Medical conditions in pregnancy
| Condition | Maternal risks | Fetal/neonatal risks | Antenatal management | Intrapartum | Postpartum/Neonatal | Use/avoid meds (key) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes (pre‑existing & GDM) | Hypo/Hyperglycemia, DKA, infections, preeclampsia, CS | Miscarriage (pre‑DM), anomalies (pre‑DM), macrosomia, shoulder dystocia, polyhydramnios, IUGR (vascular), IUFD, neonatal hypoglycemia, RDS | Preconception HbA1c, folate 5 mg; stop ACEi/ARB/statin; tight glycemic control (fasting ~70–95 mg/dL; 1‑h PP <140); diet + exercise; metformin/insulin as needed; aspirin 150 mg nightly from 12 w if risk; anatomy scan + serial growth scans; fetal echo if HbA1c high | Maintain glucose 70–110; IV insulin/dextrose protocol if on insulin; continuous CTG if indicated; avoid prolonged labour if EFW >4.5 kg (discuss mode) | GDM: stop agents after delivery; test at 6–12 w with OGTT; long‑term T2DM prevention; neonatal glucose monitoring | Use: insulin, metformin (selected). Avoid: ACEi/ARB, statins. |
| Hypertension (chronic, gestational, preeclampsia) | Severe HTN, stroke, renal/liver injury, HELLP, eclampsia, abruption, pulmonary edema | IUGR, oligohydramnios, prematurity (iatrogenic), IUFD | Target BP ≈135/85; meds: labetalol 1st line, nifedipine, methyldopa; aspirin 150 mg from 12 w to 36 w; baseline labs (CBC, LFT, creatinine, urine P/C); serial growth + Doppler; preeclampsia surveillance | MgSO4 for severe features/eclampsia; fluid restriction; continuous CTG; avoid ergometrine; aim VD unless obstetric indication | Monitor BP 72 h–2 w; adjust meds; counsel CVD risk; neonatal: observe if late‑preterm | Use: labetalol, nifedipine, methyldopa; Avoid: ACEi/ARB, NSAIDs in severe HTN/preeclampsia (PP), ergometrine. |
| Asthma | Exacerbations, hospitalization, ↑ mortality (if uncontrolled), preeclampsia | LBW, preterm, neonatal asphyxia | Avoid triggers; step‑wise therapy: SABA (salbutamol), ICS; add oral steroids for exacerbations; O2; antibiotics if infection; most worsen in 3rd tri; monitor control | O2, bronchodilators, steroids; avoid prostaglandins for induction that exacerbate asthma; VD unless CS indicated; continuous CTG if severe | Usual inhalers safe in lactation | Use: salbutamol, ICS, oral steroids if needed. Avoid: carboprost (PGF2α); use caution with labetalol in severe asthma. |
| Thyrotoxicosis (Graves’ common) | HTN, preeclampsia, heart failure, thyroid storm | Miscarriage, IUGR, preterm, IUFD, fetal hypo‑/hyperthyroidism (TSI/drugs) | TFTs each trimester; PTU preferred (less teratogenic); serial US for growth/goiter; manage symptoms; plan cord blood TFT | Close monitoring in labour; continuous CTG; aim VD | Cord TFT; adjust maternal dose; watch neonatal thyroid dysfunction | Use: PTU (early), consider switch to methimazole after 1st tri; Avoid: overtreatment causing fetal hypothyroidism. |
| Sickle cell disease | Pain crises, infections, ACS, VTE, cardiomyopathy (iron overload), stroke | Miscarriage, IUGR, prematurity, stillbirth | MDT care; partner screening; folate 5 mg, penicillin if hyposplenic; stop iron chelators; screen urine for infection each visit; crisis: analgesia, O2, IV fluids, antibiotics if infection; serial growth/Doppler; thromboprophylaxis; consider prophylactic antibiotics | Aim VD; avoid hypoxia/dehydration; continuous fetal monitoring | Thromboprophylaxis; infection vigilance | Use: folate, penicillin, LMWH if indicated. Avoid: hypoxia, dehydration; chelators during pregnancy. |
| Iron deficiency anemia | Fatigue, infections, transfusion risk, decompensation with PPH | Fetal hypoxia, abnormal FHR, fetal death if severe (Hb <6) | Screen CBC (booking, 24–28 w); ferritin <30 µg/L confirms IDA; diet + oral iron (ferrous sulfate 1st line; adjust for tolerance); IV iron if severe/intolerant; transfuse if Hb <6 g/dL with compromise | Optimize Hb before delivery; plan hemorrhage precautions | Continue iron 3 mo and at least 6 w PP; monitor | Use: ferrous salts; IV iron when needed. Avoid: tea/coffee with iron; unnecessary transfusion. |
| UTI (ASB, cystitis, pyelonephritis) | Pyelonephritis, sepsis, anemia | Preterm labour, LBW | Dipstick + confirm MSU; treat all bacteriuria: 3–7 d; cystitis: 7 d; pyelo: 10–14 d; choose pregnancy‑safe antibiotics; test of cure | Treat aggressively if pyelo; fluids; consider admission | Re‑screen if recurrent | Use: appropriate abx per local sensitivity (e.g., cephalexin, amoxicillin‑clavulanate, nitrofurantoin except near term). |
| Epilepsy | Seizures, trauma, SUDEP (rare), ↑ hypertensive d/o, hemorrhage, preterm | Congenital malformations (AED‑related), neurodevelopmental effects (valproate), fetal hypoxia if maternal seizures | Pre‑pregnancy: folate 5 mg; avoid valproate, minimize polytherapy, lowest effective AED dose; obst‑neuro co‑care; anomaly scan 18–20 w; growth scans if on AEDs | Continue AEDs; seizure treat with benzodiazepines; safe analgesia: epidural, Entonox; avoid pethidine; CS only for obstetric/poor control; continuous CTG if seizures | Seizure risk ↑ first 72 h; adjust AED dose to avoid toxicity; breastfeeding encouraged; screen for PPD | Use: levetiracetam, lamotrigine (common choices). Avoid: valproate; avoid pethidine. |
| Cardiac disease (general principles) | Decompensation, arrhythmia, HF, thromboembolism | IUGR, FGR, prematurity (iatrogenic), fetal hypoxia | MDT obst‑cardiology; baseline + 28 w echo; anticoagulate if PH, prosthetic valves, AF (LMWH preferred esp. 1st/3rd tri); monitor for fluid overload; treat triggers (anemia, infection); plan labour | Avoid supine; careful fluids; epidural beneficial; keep 2nd stage short (assisted delivery if needed); avoid induction if possible; antibiotics if structural defect; active 3rd stage with oxytocin (give slowly); avoid ergometrine | High‑level monitoring until hemodynamics stabilize; judicious oxytocin; VTE prophylaxis | Use: LMWH; carefully titrated oxytocin. Avoid: ergometrine; excessive fluids. |
Quick notes for viva
- Mode of delivery: Most conditions → vaginal delivery unless obstetric indication for CS. Keep second stage short for significant cardiac disease.
- Thromboprophylaxis: Consider in SCD, high‑risk cardiac disease, and other VTE risks.
- Continuous fetal monitoring: When maternal status unstable (e.g., severe asthma, thyrotoxicosis in labour, seizures).
- Drugs to remember to avoid: ACEi/ARB (pregnancy), valproate (pregnancy), ergometrine (HTN/cardiac), carboprost in asthma, pethidine in epilepsy, iron chelators in pregnancy.
Instruments
| Instrument | Main uses/indications | Contraindications | Key complications/notes | Image -0-0-0-0-00-0-0ok00k0k0k0k0k0k0k0k0k0k0k0k0909090 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obstetric forceps (Wrigley’s, Simpson’s, Kielland’s, Piper) | Maternal: cardiac disease, toxaemia, weakness, maternal distress. Fetal: cord prolapse, malpositions (OP, DTA, face), after-coming head, fetal distress. Prolonged 2nd stage. Aid delivery/pick head in C-section. | Hx of cephalopelvic disproportion | Maternal trauma, sepsis, shock, pelvic joint injuries, PPH, fistula/incontinence. Fetal: soft tissue compression, cranial injury. Prereq: fully dilated, engaged head, adequate pelvis/anaesthesia, empty bladder/rectum, episiotomy, experienced operator |  |
| Vacuum extractor (ventouse: metal/plastic) | Same as forceps except face/after-coming head. Can help deliver head out of lower-segment C/S. | Face, breech, after-coming head; GA <34 w; prematurity; mod/severe CPD; fetal/maternal distress needing immediate delivery; after 3 failed pulls → C/S | Fetal scalp/skull injuries (cephalohematoma, ICH, lacerations, necrosis, alopecia); vaginal/cervical injury; ↑ risk cervical incompetence. Prereq: fully dilated, engaged head, GA >34 w, adequate pelvis, experienced operator | 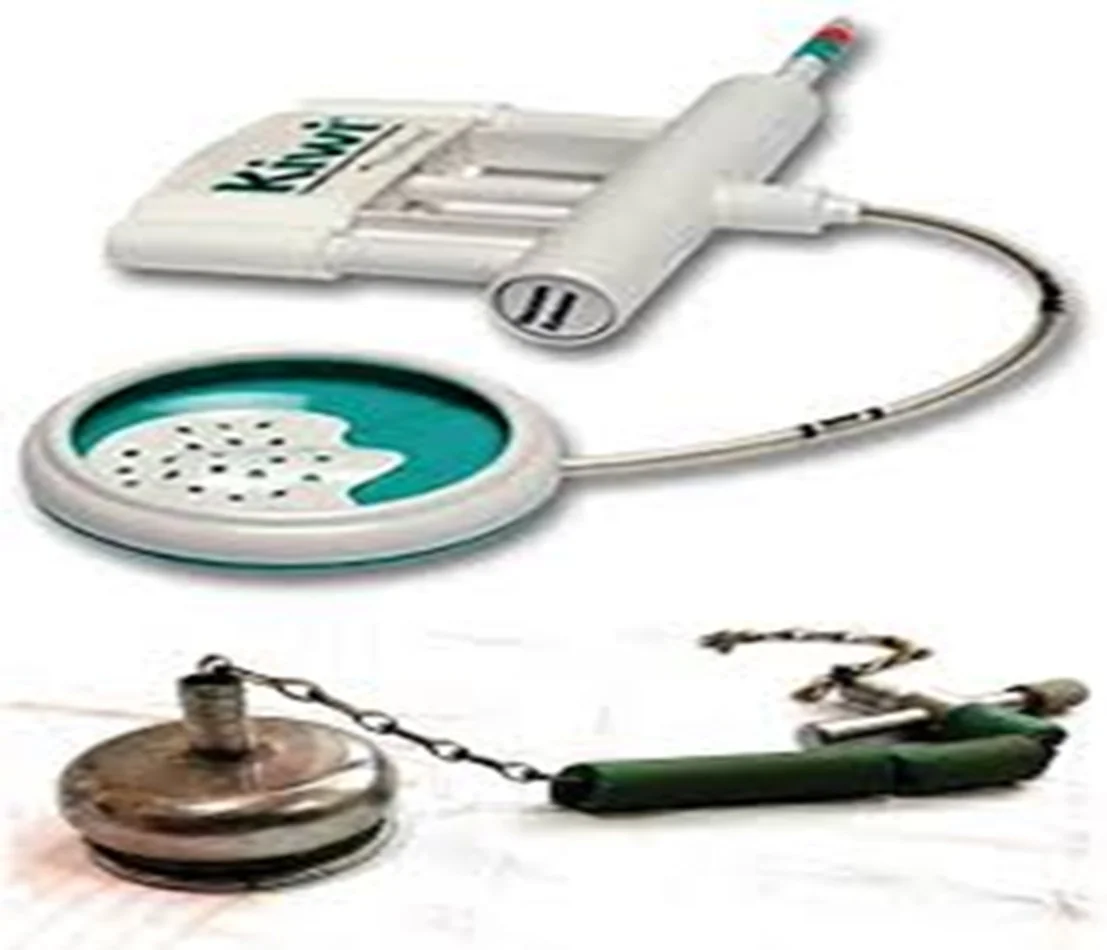 |
| Sponge holding forceps | Hold sponges/swabs; scrub abdomen pre-op | — | — |  |
| Backhaus towel clamp | Secure drapes/towels; grasp tissue; hold/reduce small bone fractures | — | Perforating clamp |  |
| Scalpel handles | Skin incisions in C-section | — | — | 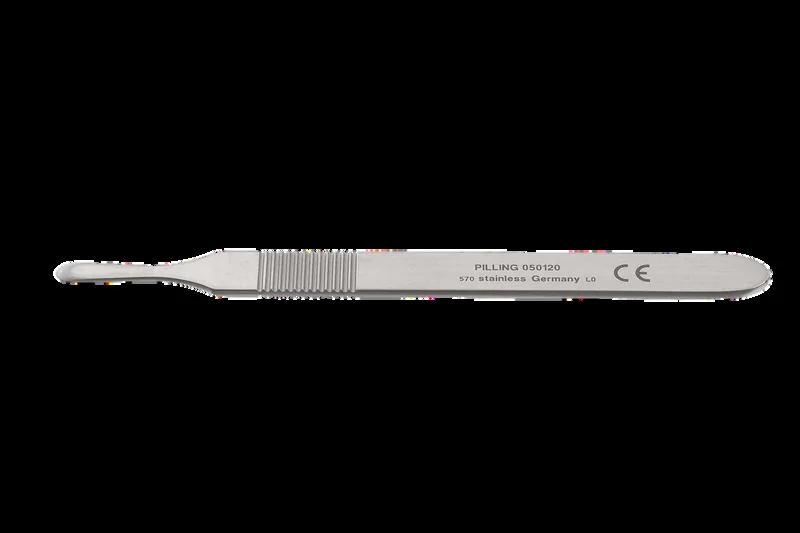 |
| Artery forceps | Hemostasis; retract tissue/skin; hold stay sutures; hold tissue/skin | — | — | 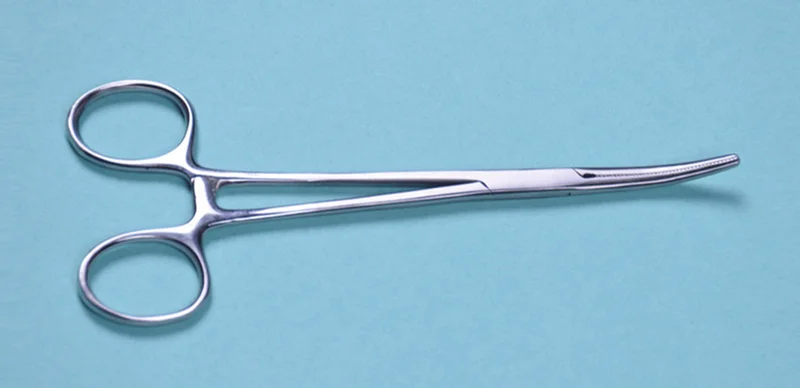 |
| Allis forceps | Hold tough tissue (rectus sheath), fascia; grasp soft tissues (breast/bowel) | — | Atraumatic for prolonged hold |  |
| Doyen’s retractor | Retract bladder during C-section; protect during uterine suturing | — | If misapplied → bladder contusion |  |
| Green Armytage forceps | Control bleeding from uterine edges; assist suturing in C-section | — | — | 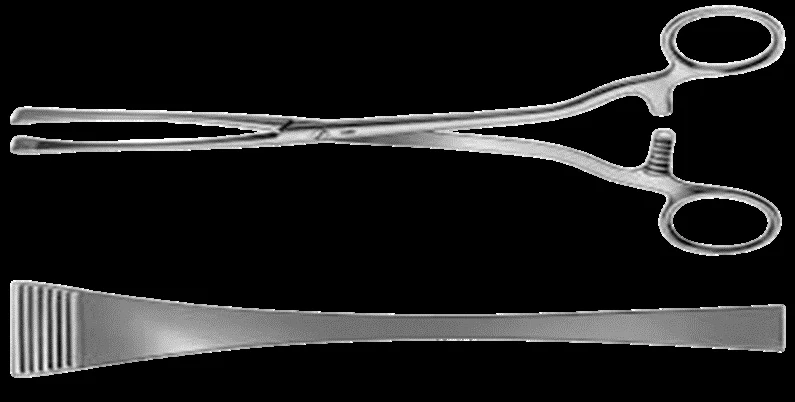 |
| Mayo scissors (curved) | Cut thick tissues (uterus, muscle) | — | — |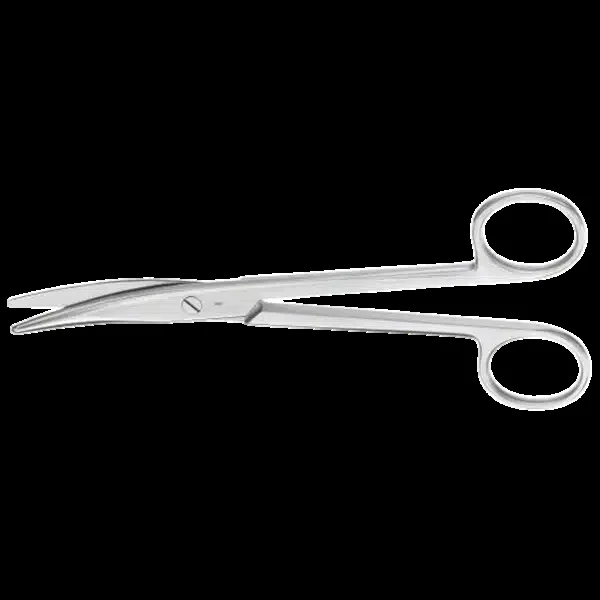  |
| Langenbeck retractors | Retract skin during closure at CS/laparotomy | — | — |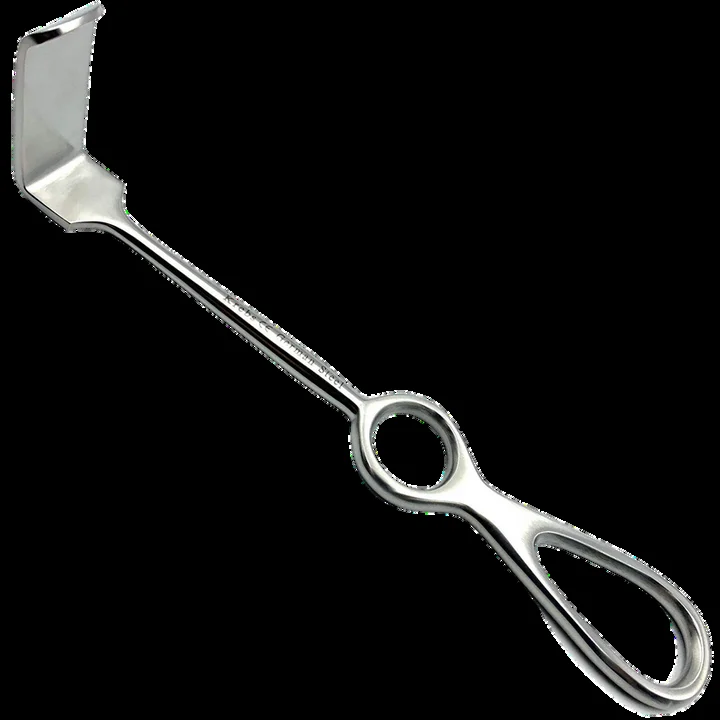  |
| Needle holders | Hold/lock needles for suturing | — | — |  |
| Cusco’s (duck’s) speculum | Expose cervix/vaginal walls; swabs; apply instruments; IUD; HSG; biopsies | — | Pros: easy, self-retaining, adjustable. Cons: hides walls unless withdrawn; limited wall protection in cautery | 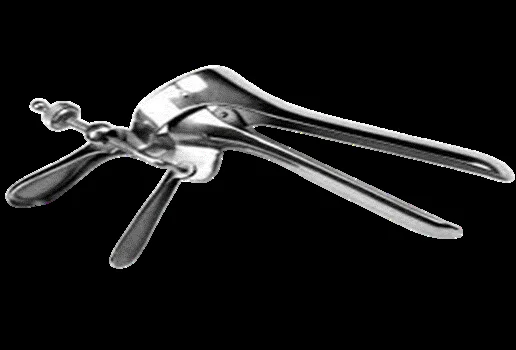 |
| Sim’s vaginal speculum | Expose anterior vaginal wall; drainage via groove; operative space | — | Needs assistant; difficult with cystocele |  |
| Tenaculum/Vulsellum (single/double/multi-tooth) | Grasp anterior cervical lip; D&C; grasp submucous myoma; hysterectomy | Soft pregnant cervix; infections | Laceration, infection, bleeding | 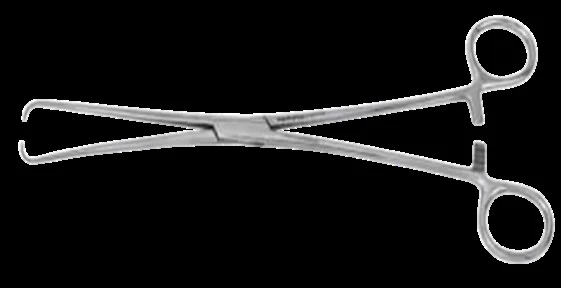 |
| Sim’s uterine sound | Measure cavity length; determine uterine direction; diagnostic differentiation | Suspicion of pregnancy; soft uterus (malignancy/infection/molar) | Perforation; ascending infection |  |
| Hegar’s uterine dilators | Gradual cervical dilatation. Dx: cervical incompetence. Rx: cervical stenosis, dysmenorrhea. Step: prior to D&C/evacuation, VH, before IUD procedures | Active genital infection; pregnant uterus (viable) | Perforation; cervical incompetence (most common) → habitual abortion; ascending infection; cervical laceration |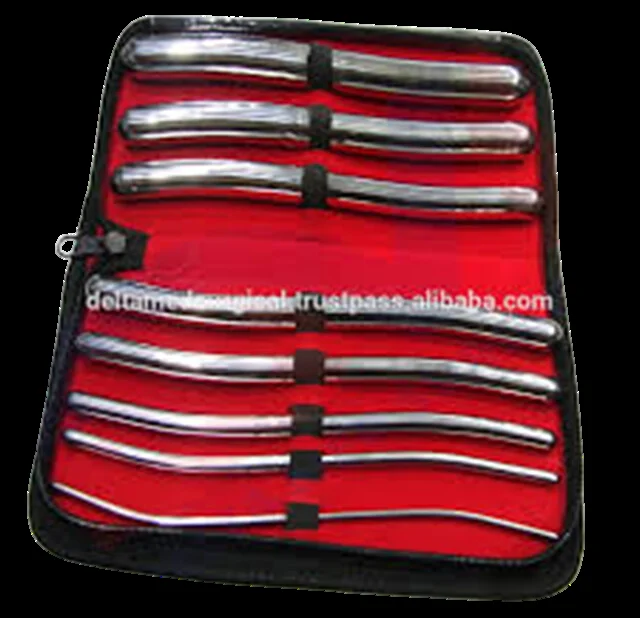  |
| Ovum forceps | Remove intact ovum; evacuate uterine contents in D&C; remove IUCD/products | — | — | 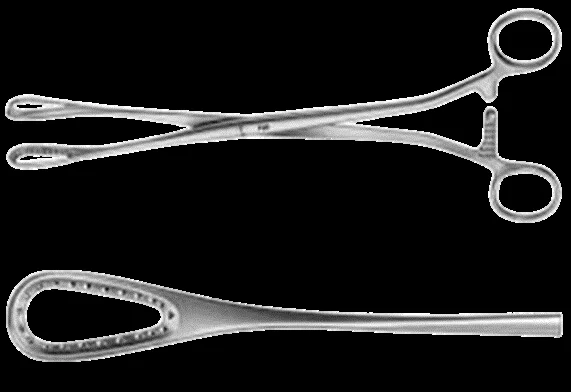 |
| Uterine curette (sharp/blunt) | Diagnostic and therapeutic curettage (abnormal bleeding, polyps, etc.) | — | Sepsis; perforation; Asherman’s; bleeding; endometriosis/peritonitis | 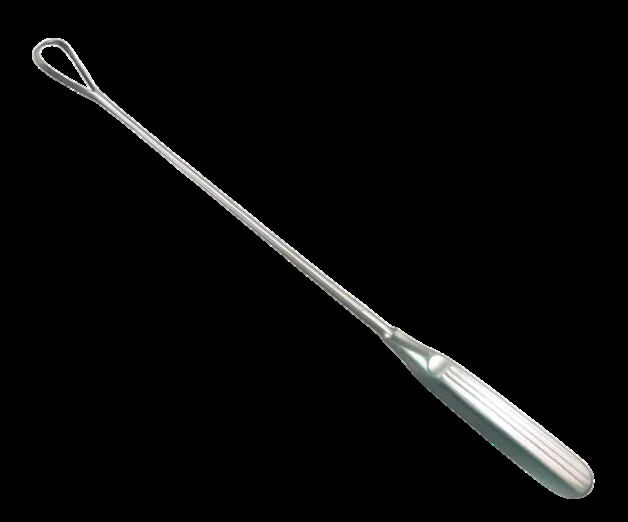 |
| Urinary catheters (metal, Foley) | Induction (Foley mechanical); prevent uterine inertia (1st stage); prevent retained placenta/PPH (3rd stage); diagnose fistula | Pressure necrosis; lower tract trauma (e.g., urethral tear) | Infections; urethral injury. Metal: sepsis intro, false passage, bladder perforation, urethral shock/fever. Metal advantages vs Foley: less infection/pain | 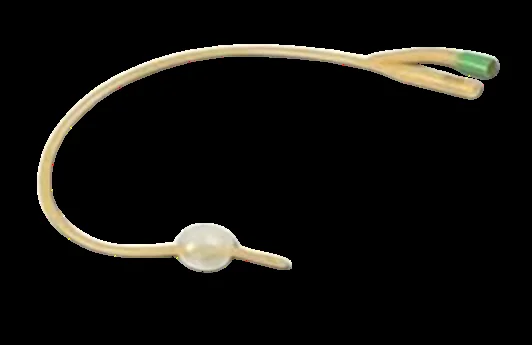 |
| Wooden spatula & cytobrush | Pap sampling; screen/diagnose cervical cancer at SCJ (transformation zone) | — | Not a true biopsy; it’s a scraping |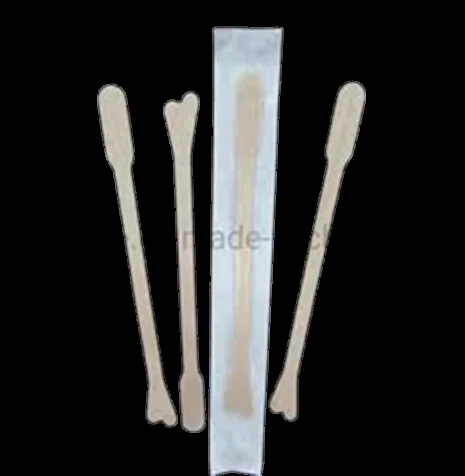  |
| Laparoscopy set (Veress, trocar/cannula, scope) | Minimally invasive access for gynecologic procedures | — | — |  |
| Amnihook (amniotome) | Artificial rupture of membranes | — | — |  |
| Umbilical cord clamp | Clamp cord postpartum | — | — | 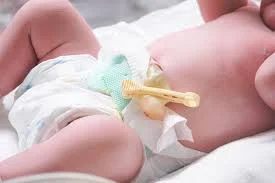 |