Dermatology
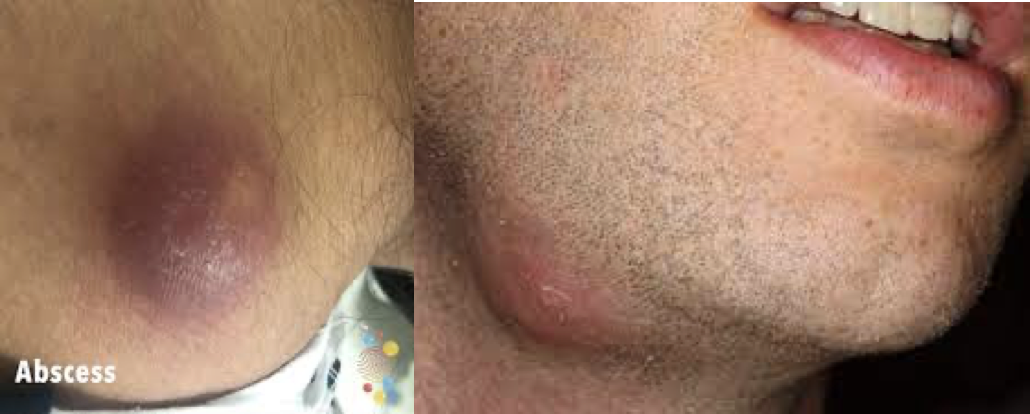
Abscess
- A skin abscess is a collection of pus within the dermis and deeper skin tissues
- Present as painful, tender, fluctuant and erythematous nodules
- Often surmounted by a pustule and surrounded by a rim of erythematous edema
- Spontaneous drainage of purulent material may occur
Treatment
-
Abscesses require incision and drainage (I & D) Most experts recommend irrigation, breaking of loculations, and packing following incision and drainage
-
Antibiotics are recommended for abscesses associated systematic symptoms
-
Wound cultures should always be sent
Infections involve hair follicles
What is the diagnosis?
History
- HPI: Mr. Hammed is a 27-year-old man with a history of “skin popping” (subcutaneous or intradermal injection of drug) who presents to the emergency department with a painful, enlarging mass on his right arm for the last two days.
- PMH: History of skin and soft tissue infections
- Medications: none
- Allergies: no known drug allergies
- Family history: father with diabetes, mother with hypertension
- Social history: lives with friends in an apartment, works in retail
- Health-related behaviors: IVDU (intravenous drug use), including skin popping. No tobacco or alcohol use.
- ROS: no fevers, sweats or chills
Case Three: Skin Exam
- Erythematous, warm, fluctuant nodule with several small pustules throughout the surface
- Very tender to palpation
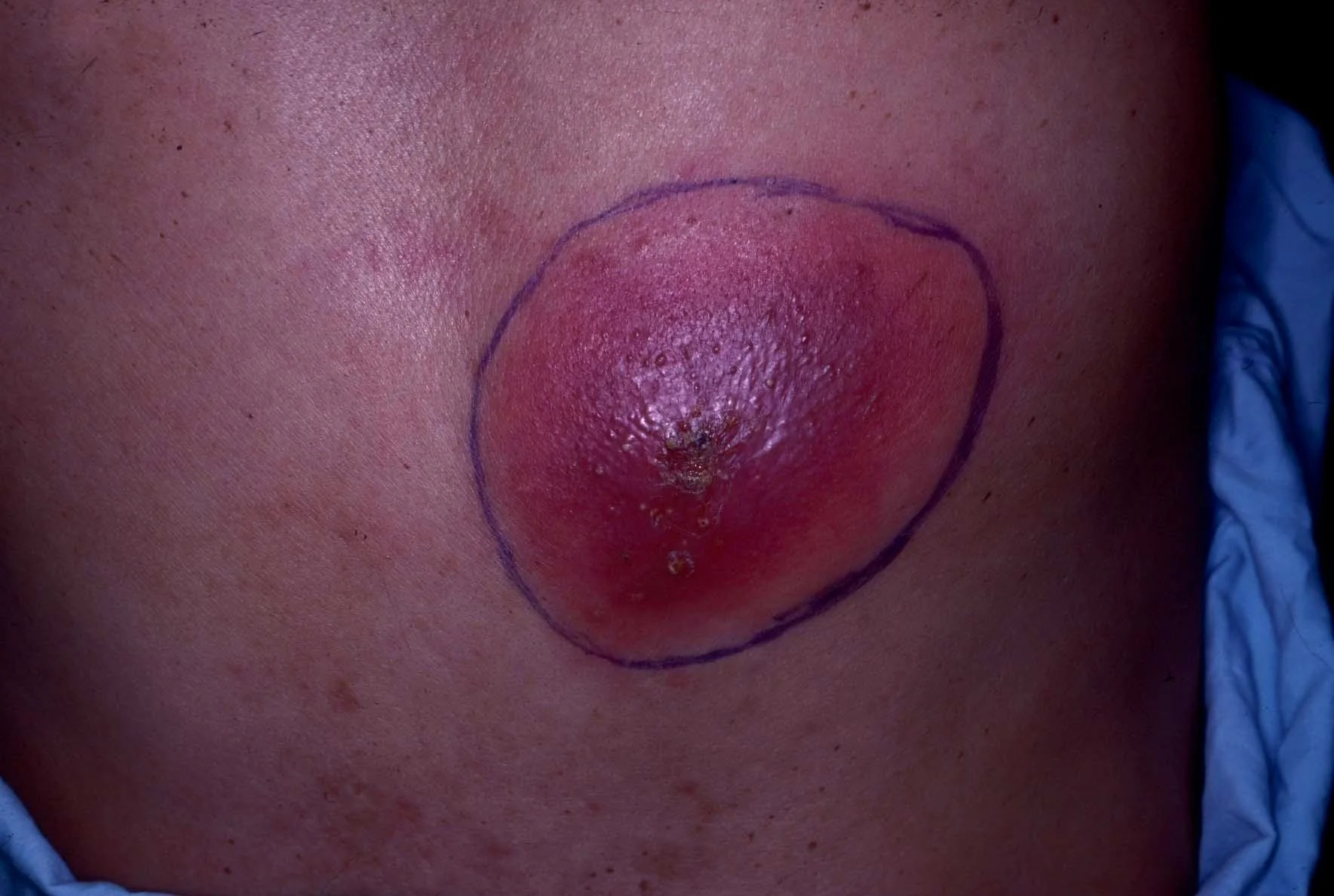
Diagnosis: Abscess
- A skin abscess is a collection of pus within the dermis and deeper skin tissues
- Present as painful, tender, fluctuant and erythematous nodules
- Often surmounted by a pustule and surrounded by a rim of erythematous edema
- Spontaneous drainage of purulent material may occur
Question 1
- What is the next best step in management?
- Incision and drainage
- Topical antibiotics
- Offer HIV test
- a and b
- a and c
Question 1 - Answer
Answer: e
- What is the next best step in management? a. Incision and drainage (incision and drainage is the treatment of choice for abscesses) b. Topical antibiotics (not effective) c. Offer HIV test (patients with risk factors for HIV should be offered an HIV test, e.g. IVDU in this patient) d. a and b e. a and c
Abscess: Treatment
- Abscesses require incision and drainage (I & D)
- Most experts recommend irrigation, breaking of loculations, and packing following incision and drainage
- Antibiotics are recommended for abscesses associated
- Wound cultures should always be sent
CM
- Subcutaneous infection
- Abscess is a Infectious pocket of pus; commonly Staph. Aureus (dead cells, exudate, bacteria) surrounded by granulation tissue; any organism can cause it (Staph. Aureus is common)
- Demographic data: no specific age, Hygiene
- Symptoms: throbbing pain worsening and awake the patient from night, patient notice red area of thickening then turn to be hard mass, +/- discharges, follow progression; ? duration; fast
- PMH: Diabetes; usually develop abscess in back, carbuncles
Four classic sign (swelling, redness, heat, pain) - site, Shape, Size, Surface, Color, Tempertaure, Tenderness, Edge, Consistency, Relations, Surrounding tissue, Lymph node assessment