Gallstones
Pathogenesis
Gallstone formation results from an imbalance of the constituents of bile (bile salts, calcium salts of bilirubin and phospholipid).
Types
-
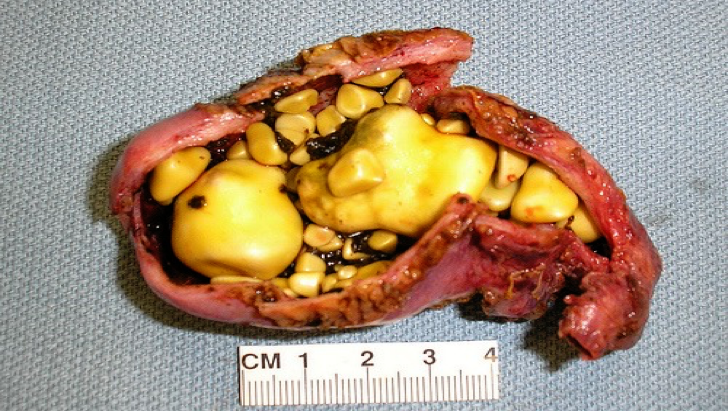
Cholesterol stones: It form when the bile becomes supersaturated with cholesterol. Supersaturation is most likely occur as the bile is concentrated in the gallbladder, and favored by stasis or decreased gallbladder contractility. Cholesterol crystals forms (nucleation) around particles of mucus, bacteria, calcium bilirubinate or mucosal cells. Pure cholesterol stones are yellowish-green with a regular shape and rough surface. They are usually solitary whereas mixed stones are darker and multiple.
Predisposing conditions included: Obesity, high calorie intake or high cholesterol diets, drastic weigh loss, diseases or resection of distal ileum, drugs (cholestyramine), Hormones (estrogen) intake like oral contraceptive pills and post-menopausal hormonal replacement, Pregnancy, familial.
-
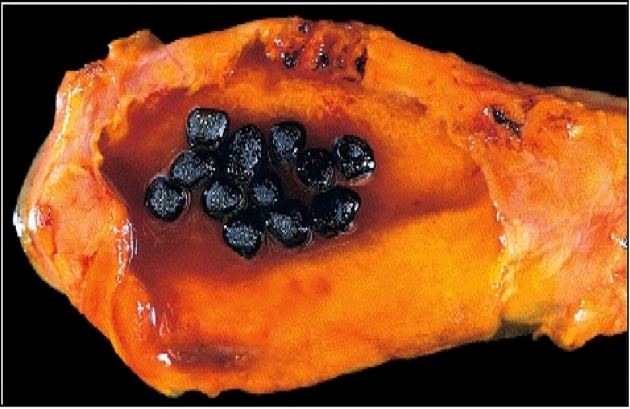
Black pigment stones They are usually composed of calcium salts of bilirubin, phosphate and bicarbonate. It occur with chronic hemolysis (spherocytosis, hemoglobinopathy and malaria) and liver cirrhosis.
-
Brown pigment stones They are usually composed of calcium salts of bilirubinate, stearates, palmitate and cholesterol. Bile stasis and infection are predisposing factors. Such patients have increased amounts of unconjugated bilirubin in the bile due to the effect of β-glucuronidase produced by E- coli, an organism that invade the biliary ducts system with bile stasis.
Cholesterol gallstones
Black pigmented gallstone
Brown pigmented gallstone

Gallstones diseases
- Asymptomatic gallstones: usually no need of treatment
- Symptomatic gallstones and related complications need treatment