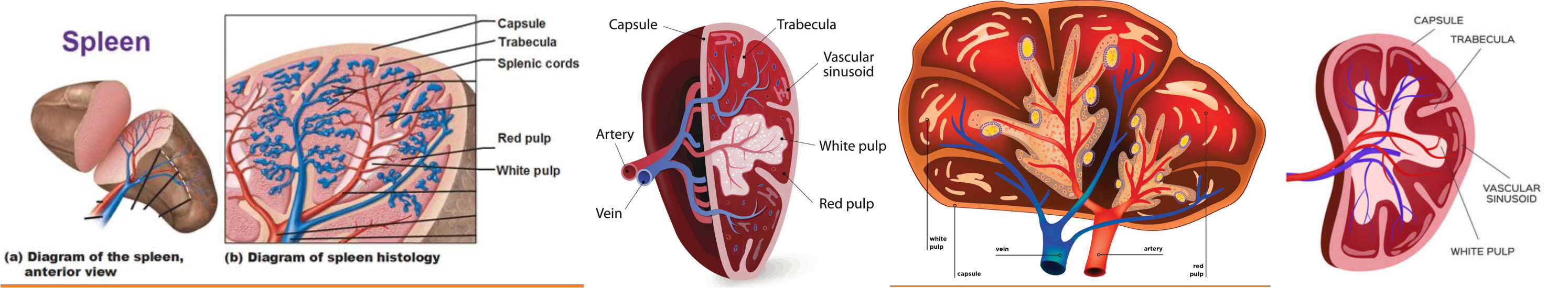
Highly vascularized (5% CO) - Largest filter of blood & a lymphoid organ - Composed of red & white pulp.
-
Red pulp:
- Made up of sinusoids
- Filters old RBC
- Phagocytose
- Iron transported back to bone marrow for new RBC
- RBC &Platelets: 1% & 20-30% respectively are sequestrated
- (Howell-Jolly bodies): Post-splenectomy- mis-shapen RBC with nuclear remnants seen in circulation
-
White pulp:
- largest aggregation of lymphoid tissue
- Composed of lymphoid follicles (Malpighian bodies), lymphocytes (T & B), macrophages, & plasma cells
- Site of antigen presentation & antibody production
Immunological function
- Largest aggregation of lymphoid tissues
- Promotion of cell mediated & humoral immunity
- Antigens engulfed by macrophages for antibody production- immunoglobulin (IgM)
- Production of opsonins, properdin from lymphocytes
- Binds to macrophage & leukocyte
- Promote phagocytosis and bacteriocidal activity
- Splenectomy impairs immunological responses
Causes of splenomegaly
- Clinically palpable spleen enlarged 3 times
- Infective: TB, abscess, HIV, malaria, schistosomiasis, hydatid cyst
- Blood disease: ITP, Hereditary spherocytosis, autoimmune haemolytic anemia, thalassaemia, sickle cell disease, polycythemia, leukaemia
- Metabolic: Gaucher’s disease, amyloidosis
- Circulatory: Portal hypertension, infarction
- Nonparasitic Cysts: Congenital/ acquired
- Neoplasms: Hodgkin’s, other lymphoma, myelofibrosis, angioma #RR - Class
References
- Principles and Practice of Surgery
- Pg 229-232