Compartment Syndrome
Overview
Prof. Mamoun Kremli
Objectives
- Pathophysiology and causes
- Clinical Picture
- Identification
- Treatment
Pathophysiology
Key Factors
- Increasing volume in a closed compartment
- Pressure increased in compartment
- Decreasing arteriovenous difference
- Hypoxia
- Dec. in blood supply
- Irreversible muscle and nerve damage
PathophysiologyZ

Causes
-
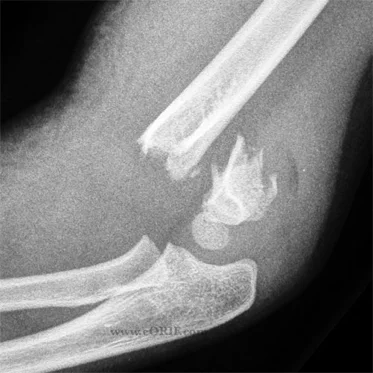
Hematoma
- Fracture hematoma
- Soft tissue trauma
- Arterial injury
- Bleeding disorders - hemophelia**
-
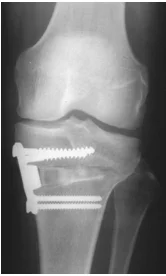
Surgery
- Post osteotomy (Tibia / Forearm)
- Circumferential tight dressings/ casting
-
Extravasation of IV infusion the fluid go to the soft tissue
-
Burns
-
Post-ischemic swelling (reperfusion)
Clinical Picture - 5P s
→ TREAT
- Pain out of proportion& expectation/ burst sensation
- passive motion / stretch → Pain is Increase
- Palpable tense swelling
- Paresthesia
→ too late, >8h
- Pallor
- Paralysis
- Pulselessness
Pain
- Absent in (high-risk patients):
- Altered consciousness because of Pain, ICU
- Children (unable to verbalize) follow the response of analgesia
- Concomitant nerve damage
- Clinical picture equivocal
- Polytrauma (Multiple injuries) patient
- Sedated patient or Epidural anesthesia
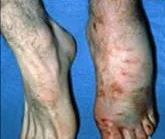
Clinical Picture - Look
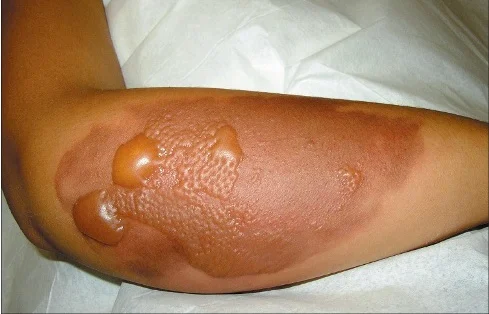
- Shiny Swelling of compartment
- Pallor / or Dusky skin
- Blisters
- Clear fluid
- serosanguinous: severe
- Bloody: worst
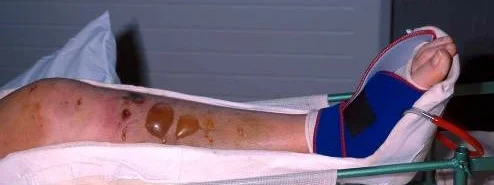
Clinical Picture - Feel
- Tense
- Tender
- Paresthesia
- Weak Pulse ?
- Too late
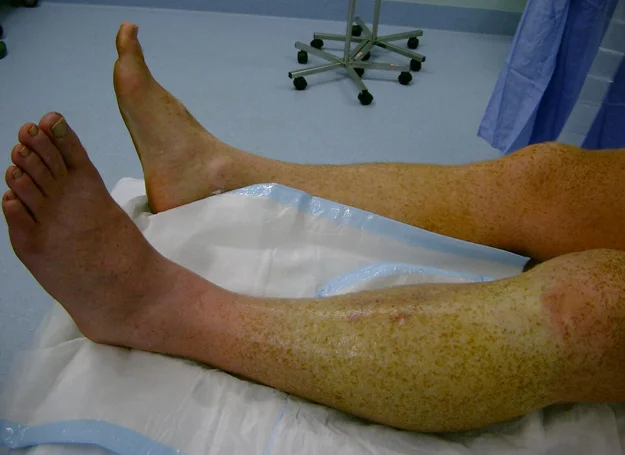
Clinical Picture - Move
- Pain on passive stretch
- Passive dorsiflexion of ankle (leg)
- Passive dorsiflexion of wrist (forearm)
Diagnosis
Open fractures DO NOT decompress an elevated compartment pressure could be open fracture but the opening not enough so it have compartment.
- High index of suspicion
- Diagnosis is clinical:
- Unrelenting bursting pain
- Not relieved by analgesia
- Swollen compartment
- Pain on passive stretching
- Sensory deficit?
- Pulses always palpable
Management
- ABC’s.
- Correct hypotension
- Supplemental oxygen administration
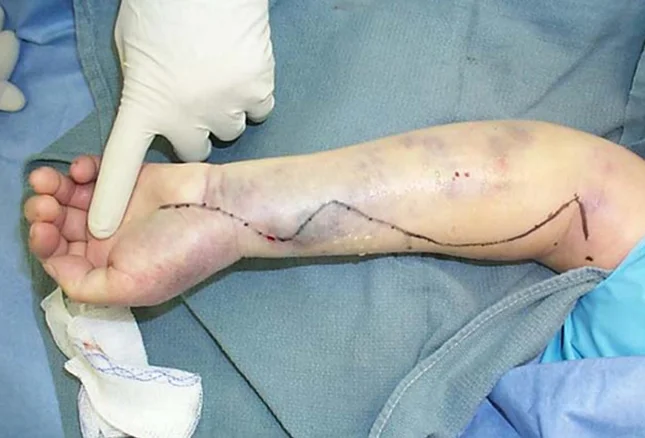
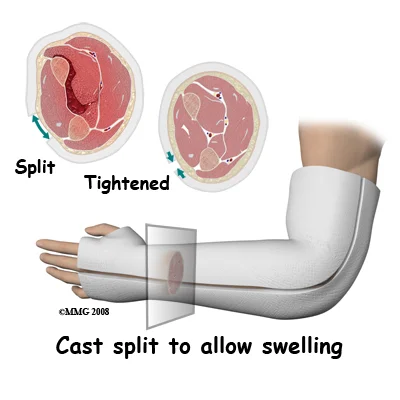
If in cast:
- Bivalve down to skin or remove
- Remove circumferential bandages
- Raise limb at level of the heart
- Higher elevation reduces the arterial inflow
Surgical Management
- Urgent. Should not be delayed
- No response to medical management within one hour
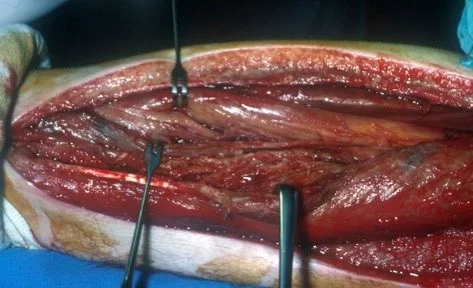
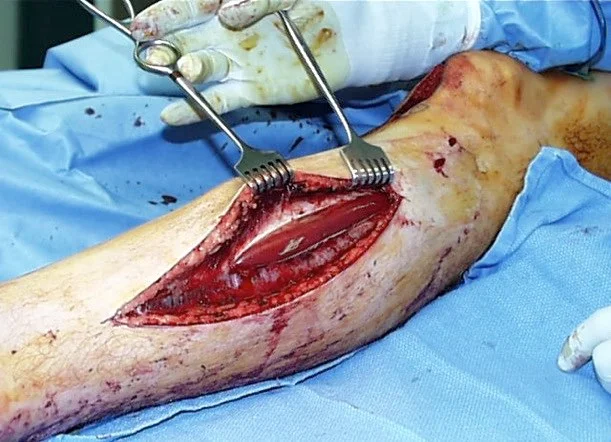
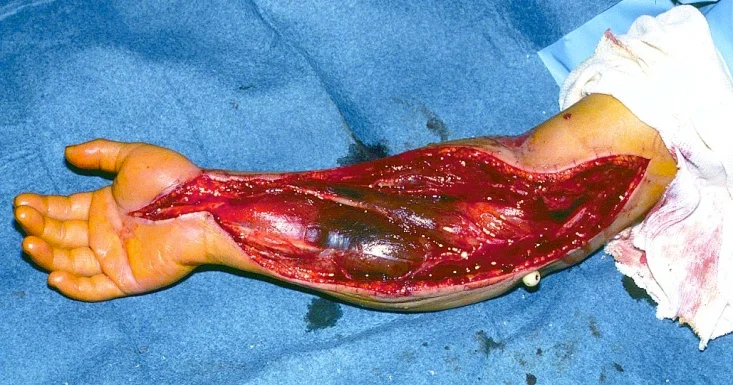
- Fasciotomy
- Skin and All compartments
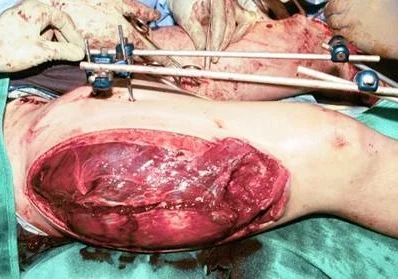
Fasciotomy Indications
- High risk patients
- Prophylactic with major corrective osteotomy of the leg & forearm
- S&S not resolved within 30-60 min. of appropriate precautions
- Significant tissue injury
- Suspicion: Equivocal clinical findings
- Based on measurements:
- Delta pressure (DBP - compartment P.) 25 mm Hg.
- Compartment pressure > 30mm Hg.
Fasciotomy Principles
Key Principles
- Long skin incisions
- Release all compartments
- open it all
- Debride necrotic muscles (4C’s):
- color, consistency, contraction, circulation
- pink, soft, capability to bias
- not dark
- criteria to access the muscle
- color, consistency, contraction, circulation
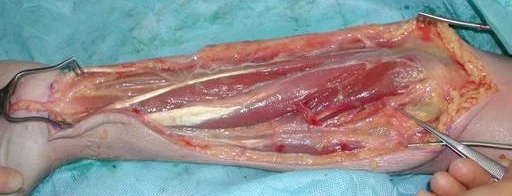
- Preserve neurovascular structures
- Never close fascia, Keep wound open
- fill the swelling subfida
- Repeated looks x48h as needed
- Coverage (within 3-5 days)
Visual Representation
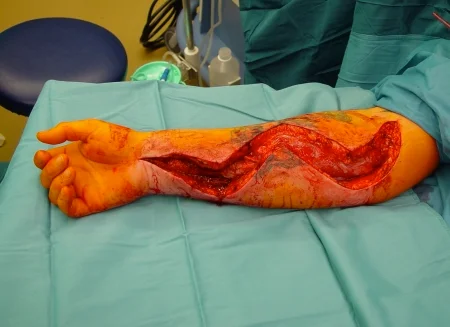
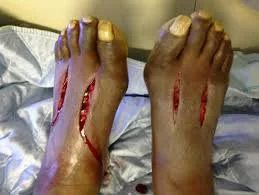
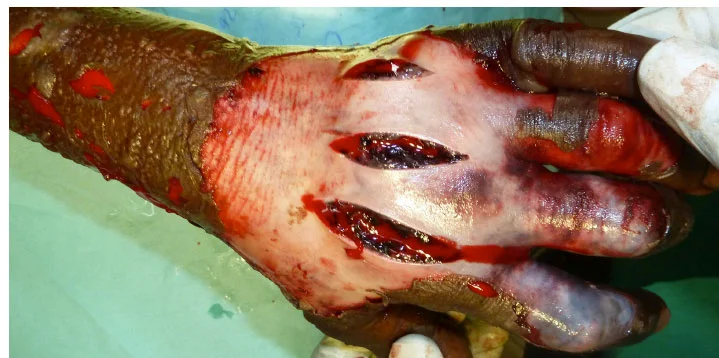
Treatment -
early
- Color red
- Consistency normal
- Capable of bleeding
- Contracts when pinched
lateY
- Color dark
- Consistency abnormal
- Not bleeding
- No contractions when pinched
Fasciotomy Principles Continued
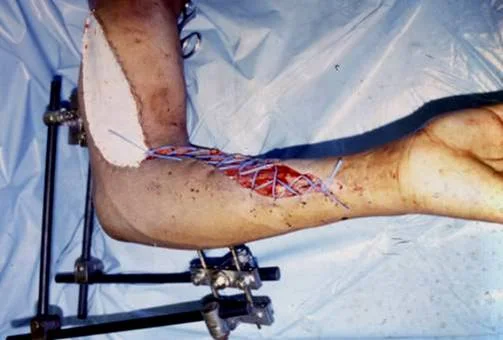
- No skin wound closure
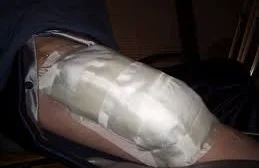
- Bulky dressing with a splint
- V.A.C” dressing (Vacuum Assisted Closure)
- ? “Boot lace” vessel loop closure (gradual)
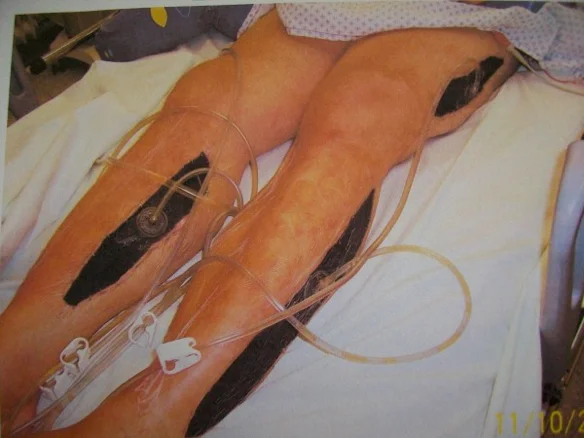
Late Stage Fasciotomy
- Later skin graft / flap:
- Usually skin graft
- Flap coverage needed if nerves, vessels, or bone exposed
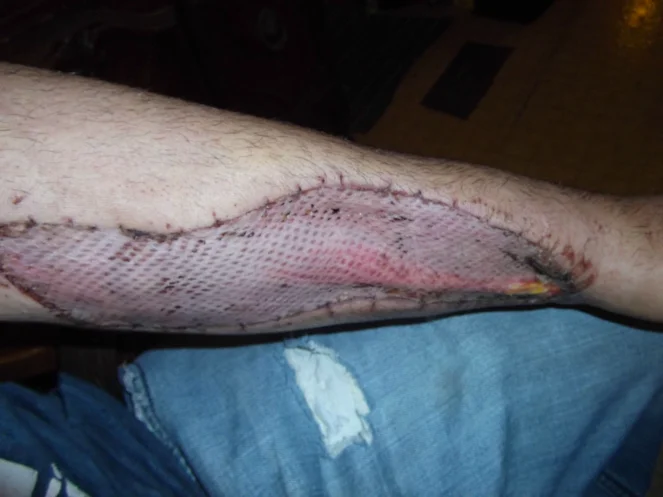
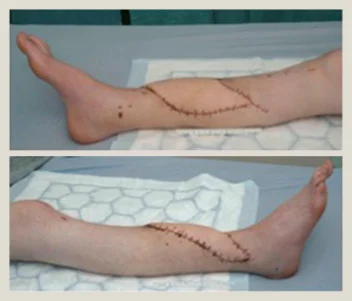
Fasciotomy Contraindication
-
Confirmed acute compartment syndrome diagnosis for > 48 hours
- Damage cannot be reversed, and
- High infection rate when dead tissues are exposed
-
Already dead muscles, as in crush injuries
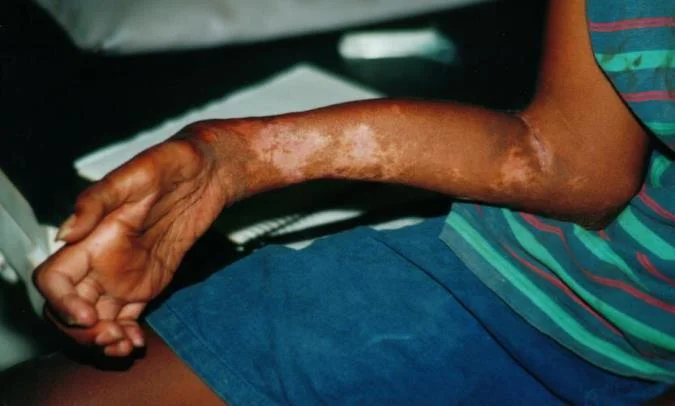
Complications of untreated C.S.
- Volkmann’s contracture :
- Muscle weakness
- Sensory loss
- Chronic pain
Summary
- Compartment syndrome is a clinical diagnosis
- Should not be missed - Disaster
- Requires urgent management
- If in doubt perform fasciotomy
- “Time” is the important factor to avoid irreversible complications
- Do NOT apply circumferential dressings