Mechanism of Action
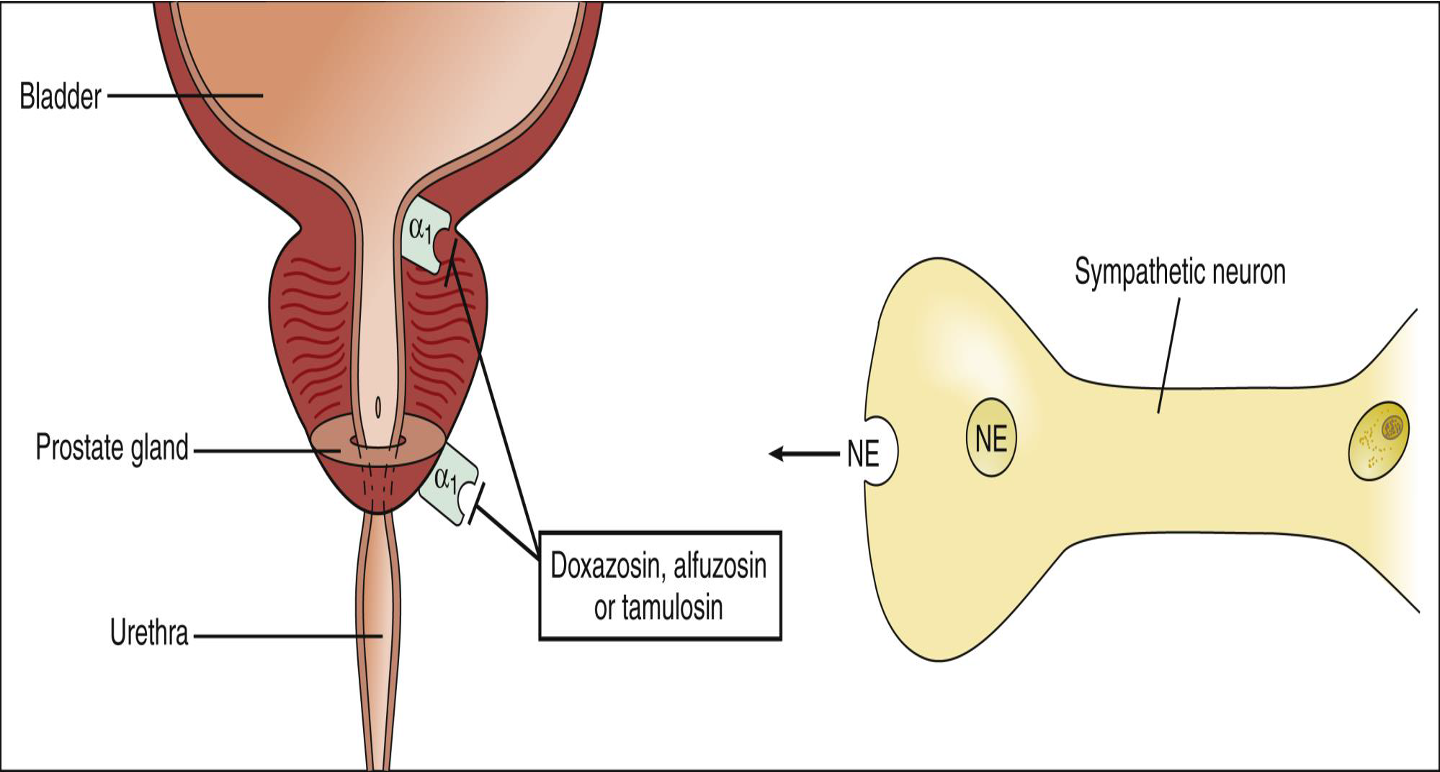
(Selective a1 blocker).
Pharmacological Effects
V.D. of arteries and veins lowering the blood pressure.
Therapeutic Uses
- Treatment of mild to moderate hypertension.
- Treatment of acute congestive heart failure (decreases pre- and after-load).
- Impaired bladder emptying due to prostate obstruction (decreased the tone of trigone) *leads to decreased resistance to flow of urine. (tamsulosin) a1 blocker potentates relaxation of sphincter; symptomatic treatment’
- Peripheral vascular disease (Raynaud’s disease)
Adverse Effects
First dose effect: (to avoid, give small initial dose rather than full dose & avoid diuretics)
- The initial dose especially if large can produce postural hypotension and syncope. - It occurs most commonly in salt and water depleted patients (start with a small dose and at bedtime).
- Dizziness, headache, drowsiness, and palpitation (disappears with continued treatment).
- False positive tests for antinuclear factor.
- Salt and water retention. (all drugs cause this except diuretics)
- Flushing , ,Nasal congestion, Failure of ejaculation in males.
TERAZOSIN , alfuzosin and TRIMAZOCIN Similar to prazosin but it does not produce first-dose syncope.