Sideroblastic Anemia
- Disorder in the synthesis of hemoglobin characterized by trapped iron in the mitochondria of nucleated RBCs.
- Hereditary form: defect in aminolaevulinic acid synthase or an abnormality in vitamin B6 metabolism.
- The acquired form: drugs such as chloramphenicol, isoniazid, or alcohol. Z
- No specific finding that will be sufficiently suggestive of sideroblastic anemia.
Elevated Serum Ferritin
- Elevated serum ferritin
- Very high transferrin saturation, and very low TIBC
- High serum iron (the only microcytic anemia with elevated iron)
- Prussian blue stain (most specific test) of RBCs in the marrow will reveal the ringed sideroblasts.
- Treatment: Remove the offending drug. Consider transfusion for serious cases.
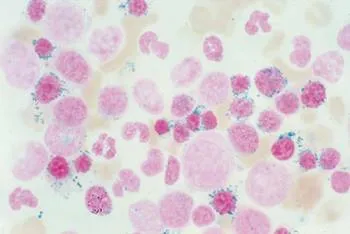 Ring sideroblast Z OSPE
Ring sideroblast Z OSPE
 Ring sideroblast
Ring sideroblast