Benign Tumors
-
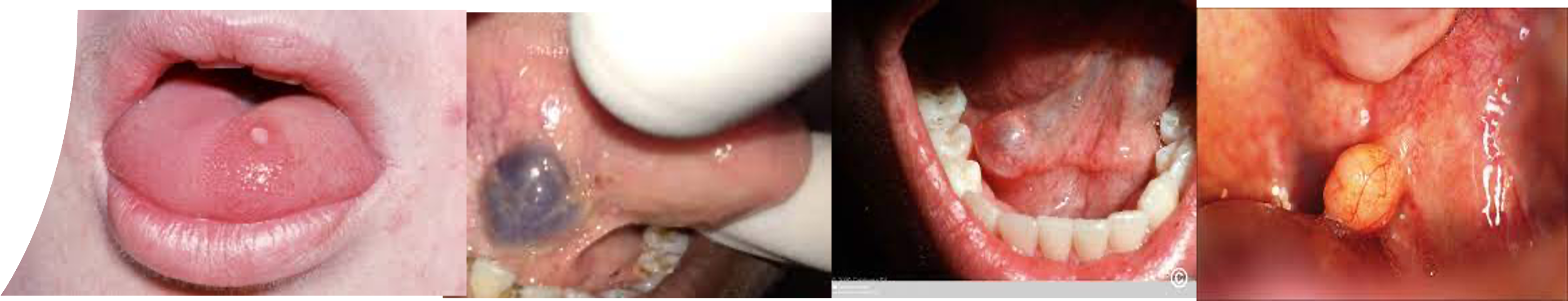
Papilloma: Usually asymptomatic, treated with surgical excision.
-
Haemangioma: May be capillary or cavernous. Treatment includes diathermy coagulation or injection of sclerosing agents. Cryotherapy and laser coagulation are also effective.
-
Pleomorphic adenoma: mostly seen submucosally on the hard or soft palate. It is potentially malignant and should be excised totally
-
Mucous cyst: usually seen in vallecula. Surgical excision is the treatment of choice in case of symptomatic cysts
-
Lipoma
Malignant Tumors
- Common Sites: Base of tongue, tonsil and tonsillar fossa, faucial palatine arch (soft palate and anterior pillar), posterior pharyngeal wall.
- Gross Appearance: Superficially spreading, exophytic, ulcerative, infiltrative.
Treatment
Depends upon the site and extent of the disease, patients general condition, experience of treating surgeon and facilities available.
Options of treatment are: - Surgery alone - Radiation alone - Surgery+radiotherapy - Chemotherapy+surgery+radiotherapy - Palliative therapy
Team approach:
-
surgeons and Radiation Oncologists SLP
-
T1 and T2 –surgery or radiation
-
T3 and T4 –combined modality