Abortion
Medicolegal view
Objectives:
To know the following
- definition and classification of Abortion*
- the type of Abortion*
- factors affecting the wound
- estimate the date of Abortion*
- different types of Abortion*
- complications of Abortion*
Definition of Abortion
Abortion is premature expulsion of products of conception from womb, either spontaneous or induced
Medicolegal meaning
-
Abortion means expulsion of products of conception in the first trimester of pregnancy.
-
Miscarriage means expulsion of product of conception in second trimester.
-
Premature delivery refers to expulsion of fetus after 7 months of pregnancy but before term.
- Legally there is no difference between Abortion
Classification of Abortion
classified into following two major groups
- Natural (spontaneous)
- Artificial (Induced)
- Induced abortion may be
- Justifiable abortion (therapeutic)
- Criminal abortion
- Unsafe Abortion and Fabricated Abortion
- Induced abortion may be
CRIMINAL ABORTION
Any abortion, which does not come under the rules of the Medical Termination of pregnancy (MTp), is considered as criminal abortion.
Thus, in other words, it is an unlawful expulsion of product of conception at any stage of gestation by any unqualified person or a qualified doctor and is punishable under the law.
MOTIVES FOR CRIMINAL ABORTION
- Unmarried girls
- A poor family
- Female infanticide
Pregnancies in the world
- 210 million women get pregnant annually
- 15% miscarriages, stillbirths
- 22% induced abortions
- 63% live births
- miscarr., stillbirths
- induced abortions
- live births

METHODS TO INDUCE CRIMINAL ABORTION ARE
- Use of abortifacient drugs
- Application of . mechanical violence
I. Use of abortifacient drugs
Ecbolics: These drugs initiate uterine contraction and causes abortion. Examples are
- Ergot preparations Synthetic estrogen and Quinine Emmenagogues: These drugs promote uterine congestion and induce bleeding .2 :thus expelling product of conception. Examples are
- Borax ** Oil of savin
Irritants: These are of following types .3
- Genitourinary tract irritants - these agents produce inflammation of genitourinary tract and reflexly irritate the uterus and induce uterine contraction example .Cantharides, turpentine oil
- Gastrointestinal tract irritants these agents cause reflex contraction of uterine .muscles - example; croton oil etc
- Systemic poisons - For example: arsenic, mercury etc
- Abortion pills etc
B) Criminal (unlawful) abortion
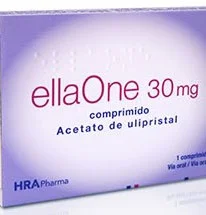
Therapeutics and Medicational abortion
- Abortions completed with medication, called medical abortions, can be performed within 64 days of gestation from last menstrual period.
- 2% to 3% of women who have a medical abortion will need to have a surgical procedure.
Medications used to induce abortion :include
- Mifepristone (Mifeprx): Known as RU-486, it’s taken as a pill. this drug counters the effect of progesterone.
- Misoprostol (Cytotec): Misoprostol is almost always u: in conjunction with mifepristone to induce a medical abo Misoprostol is a prostaglandin-like drug that causes the u to contract. it’s taken orally or vaginally.
- Methotrexate: Methotrexate is used less often. Howev., methotrexate may be used in women who are allergic to mifepristone or when mifepristone is not available. it’s injected into a muscle.
A woman should not have a medical abortion if she
- Is more than 64 days pregnant (counted from the first day of the last menstrual period).
- Has bleeding problems or is taking blood thinning medication.
- Has chronic adrenal failure or is taking certain steroid medications.
- Cannot attend the medical visits necessary to ensure the abortion is completed.
- Does not have access to emergency care.
- Has uncontrolled seizure disorder (for misoprostol).
- Has acute inflammatory bowel disease (for misoprostol).
II. VIOLENCE
- General violence - may act directly or indirectly on uterus.
- Severe form of exercise -Application of blows or kicks over abdomen or pressure on abdomen .
- Cupping: a flame light is placed on abdomen and a metal mug is placed over the flaming light.
- 2. Local method
- A. By unskilled or semiskilled person.
- Rupture of membrane by abortion stick, metal rod, knitting needle, hair Pin etc.
- Application of abortion Paste.
- Use of root of plant as Abortifacient agent.
- Syringing: either for aspiration of fluid or forced filling of uterine cavity with fluid and air.
- Rupture of membrane by abortion stick, metal rod, knitting needle, hair Pin etc.
- B) By skilled Person
- Low rupture of membrane
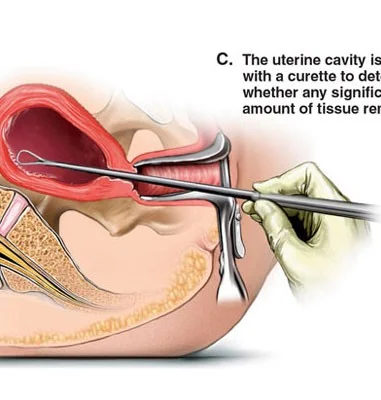
- Vacuum aspiration
- Dilatation and evacuation
- Use of Prostaglandins.
- A. By unskilled or semiskilled person.
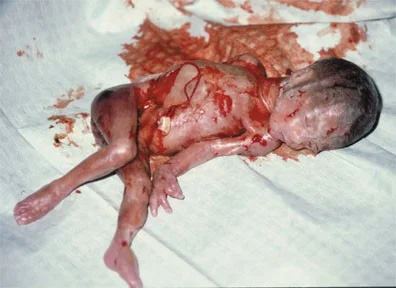
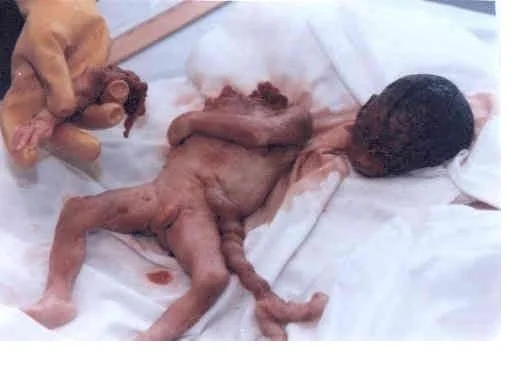
COMPLICATION OF CRIMINAL ABORTION
Immediate
- Hemorrhage
- Perforation of uterus
- Shock due to vagal inhibition resulting from instrumentation
- Fat embolism
- Air embolism
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Incomplete abortion
- Local injury
Delayed
- Septicemia.
- Tetanus.
- Endometritis.
- Renal failure.
- Peritonitis.
- Sterility.
- Recurrent abortion.
Causes of Death in Criminal Abortion
- Vaso-vagal shock
- Hemorrhagic shock
- Perforation of uterus
- Septicemia
- Embolism
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
DUTIES OF REGISTERED MEDICAL PRACTITIONER IN CRIMINAL ABORTION
Doctor should record history of the incident, the method adopted to procure abortion
- If death is imminent, doctor must arrange for dying declaration
- If female dies, he should report matter to the police
Medical Evidence of Abortion
- Examination of female
- Examination of aborted material
EXAMINATION OF FEMALE (DURING LIFE)
- General: Female will have exhaust look, increase temperature, increase pulse.
- Breasts; Are heavy, enlarged, areola and nipples are pigmented, colostrum/milk may ooze on squeezing the breasts .
- Abdomen: Is lax and wrinkled. Striae may be present along with linea nigra. Involuting uterus may be palpable.
- Perineum: Laceration or bruises may be noted, inflammation is evident
- Labia: majora and minora will be inflamed and bruised
- Vagina: Tags of membrane, partial aborted material, blood, foreign body, abortion stick etc. may be found. The vaginal wall is contused, abraded or lacerated. The wall is lax, dilated.
- Cervix: The external os would be patulous, ulceration or erosions may be present. Cervical canal may be dilated with abrasions or lacerations.
- Uterus: May be enlarged on bimanual examination or may be showing signs of involution.
- Swab from cervical canal will reveal chemical used for procuring abortion and can be used for bacteriological examination.
- Urine examination: hCG may be detected up to 7 days.
EXAMINATION OF FEMALE (AFTER DEATH)
- Clothes: Undergarments may show blood, clots, pieces of product of conception, stains of chemicals used etc.
- Uterus: Enlarged, cavity may show presence of partially separated product of conception, foreign body, blood clots, presence of any paste or chemical, evidence of injury or perforation etc.
- Evidence of infection .
- Ovaries: Presence of corpus luteum
- EXAMINATION OF ABORTED MATERIAL “Police may request medical examiner to examine a substance alleged to have been expelled from uterus as product of conception.
Medicolegal importance of placenta
- At term placenta is about 500 gm in weight.
- Period of gestation can be estimated.
- Some poisons may be detected in placenta.
- Retained placenta or pieces of placenta may be found in criminal abortion and may be the cause of death due to hemorrhage.
- Disease can be ascertained.
- Transfer of poisons, drugs, bacteria or antibodies across placenta (placental barrier) may result in fetal death, fetal infections or fetal malformations.
Medical Termination of Pregnancy
INDICATIONS
- Therapeutic
- Eugenic
- Humanitarian - When the pregnancy is caused by Rape
- Social When pregnancy has resulted due to failure of contraceptive method adopted by married woman or her husband for the purpose of limiting the number of children, then such pregnancy can be terminated on social grounds. *In an emergency, a Registered Medical Practitioner can terminate pregnancy at any place, irrespective of duration of pregnancy.
Rules for Doing MTPZ
-
Only qualified Registered Medical Practitioner, who has assisted in at least 25 cases of MTP in a recognized hospital A Doctor with MD in Gynecology and Obstetrics.
-
Place - MTP can be Carried Out at A hospital maintained or established by government. Non-government hospital approved by government
-
Consent A female above 18 years of age with sound mind can give consent for MTP. In minor females (i.e. age less than 18 years) or mentally ill , consent of parents or guardian is necessary.
-
Duration of Pregnancy . When duration of pregnancy is below 12 weeks of gestation, one Registered Medical Practitioner (RMP) can terminate the pregnancy. . When duration of pregnancy is above 12 weeks but less that 20 weeks (i.e. 12-20 weeks), then two RMP are required to terminate the pregnancy.
-
Documentation and Record Date generated by mentioning the year against the serial number . The admission register is a secret document. It should be maintained for at least 5 years from the last entry.Z
Methods of Inducing MTP
-
Up to 12 Weeks
- Manual vacuum aspiration
- Suction evacuation and/or curettage
- Dilatation and curettage
- Mifepristone
- Methotrexate and misoprostol
-
Between 13 to 20 Weeks
- Dilatation and evacuation
- Oxytocin infusion
- Induction by prostaglandins E, (misoprostol) (Used as intravaginally, intramuscularly or intra amniotically)
- Hysterotomy - less common method
Complications of MTP
-
Immediate
- Hemorrhage and shock.
- Perforation of uterus, intestine.
- Laceration of cervix or vagina.
- Incomplete abortion.
- Endometritis.
- Embolism.
-
Delayed
- Menstrual disturbances.
- Sterility.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Recurrent abortion or premature labor.
- Psychological sequelae.
MEDICOLEGAL IMPORTANCE OF ABORTION
When abortion is induced without proper indication or in contravention to the provisions of MTP Act, it is considered as criminal abortion and is punishable by law.
When Doctor violates the provisions of MTP Act, he is liable to be punished by the law and similarly his act amount to misconduct in professional sense.
To bring a false charge of assault against any person, a female may plead that she has been assaulted and due to assault, abortion was induced.
A female may be falsely charged or implicated for inducing criminal abortion