Cannabinoids
- Any chemical that activates the body’s cannabinoid receptors.
- Most commonly understood through the use of the Cannabis plant, marijuana (a dry, shredded green and brown mix of flowers, stems, seeds, and leaves).
- Arguably the most controversial and commonly abused drug.
Diagnostic Criteria for Cannabis Intoxication
-
A. Recent use of cannabis.
-
B. Clinically significant maladaptive behavioral or psychological changes (e.g., impaired motor coordination, euphoria, anxiety, sensation of slowed time, impaired judgment, social withdrawal) that developed during, or shortly after, cannabis use.
-
C. Two (or more) of the following signs, developing within 2 hours of cannabis use:
- (1) conjunctival injection
- (2) increased appetite
- (3) dry mouth
- (4) tachycardia
-
D. The symptoms are not due to a general medical condition and are not better accounted for by another mental disorder.
-
Specify if:
- With Perceptual Disturbances
-
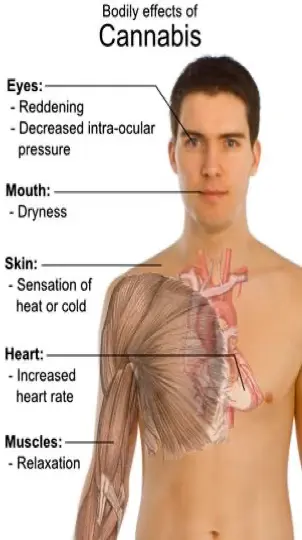
Bodily effects of Cannabis
- Eyes:
- Reddening
- Decreased intra-ocular pressure
- Mouth:
- Dryness
- Skin:
- Sensation of heat or cold
- Heart:
- Increased heart rate
- Muscles:
- Relaxation
- Eyes:
Mechanism of Action
- The main active chemical in marijuana is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), a cannabinoid.
- It acts on the cannabinoid receptors, namely the:
- CB1 (Primarily found in CNS neurons)
- CB2 (Primarily found in PNS immune cells)
Effects
- Psychoactive
- alteration of conscious perception, euphoria, feelings of well-being
- 20-30% of users experience panic attacks
- marked distortions in the perception of time and space
- depersonalization and derealization
- Withdrawal
- Occurs in long-term abusers.
- Symptoms:
- irritability, sleeplessness, decreased appetite, anxiety, and drug craving
- It starts 1 day following abstinence, peaks at 2-3 days, and subsides within 1 or 2 weeks following drug cessation.
Mental Disorders Due to Use of Cannabinoids
- Marijuana (marihuana) is a colloquial term for dried leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa L.).
- Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) is responsible for the psychoactive properties of the cannabis plant.
- Complex physiological functions of the cannabinoid system: motor coordination, memory procession, control of appetite, pain modulation, and neuroprotection.
- Summary of adverse effects:
- acute: anxiety, panic, impaired attention, memory, reaction time and psychomotor performance and coordination, increased risk of road accidents, and increased risk of psychotic symptoms among vulnerable persons.
- chronic: chronic bronchitis, a cannabis dependence syndrome, subtle impairments of attention, short-term memory, and ability to organize and integrate complex information.