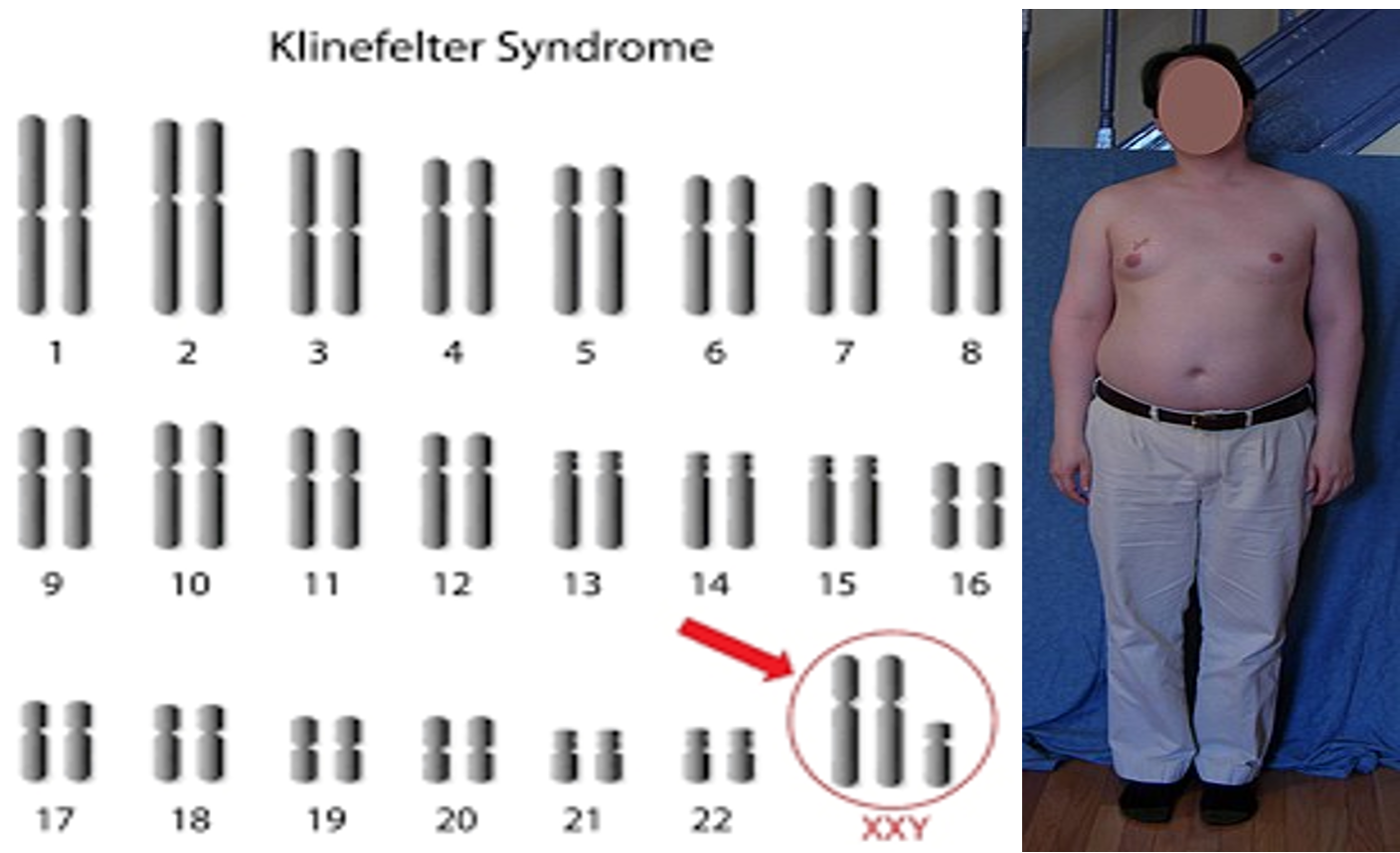
Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY)
- Most common chromosomal disorder associated with male hypogonadism and infertility
- Defined by a 47,XXY karyotype with variants that demonstrate additional X and Y chromosomes
Clinical Presentation
- Language impairment
- Academic difficulty
- Poor self-esteem
- Behavioral problems
- Fatigue and weakness
- Osteoporosis
- Hypogonadism (pathognomonic)
- Subnormal libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Small penis
- Infertility (azoospermia)
- Delayed secondary sexual characteristics
- Tall with gynecomastia
Risk of cancers: Increased risk of extra testicular germ cell tumors and possibly increased risk of breast cancer
Increased risk of: Pulmonary disease, Varicose veins, ADHD
Laboratory Findings
- Low serum testosterone levels
- High luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) levels, often elevated estradiol levels
- The decline in testosterone production is progressive over the lifespan, and not all men suffer from hypogonadism
Treatment
- Testosterone replacement therapy