SURGERY
Lymphedema
-
Interstitial oedema of lymphatic origin
-
Primary lymphedema: Congenital, due to poorly developed lymphatics
-
Secondary: Infective (Filariasis) or neoplastic (secondary deposits)
| Causes of Lymphoedema | |
|---|---|
| Primary | |
| Congenital < 1 year: sporadic, Milroy’s disease | |
| Onset 1-35 years: sporadic, Meige’s disease | |
| > 35 years: Tarda | |
| Secondary | |
| Bacterial/fungal/parasitic infection (filariasis) | |
| Lymphatic malignancy | |
| Radiotherapy to lymph nodes | |
| Surgical resection of lymph nodes | |
| DVT | |
| Thrombophlebitis |
CL
Lymphedema
Interstitial oedema of lymphatic origin - Types:
-
Primary lymphedema: Congenital, due to poorly developed lymphatics
-
Secondary: Infective (Filariasis) or neoplastic (secondary deposits) Filariasis is a parasitic disease caused by an infection with roundworms of the Filarioidea type
History
- Age of onset:
- Types:
- Primary: Congenital- from birth, Praecox- early life, Tarda- late in life
- Secondary: middle to old
- Gender: F> M
- Nationality: Filariasis in tropical areas
- Slowly progressive swelling
- Painless
- Past Med Hx: malignancy, radiotherapy, recurrent infection,
- Surgery: lymph node excision
- Family history: primary type can be familial
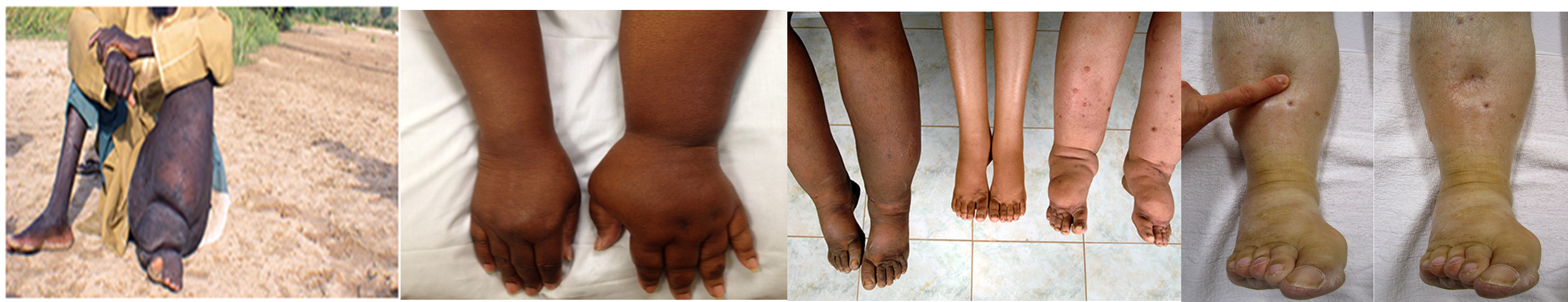
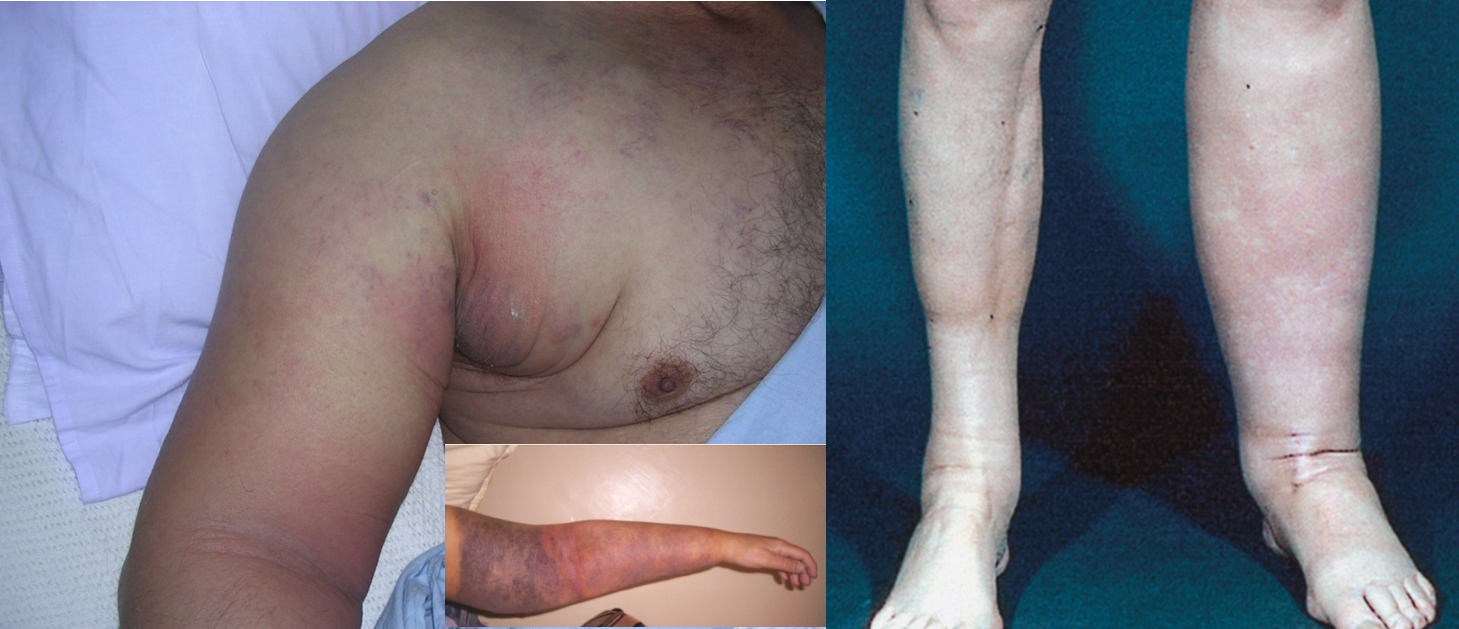
Inspection:
Unilateral swollen limb, swollen foot in lower limb , toe usually spared
Palpation:
Initially pitting, later non-pitting due to fibrosis, thickened skin, hair loss, hyperkeratotic, scaly
Draining lymph nodes:
-
Primary lymphedema- not enlarged.
-
Malignancy- enlarged or excised
Complete examination of the patient
Absence of renal, cardiac, abdominal and venous diseases helps in the diagnosis of lymphedema