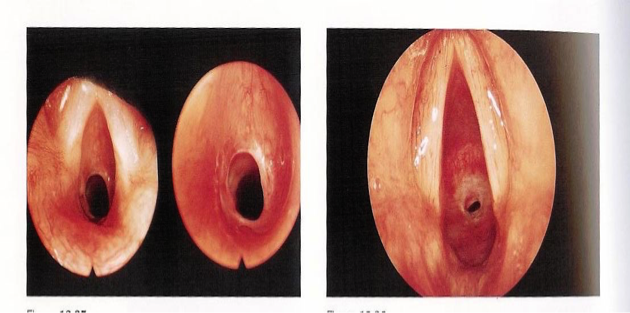
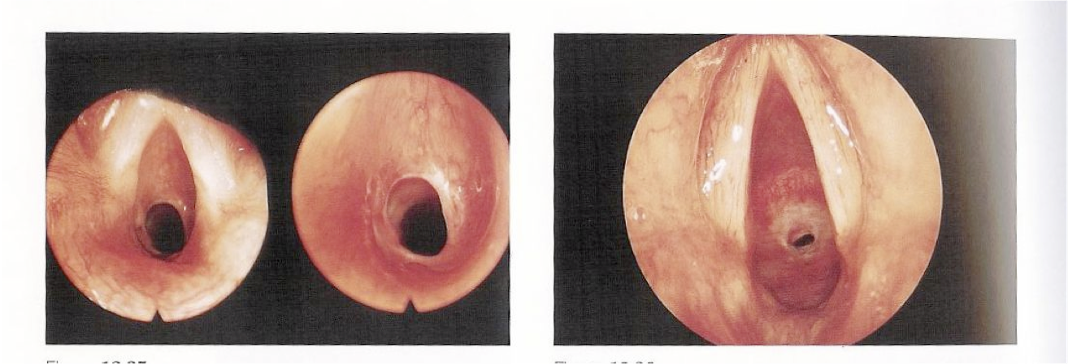
Subglottic Stenosis
- Incomplete recanalization, small cricoid ring
- Types:
- Membranous
- Cartilaginous
- Mixed
- Grades:
- I <50%
- II 51-70%
- III 71-99%
- IV complete obstruction (no detectable lumen)
- Symptoms:
- Biphasic stridor, failure to thrive.
- Diagnosis:
- Chest and neck X-ray, flexible endoscope
- Treatment: Z
- Tracheotomy
- Grade I - II: Endoscope (CO2 or excision with dilation)
- Grade III – IV: Open procedures: Anterior cricoid split, LTR OR CTR
Risk Factors
- Prolonged intubation
- Size of the tube, material
- Care of intubated patient
- High-pressure cuffs tube
- Difficult intubations
- Multiple intubations
- GERD
- Tracheobronchial infection
Pathophysiology
- Laryngeal ➔ granulation tissue ➔ ulceration ➔ perichondritis ➔ subglottic stenosis

Treatment
- Grade I & II: Observation, balloon dilation, laser excision
- Grade III & IV: Tracheostomy, laryngotracheal reconstruction, cricotracheal resection


