Treatment
- Life-style modification: e.g.
- Diet: should have low glycemic index (i.e. ↑ vegetables and ↓ CHO).
- Weight reduction.
- Encourage physical exercise.
- Correction of the precipitating factors: e.g. infection.
- Metformin: it ↓hepatic output of glucose and ↓ intestinal glucose absorption so it ↓ plasma insulin levels.
- Insulin sensitizers e.g. pioglitazone or sulphonylureas to ↑ insulin receptors sensitivity.
- Small dose of fluorinated corticosteroids e.g dexamethazone : because it has anti-immunological effect e little or no hyperglycemic effect.
- In case of local insulin resistance: -Change the site of injection regularly. -Give aprotinin (trasylol) with insulin at the injection site to inhibit the proteolytic enzymes.
Counter regulatory Hormones
They counteract the storage functions of insulin in regulating blood glucose levels during periods of fasting, exercise, and other situations that either limit glucose intake or deplete glucose stores.
- The catecholamines,
- Growth hormone, and Thyroid Hormone
- Glucagon, Glucocorticoids.
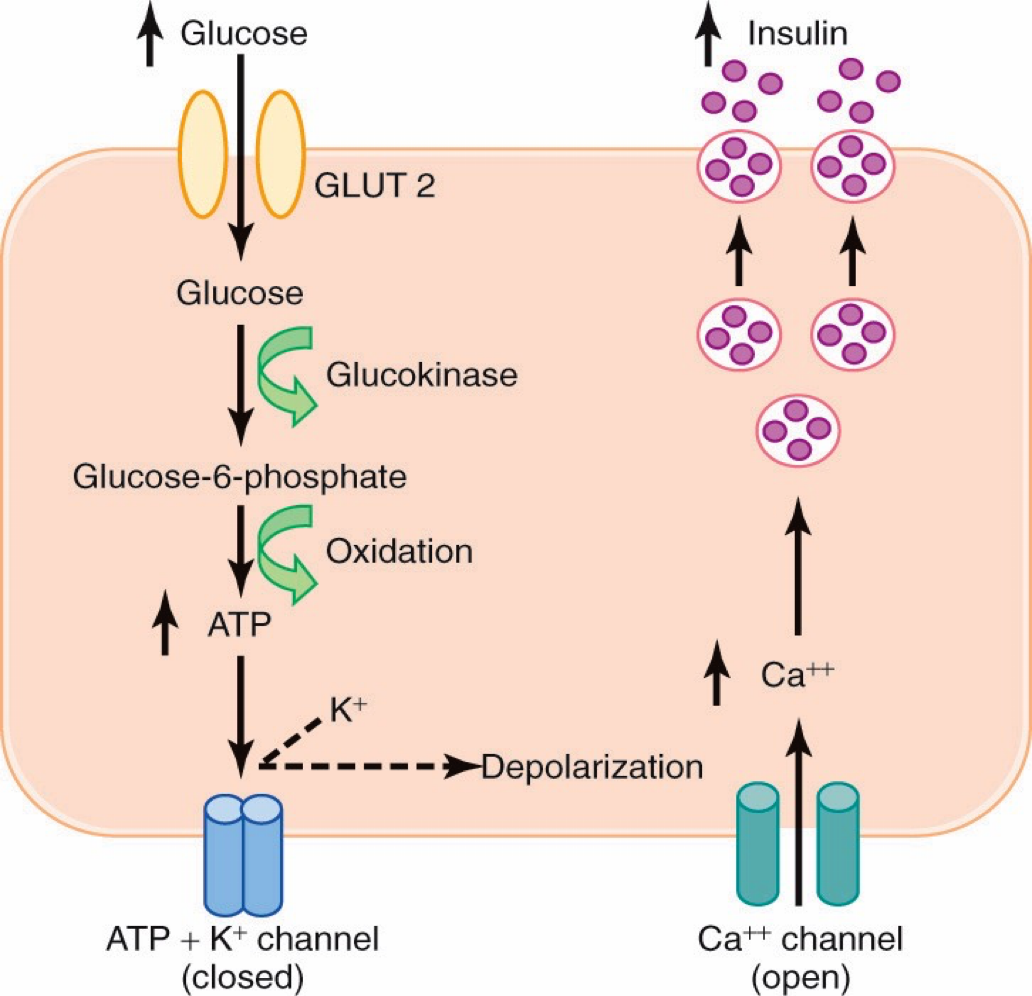
Mechanism of Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion
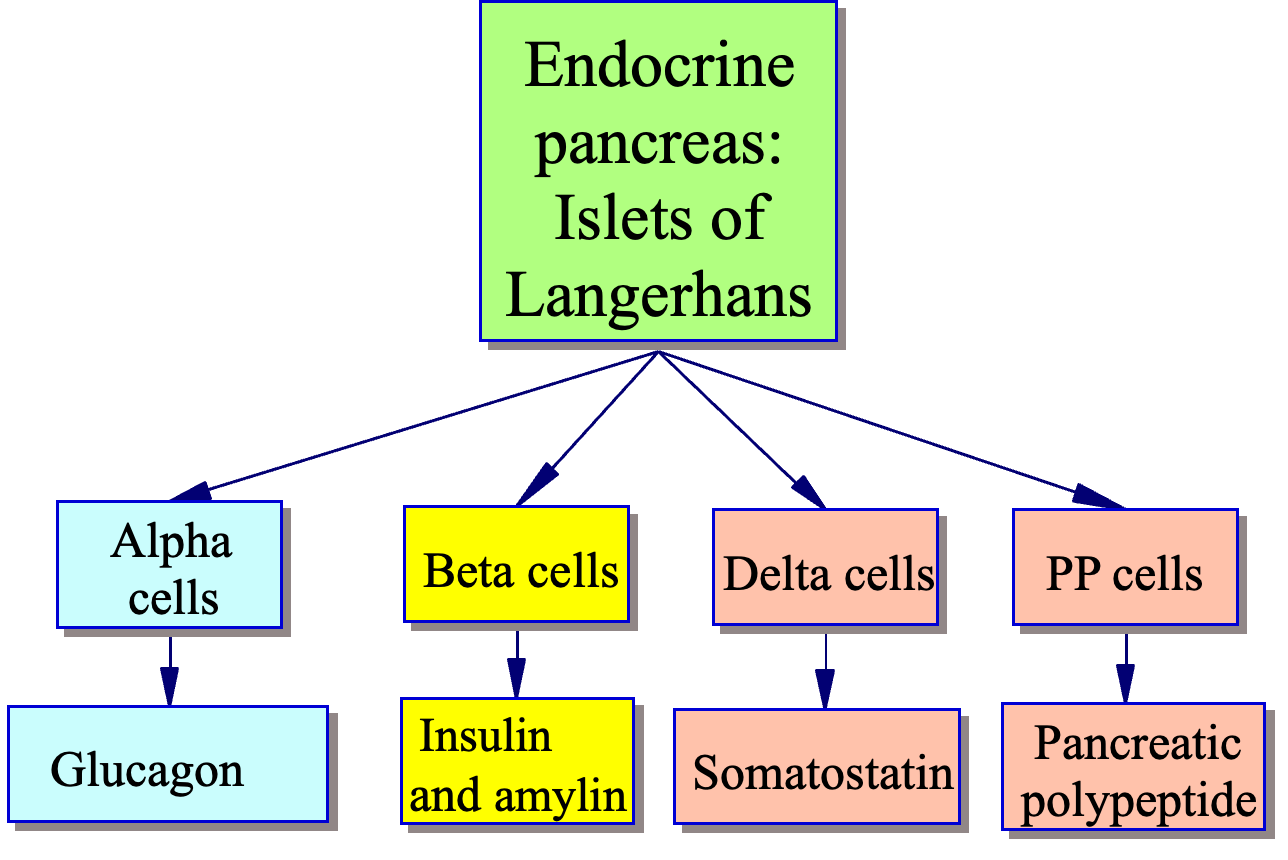
| Function | Cell Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin Secretion | Beta Cells (70-80%) | Produce and secrete insulin to regulate blood sugar levels |
| Glucagon Secretion | Alpha Cells (15-20%) | Produce and secrete glucagon to raise blood sugar levels |
| Somatostatin Secretion | Delta Cells (5-10%) | Inhibit insulin secretion and glucagon release to regulate blood sugar levels |
| Pancreatic Polypeptide Secretion | PP Cells (1-2%) | Regulate pancreatic secretions and gut motility |
| Regulation of Blood Sugar Levels | All Islet Cell Types | Maintain blood sugar levels within a narrow range (70-110 mg/dL) |
| Feedback Regulation | All Islet Cell Types | Adjust secretory activity based on changing glucose levels |
| Autoregulation | Beta Cells | Regulate their own function through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms |
| Inflammation Regulation | All Islet Cell Types | Produce cytokines to regulate inflammation in response to immune challenges or tissue damage |
| Tissue Remodeling | All Islet Cell Types | Participate in angiogenesis, fibrosis, and other processes that maintain pancreatic structure and function |
| Hormone Regulation | All Islet Cell Types | Regulate the secretion of other hormones, such as growth hormone |