IM
Pathophysiology
- Airway hyper-reactivity (AHR) - means tendency of airways to contract too easily in response to triggers that have little or no effect in normal person
- In chronic asthma - remodeling of airway occurs, leading to fibrosis of the airway wall, fixed narrowing of airway.
- Relationship between IgE and bronchial asthma is well established
- Allergen inhalation is followed by broncho-constriction
- E.g. Inhalation of house dust mites, pets e.g. cats, dogs, pests such as cockroaches and fungi (aspergillus)
- Allergic mechanism are also responsible in some cases of occupational asthma
- Aspirin sensitive asthma - due to production of leukotrines
Exercise induced asthma
- Hyper ventilation results in water loss from respiratory mucosa, dehydration of airways, which triggers release of Leukotrines from mast cell, which causes broncho constriction.
Drugs causing Bronchial Asthma
- ẞ-blockers - given orally or even eye drops
- Aspirin
- NSAIDS
- Oral contraceptive pill
- Cholinergic agents
- Prostaglandin F2
Clinical Features
Typical symptoms include
- Recurrent episodes of wheeze
- Chest tightness
- Breathlessness
- Cough
Exacerbation of Asthma
- Exacerbation are characterized by increased symptoms, deterioration in lung function, PEF<60% of patient’s best recording
- Exacerbation are precipitated by
- Viral infection
- Pollen
- Air pollution
- Management - short course of oral predinisolone corticosteroids 30-60mg/day
Churg-Struss Syndrome Z
- Bronchial asthma with systemic and pulmonary Vasculitis
- Eosinophilia (> 1000/mm³) - Absolute count. OR Eosinophil > 10 % in peripheral blood.
- Systemic Vasculitis in small vessel associated with purpura, mononeuritus multiplex
- Rarely diffuse alveolar hemorrhage
FM
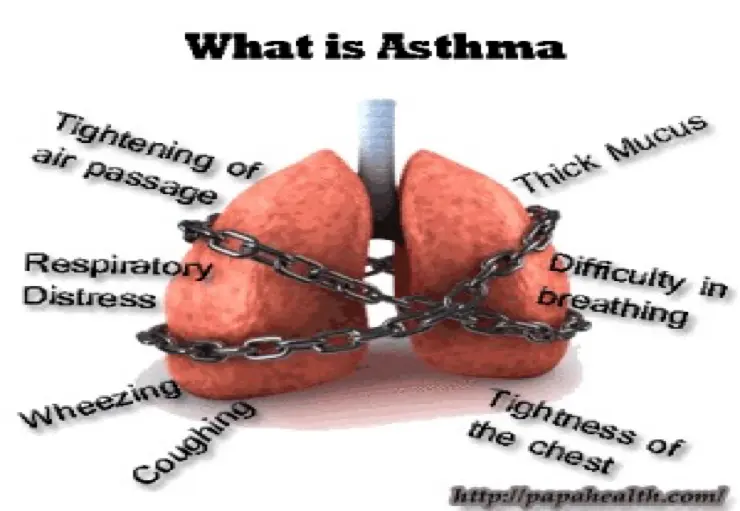
What is Asthma?
- Asthma is a common heterogeneous chronic disorder of the airways, characterized by variable usually reversible and recurring symptoms related to one or more of airflow obstruction, bronchial hyper-responsiveness, and underlying inflammation.
Symptoms of Asthma
- Tightening of air passage
- Thick mucus
- Difficulty in breathing
- Respiratory distress
- Wheezing
- Coughing
- Tightness of the chest
Pathophysiology
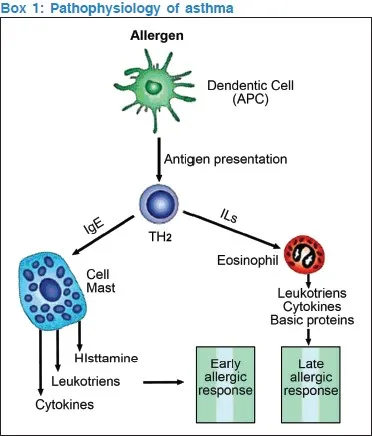
Asthma is an inflammatory disease and not simply a result of excessive smooth muscle contraction.
- Increased airway inflammation follows exposure to induders such as allergens or viruses, exercise, or inhalation of nonspecific irritants.
- Increased inflammation leads to exacerbations characterized by dyspnea, wheezing, cough, and chest tightness.
- Abnormal histopathology including edema, epithelial cell desquamation, and inflammatory cell infiltration.
Phases of Asthma
-
Early phase (Acute):
- Due to bronchial smooth muscle spasm & excessive secretion of mucus.
-
Chronic phase:
- Continuous inflammation, fibrosis, edema, necrosis of bronchial epithelial cells.
Box 1: Pathophysiology of Asthma
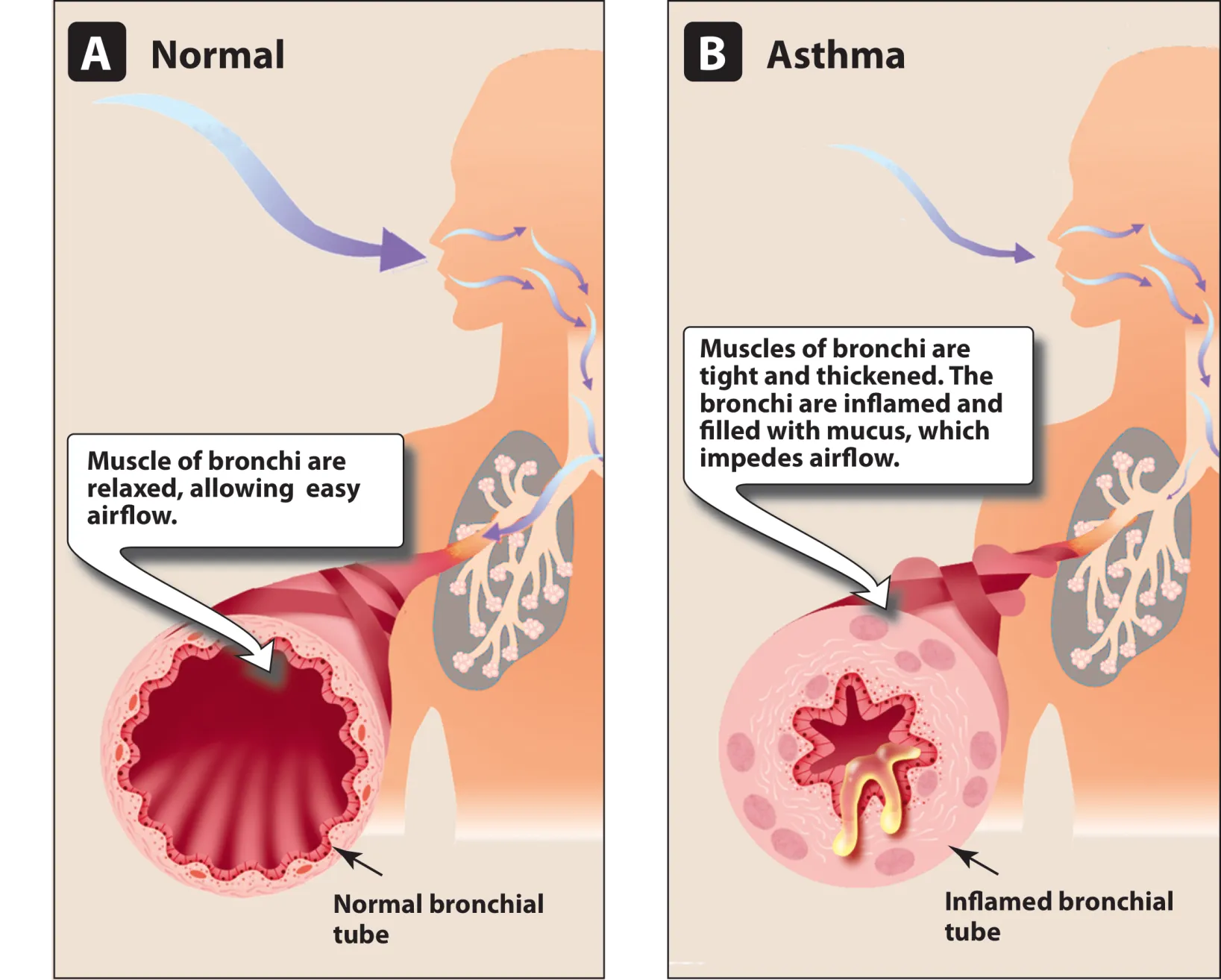
Normal vs Asthma
A. Normal
-
Muscle of bronchi are relaxed, allowing easy airflow.
-
Normal bronchial tube
-
Muscles of bronchi are tight and thickened.
-
The bronchi are inflamed and filled with mucus, which impedes airflow.
-
Inflamed bronchial tube
Types of Asthma
- Allergic asthma (extrinsic)
- Non-allergic asthma (intrinsic)
- Cough variant asthma
- Occupational asthma
- Exercise-induced asthma
- Medication-induced asthma
- Nocturnal asthma
Triggers
- Allergies
- Tobacco smoke
- Environmental factors
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Stress
- Genes
- Atopy
Asthma Triggers
- Pets
- Exercise
- Pollen
- Bugs in the home
- Chemical fumes
- Cold air
- Fungus spores
- Dust
- Smoke
- Strong odors
- Pollution
- Anger
- Stress

Drugs Causing Bronchial Asthma
- Aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) hypersensitivity, sulfite sensitivity
- Use of beta-adrenergic receptor blockers (including ophthalmic preparations)
- Oral contraceptive pill
- Cholinergic agents
- Prostaglandin F₂
Thera
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease in which many cells play a role in particular mast cells, eosinophils, and T lymphocytes - paroxysmal reversible generalized obstructive airway disease.
with the following characteristics:
- Periodicity of symptoms.
- Airflow obstruction; wheeze
- Diurnal variability of symptoms.
- Airway hyperresponsiveness.
Lung innervations:
- Air ways are rich supplied with afferent and efferent vagal nerves responsible for bronchoconstriction (parasympathetic tone) ,so M3 blockers can dilate the constricted air ways.
- In contrast, noradrenergic sympathetic innervations of air way is sparse, whoever β2 adrenergic receptors are present in airways.
- Airway cell surface have receptor for adenosine which causing contraction of airway smooth muscle and histamine release from airway most cell.
h1=anaphylactic shock h2=? h3=?
Cells and Mediators #T
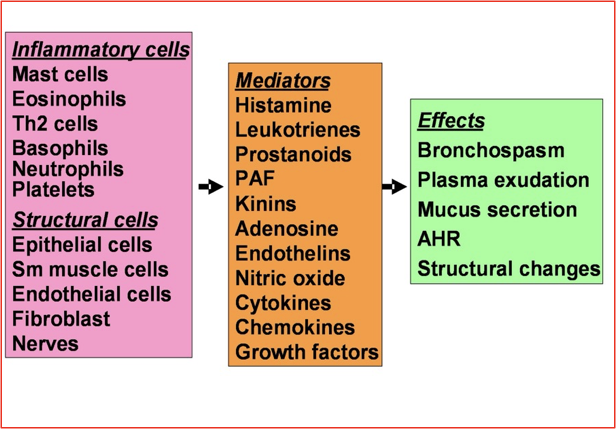
Etiology
Due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Environmental Factors
Immunoglobulin E - antigen antibody interaction mast cell destruction = histamines
- Indoor allergens;
- Outdoor allergens;
- Occupational sensitizers
- Tobacco smoke
- Air Pollution
- Respiratory Infections
- Parasitic infections
- Socioeconomic factors
- Family size
- Diet and drugs
- Obesity
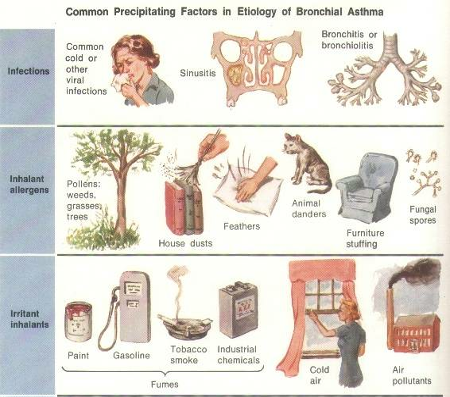
Factors that Exacerbate Asthma
- Allergens
- Respiratory infections
- Exercise
- Weather changes
- Food, additives Sulfur dioxide and drugs
- Psychological ? (40%)
Causes:
-
1-Extrinsic= Atopic Asthma= Secondary to hypersensitivity to one or more antigens e.g. pollen grain. Pathogensis
-
Early or immediate phase (bronchospasm): due to mediators release from mast cells as histamines and leucotriens.
-
Late phase (inflammation): due to release of secondary mediators e.g. cytokines and interleukins.
best to treat with anti inflammatory and bronchodilators as these two present simultaneously
-
-
2-Intrinsic=cryptogenic= usually suddenly presents in middle/old age Secondary to non antigenic etiology e.g. neuronal imbalance; = = bronchospasms’s
-
Pathology: bronchospasm, mucosal oedema and viscid sputum.
Pathophysiology
Best described as chronic eosinophilic bronchitis/bronchiolitis.
Airway obstruction due to: 1- Smooth muscle contraction. 2- Mucosal edema. 3- Lumen secretion.
Symptoms
- Cough
- Dyspnea
- Wheeze
- Nocturnal Symptoms; all above combined
“…he found himself getting out of breath and feeling wheezy…”
Signs “In-between the attacks”; Patient may be entirely normal on examination .
Is it Asthma?
- Recurrent episodes of wheezing
- Troublesome cough at night
- Cough or wheeze after exercise or chest tightness after exposure to airborne allergens or pollutants
Signs “during acute asthma”
General examination:
- Tachypnea, tachycardia, use of accessory muscle of respiration.
- “His pulse was 100/minute, respiratory rate 22/min….”
Local (Chest) examination:
- Inspection: Hyper expanded chest
- Palpation: Limited chest expansion
- Percussion: Low diaphragm
- Auscultation: z Expiratory wheeze, may be silent chest (life threatening asthma)
Manifestations
A- Clinical Manifestations
- Attacks of expiratory dyspnea
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Chest tightness
- Wheezing (high-pitched whistling sounds when breathing out)
B- Lab Investigations 1-Blood:
- Eosinophilia,
- Moderate leukocytosis
- Increased serum level of Ig E.
2-Sputum:
- Inflammatory cells,
- Curschmann’s spirals (viscous mucus which copies small bronchi)
- Charcot-Leyden crystals (crystallized enzymes of eosinophils and mast cells).
C- Chest X-ray reveals:
- Hyperlucency of lung fields
- Low standing and limited mobility of diaphragm
- Expanded intercostal spaces
- Horizontal rib position.
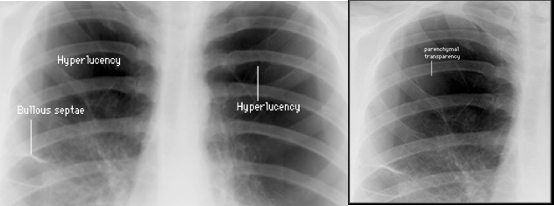 usually don’t appear in presenting asthma patient, unless these pneumonic manifestations - so history is best determinant factor with diagnosis of asthma.
usually don’t appear in presenting asthma patient, unless these pneumonic manifestations - so history is best determinant factor with diagnosis of asthma.